In pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) an association with a polymorphism in the endothelin gene (EDN1) has been described. The main objective of this study was to analyse the polymorphism K198N in the gene EDN1 in patients with PAH, correlating the results with clinical and hemodynamic parameters.
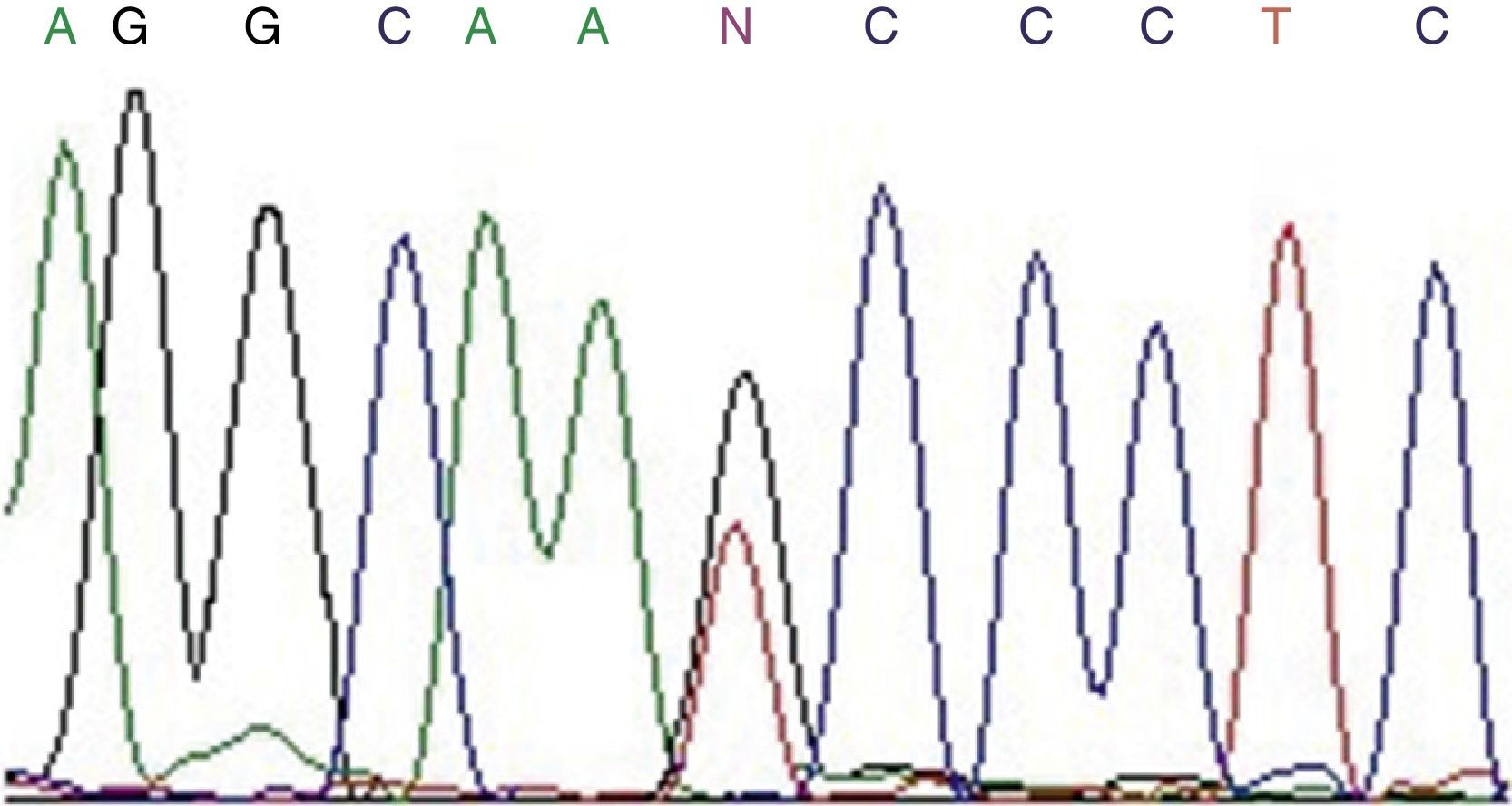
Patients and methodsWe compared 41 patients diagnosed with idiopathic and associated PAH of group I with 50 healthy controls. Polymerase chain reaction and direct sequencing were used to analyse the polymorphism K198N. We compared the genotype distribution and searched for a correlation with clinical, hemodynamic and therapeutic response.
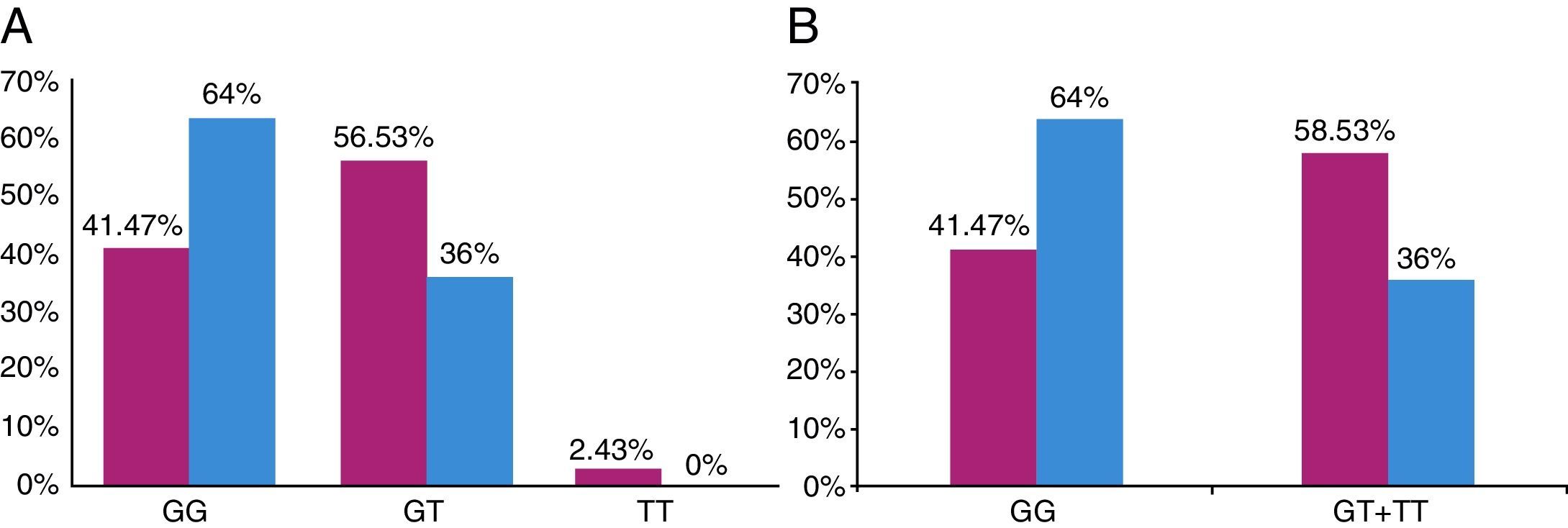
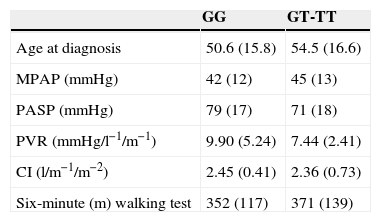
ResultsGenotype GG was present in 42% of patients in this study and 65% of controls. The GT+TT genotypes appeared in 58% of patients and in 35% of controls. Statistically significant differences between patients and controls (P=.032) were detected, with a relative risk in carriers of having the T allele of 2.51 (95% CI 1.07 to 5.86). The analysis by PolyPhen software defined K198N change as pathogenic. No significant differences in the response to treatment at medium term were found.
ConclusionsThe genotype analysis of the EDN1 gene polymorphism shows statistically significant differences in patients with PAH compared to healthy individuals. Individuals carrying at least one T allele exhibit a higher relative significant risk to develop HAP.
En la hipertensión arterial pulmonar (HAP) se ha demostrado la asociación de un polimorfismo en el gen de la endotelina (EDN1) con un incremento de la acción de esta proteína favoreciendo la aparición de HAP. El objetivo de este estudio ha sido analizar el polimorfismo K198N del gen EDN1 en pacientes con HAP, correlacionando los resultados con parámetros clínicos y hemodinámicos.
Pacientes y métodosSe compararon 41 pacientes diagnosticados de HAP idiopática y asociada del grupo i con 50 individuos sanos. Se utilizaron los métodos de reacción en cadena de la polimerasa y secuenciación directa para estudiar el polimorfismo K198N. Se comparó la distribución de los genotipos y se correlacionaron con parámetros clínicos, hemodinámicos y de respuesta terapéutica.
ResultadosEl genotipo GG estaba presente en el 42% de los pacientes estudiados y en el 65% de los individuos control. Los genotipos GT+TT aparecieron en el 58% de los pacientes y en el 35% de los controles. Las diferencias fueron estadísticamente significativas (p=0,032), siendo el riesgo relativo de desarrollar HAP en portadores del alelo T de 2,51 (intervalo de confianza del 95% [IC 95%] 1,07–5,86). El análisis mediante el software PolyPhen definió el cambio K198N como patogénico. No se encontraron diferencias significativas en aspectos clínicos ni en respuesta al tratamiento a medio plazo en función del genotipo.
ConclusionesEl análisis genotípico para el polimorfismo K198N muestra diferencias estadísticamente significativas en pacientes con HAP respecto a individuos sanos. Los portadores de al menos un alelo T presentan un riesgo relativo significativamente mayor de padecer HAP.