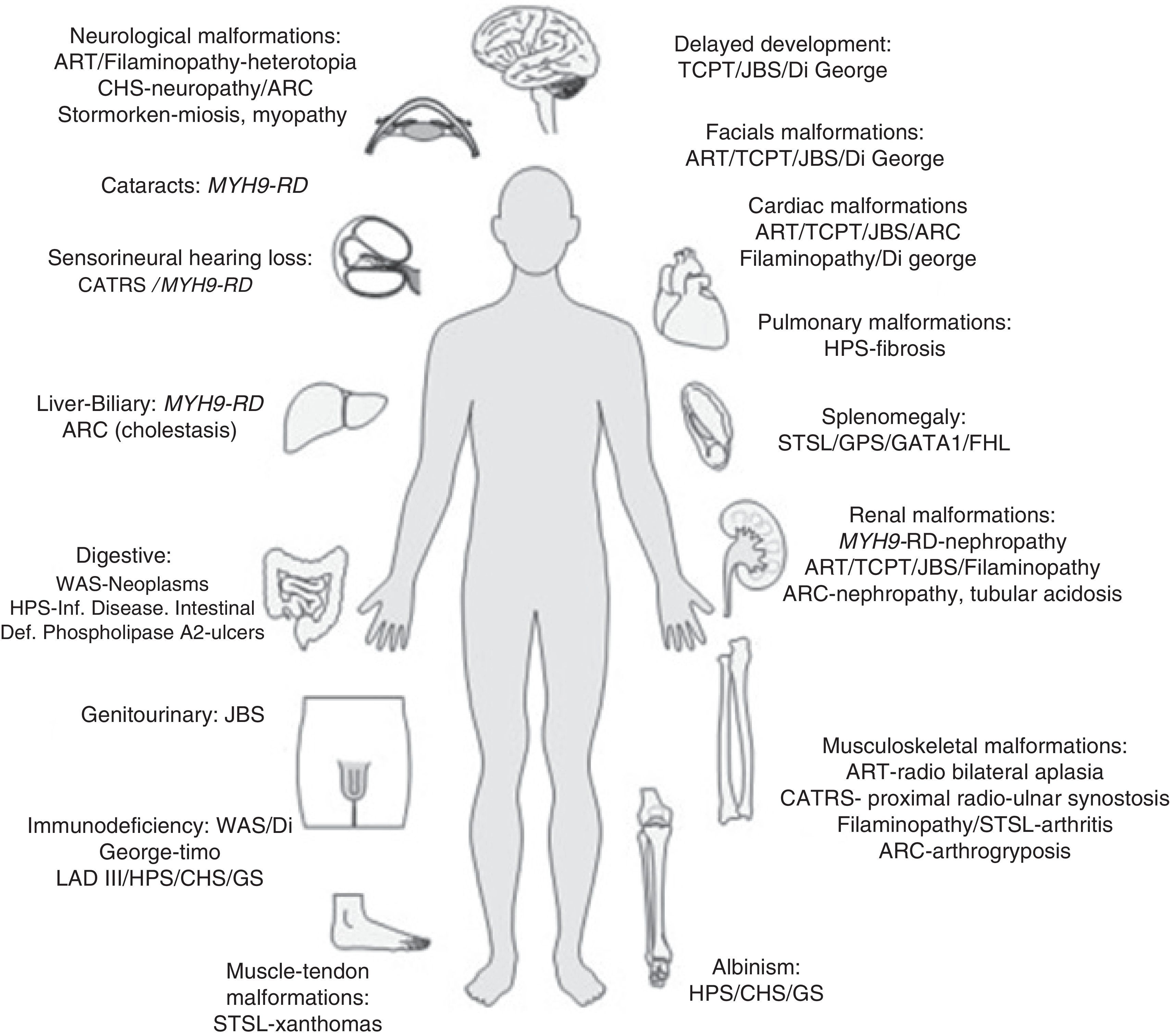
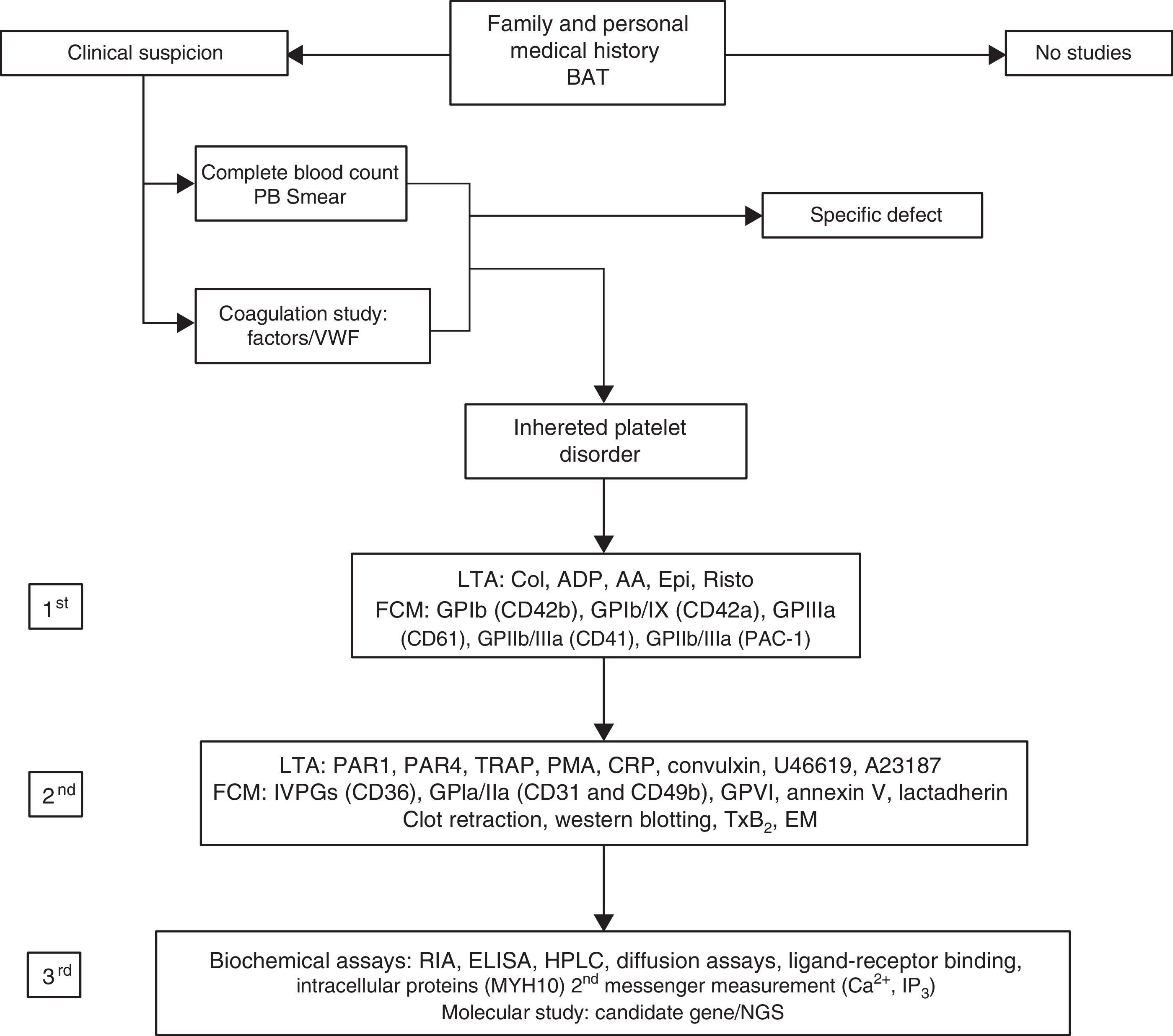
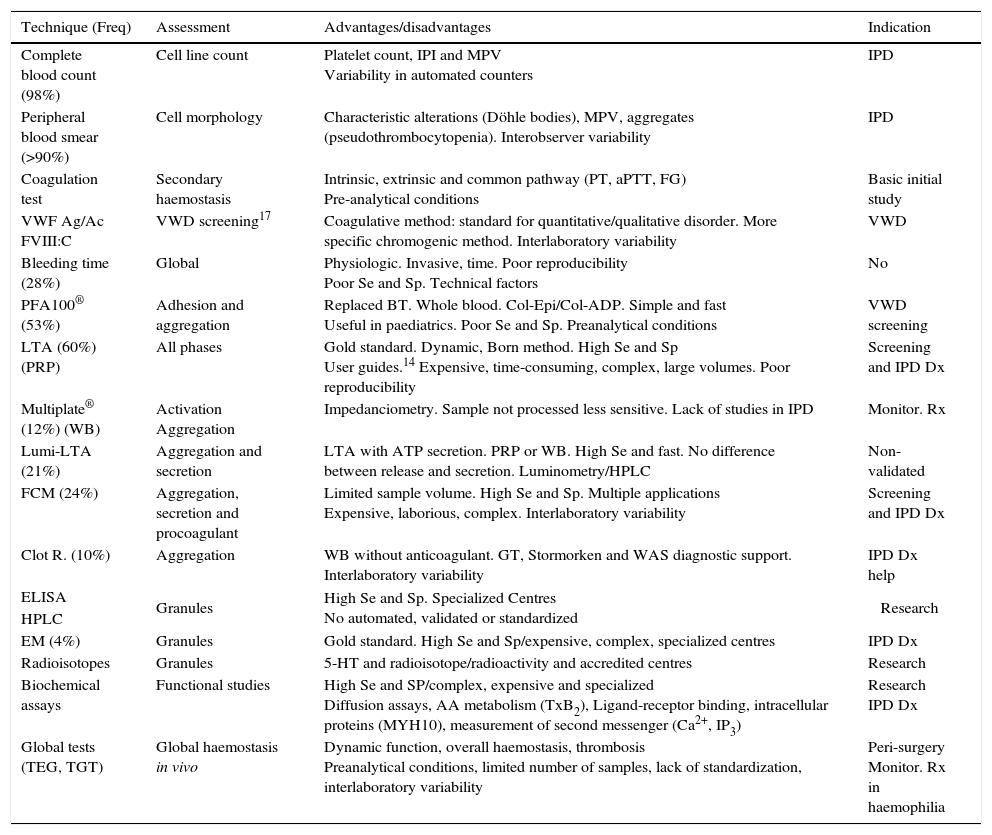
Inherited platelet disorders diagnosis is based on the clinical history and bleeding assessment tools. The laboratory functional assays as well as the molecular test to identify the pathogenic genetic variant are essential to confirm the accurate diagnosis of these disorders. Nowadays, the main challenges to developing a new diagnostic system are involved in reducing the samples’ volume, and faster and more helpful analysis. Moreover, there are no widely available and standardized global tests. High throughput genetic testing such as next-generation sequencing has revolutionized DNA sequencing technologies as it allows the simultaneous and faster investigation of multiple genes at a manageable cost. This technology has improved the molecular characterization of inherited platelet disorders and has been implemented in the research studies and the clinical routine practice.
El diagnóstico de una diátesis hemorrágica hereditaria y en particular de un trastorno plaquetario hereditario se basa en la historia clínica así como en la aplicación de las escalas de sangrado, el estudio funcional de laboratorio y en la caracterización molecular. En la actualidad se están desarrollando métodos rápidos, que requieran escaso volumen de muestra en su aplicación como cribado funcional de estas enfermedades. El principal avance en el diagnóstico de los trastornos plaquetarios hereditarios ha sido su caracterización molecular, gracias al desarrollo y evolución de las técnicas de secuenciación masiva. Esta tecnología ha permitido incorporar los paneles de genes en la práctica clínica habitual, así como el análisis del exoma completo en la investigación de estas enfermedades.