The outcome and prognosis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in long-term kidney transplantation (KT) is variable. The objective of this study was to analyze the survival of the graft and the patient, comparing rates with a control group (primary glomerulonephritis [PGN]).
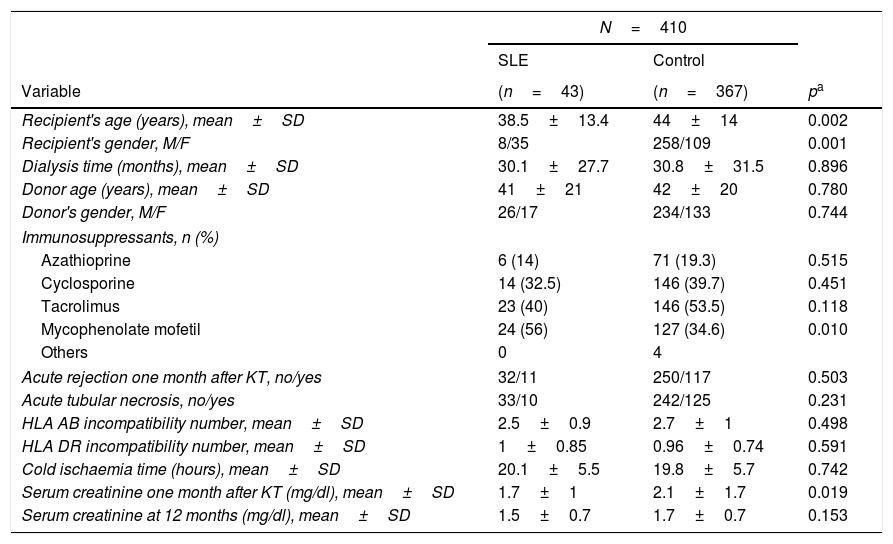
Materials and methodsForty-three patients receiving a KT with diagnosis of lupus nephritis (LN) and 367 patients with PGN were compared between January 1980 and December 2014. The survival causes of loss and death of the graft and the patient were analyzed.
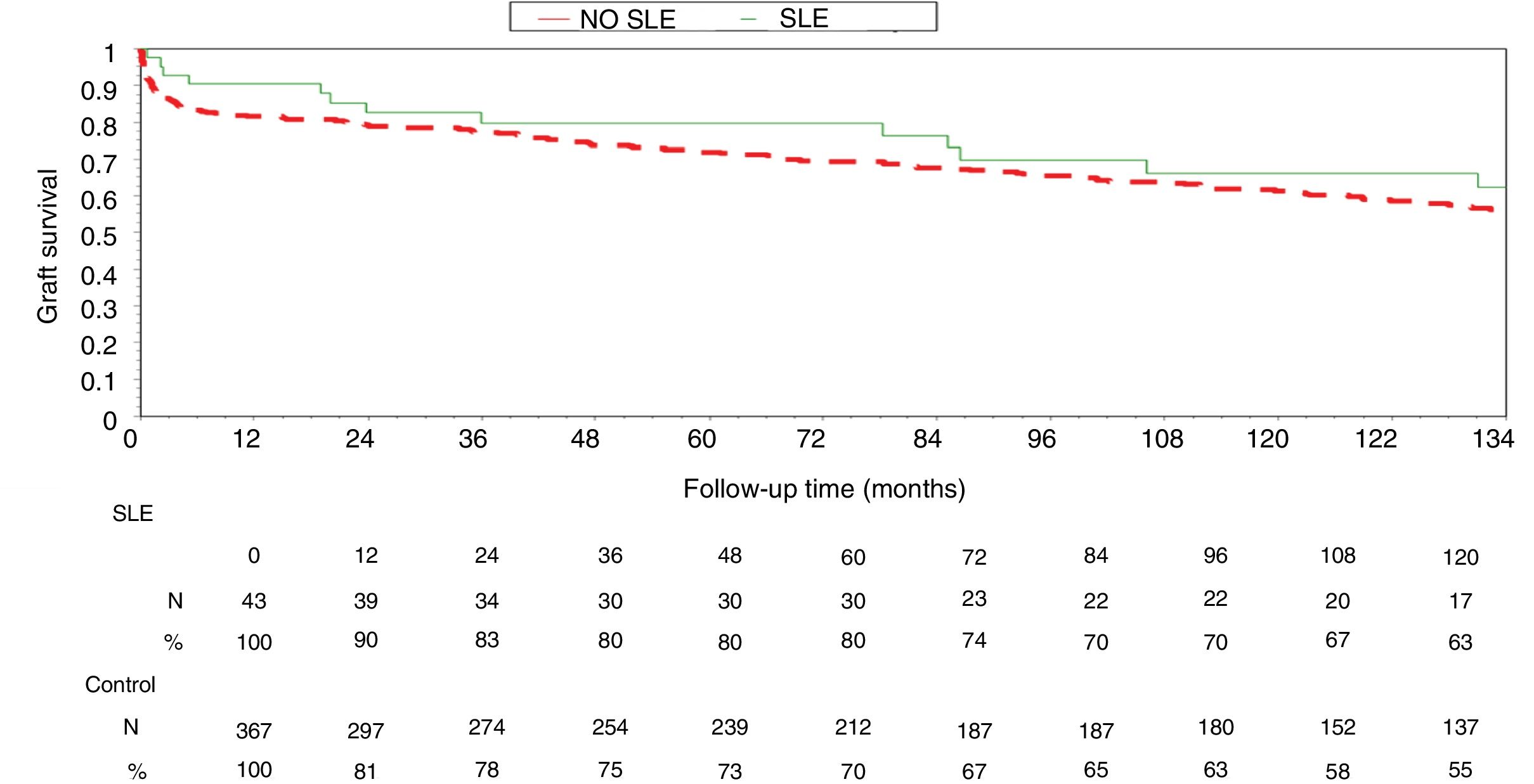
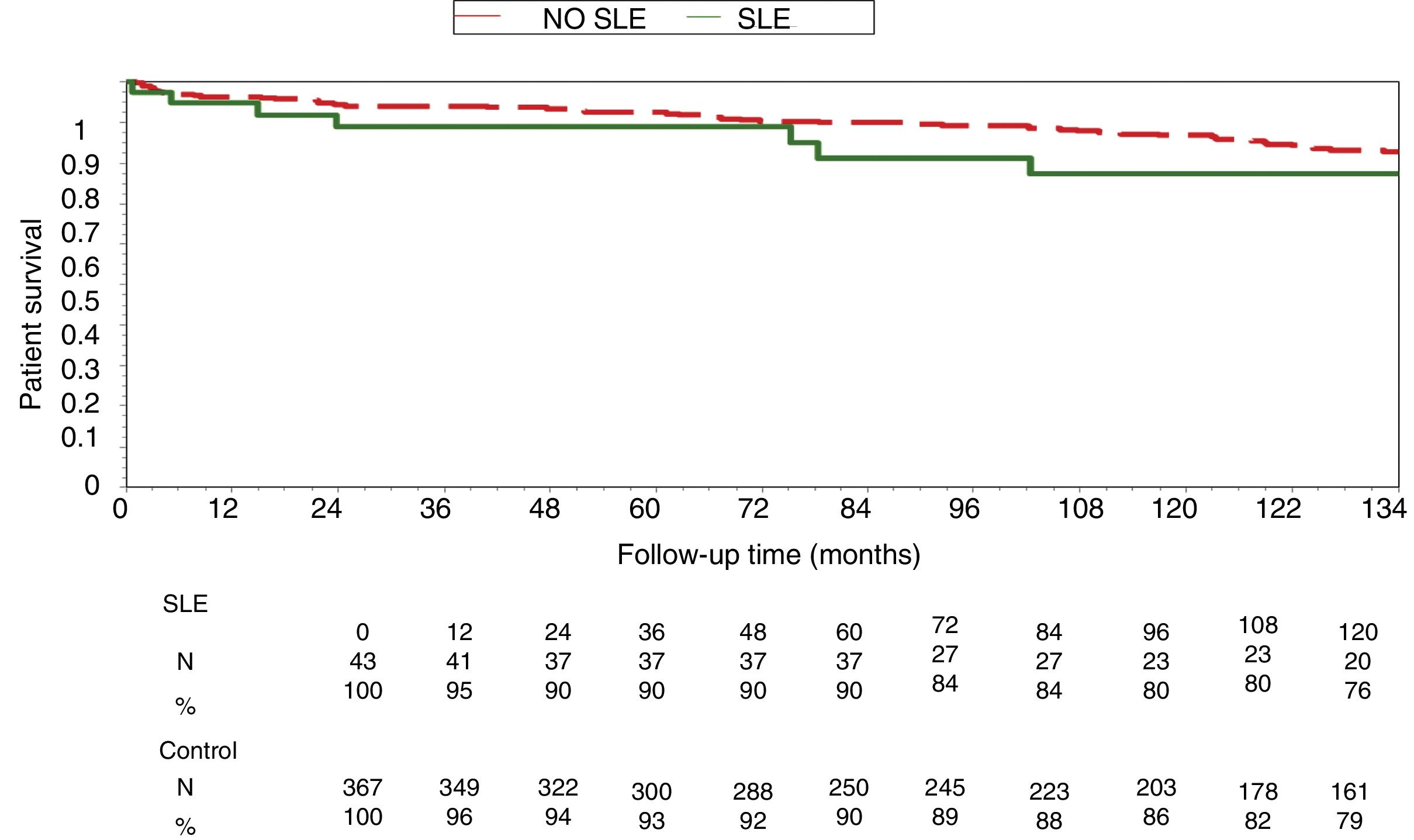
ResultsThere were no significant differences between the variables analyzed. The graft survival at five years (80% SLE vs. 70% PGN) and 10 years (63% SLE vs. 55% PGN) and the patient at 5 years (90% SLE vs. 90% PGN) and 10 years (76% LES vs. 79% PGN) were similar. Not recurrence of LN was observed in any patient.
ConclusionsPatients with SLE are similar candidates to KT than that with other immunological kidney diseases. There was no recurrence of the disease in any patient.
Los resultados del lupus eritematoso sistémico (LES) en el trasplante renal (TR) a largo plazo son variables. El objetivo de este estudio fue analizar la supervivencia del injerto y del paciente comparándola con la relativa a las glomerulonefritis primarias (GNP).
Materiales y métodosSe compararon 43 pacientes a los que se les había realizado TR con diagnóstico de nefritis lúpica (NL) y 367 con GNP entre enero de 1980 y diciembre de 2014. Se analizó la supervivencia y las causas de pérdida y muerte del injerto y del paciente.
ResultadosNo hubo diferencias significativas entre las variables analizadas en ambos grupos. La supervivencia del injerto a los 5 años (80% LES vs. 70% GNP) y 10 años (63% LES vs. 55% GNP) y del paciente a los 5 años (90% LES vs. 90% GN) y 10 años (76% LES vs. 79% GN) fueron similares. Ningún injerto se perdió por recidiva de la NL.
ConclusionesLos enfermos con LES son unos candidatos a trasplante similares a los de otras enfermedades renales de etiología inmunológica. No se observó recidiva de la enfermedad en ningún paciente.