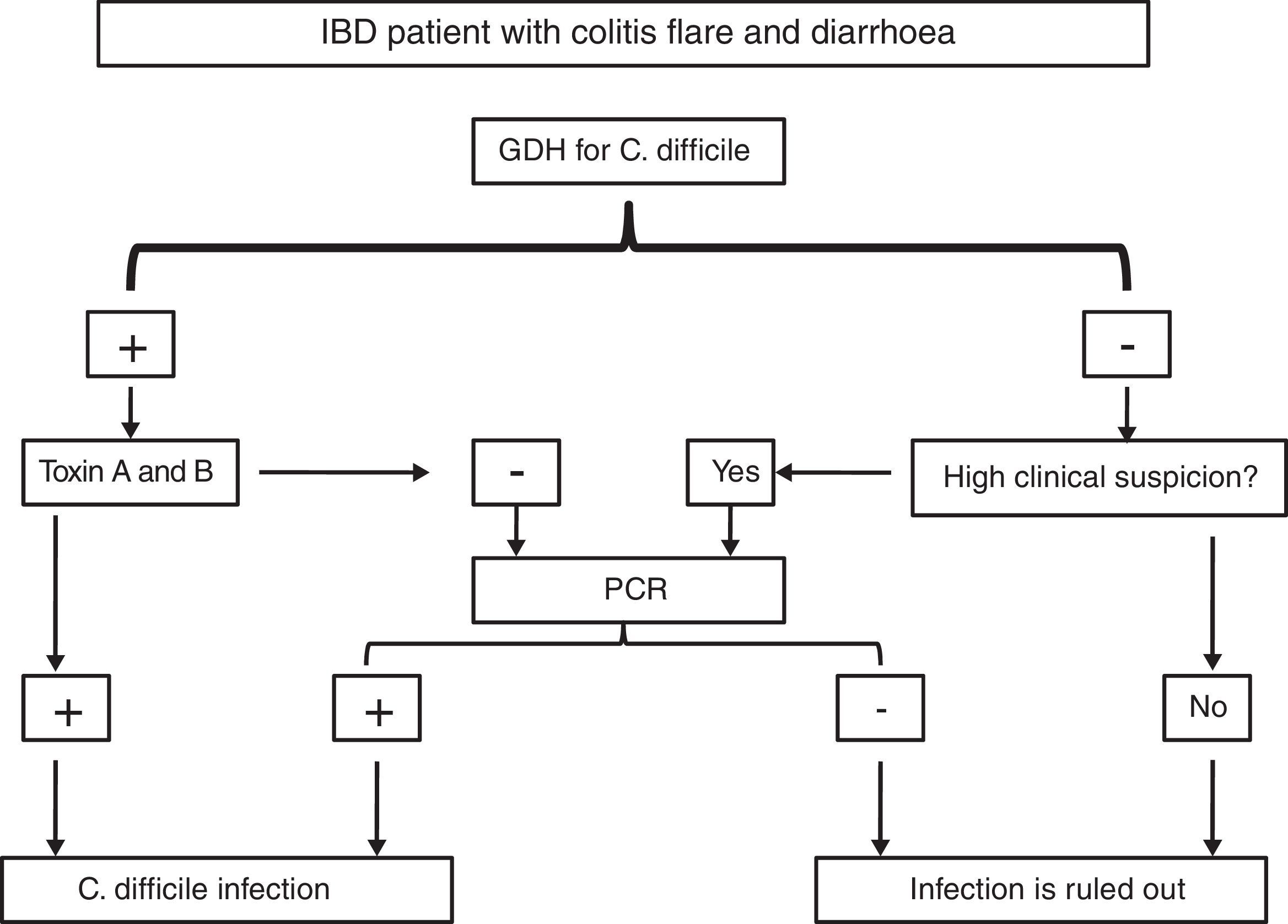
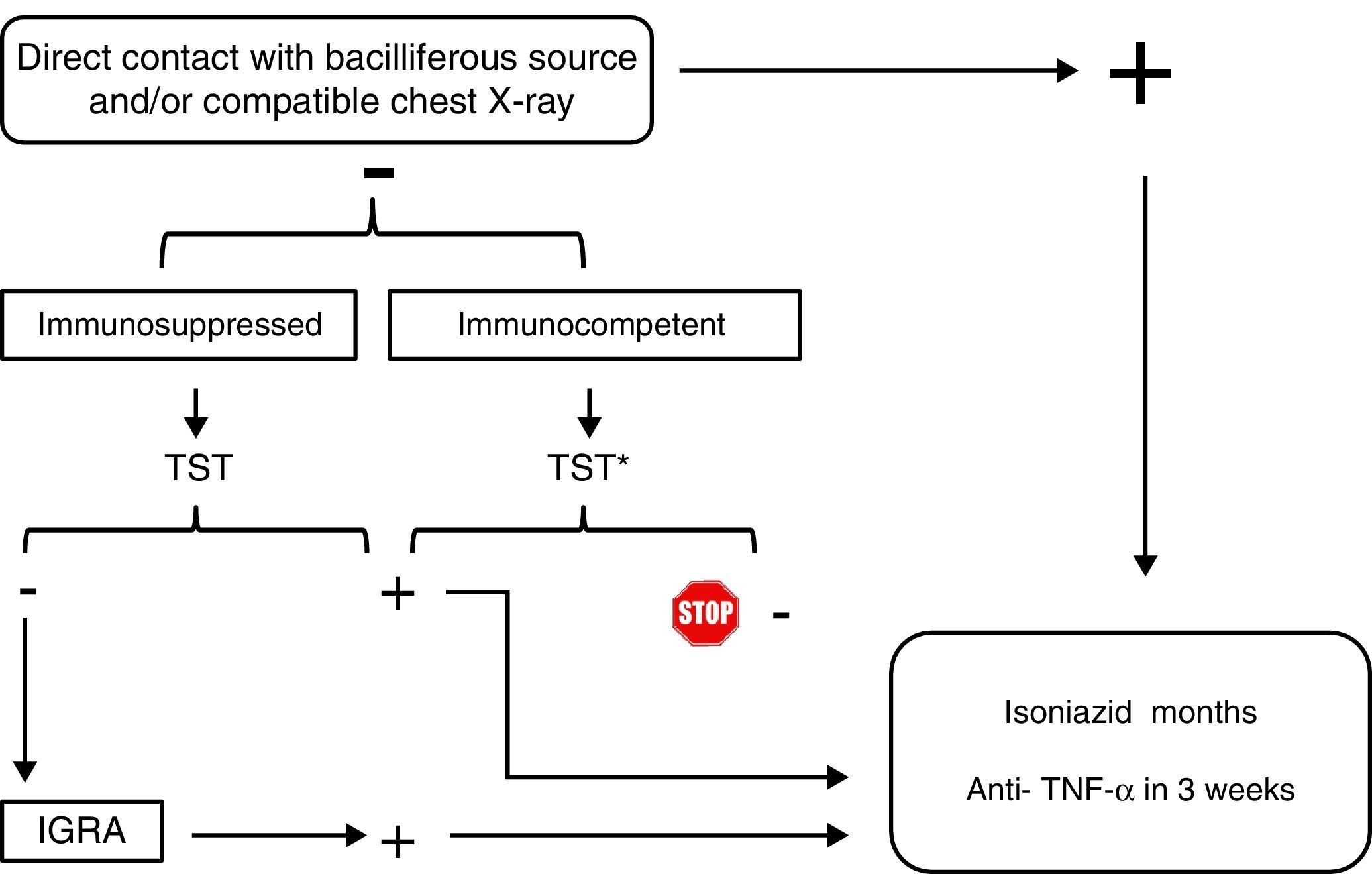
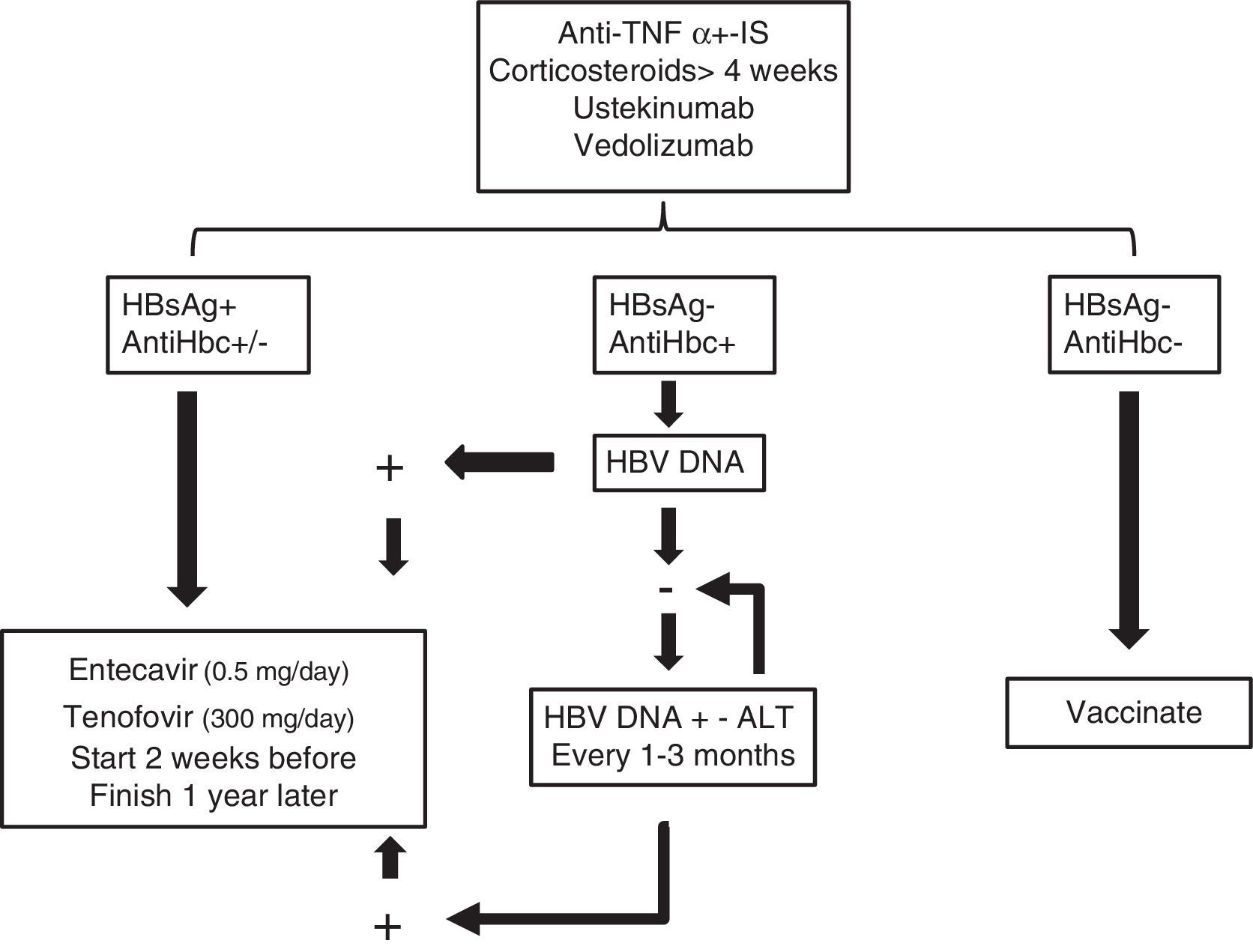
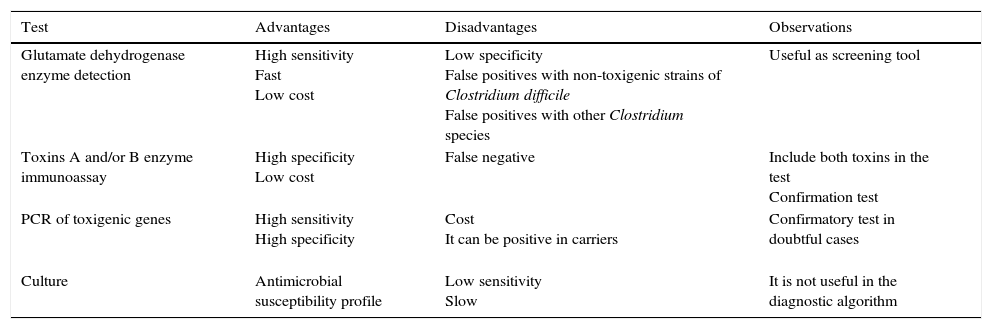
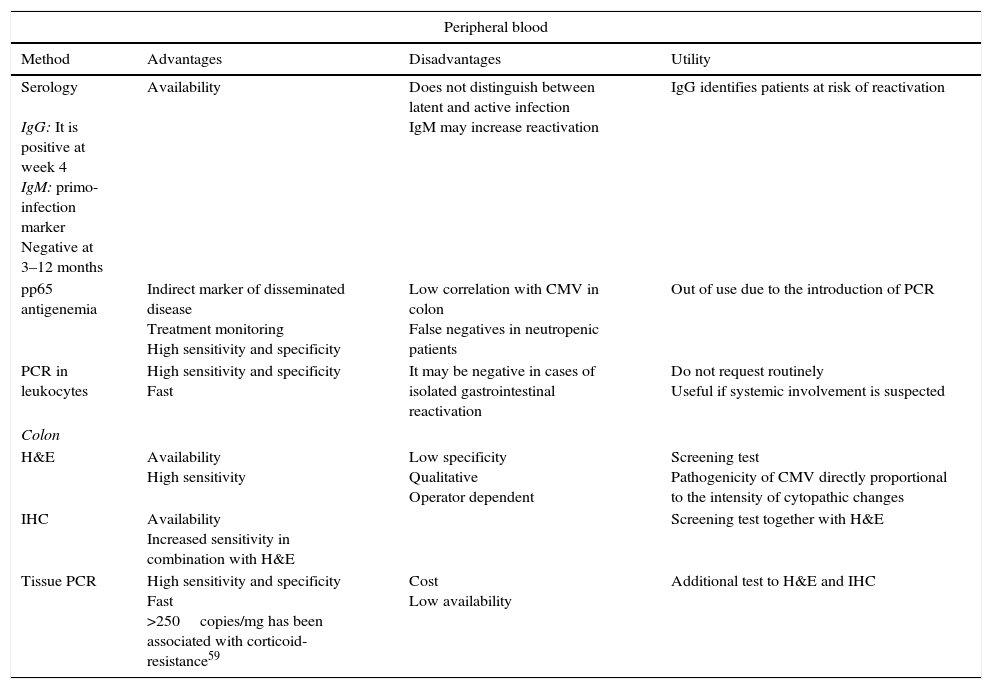
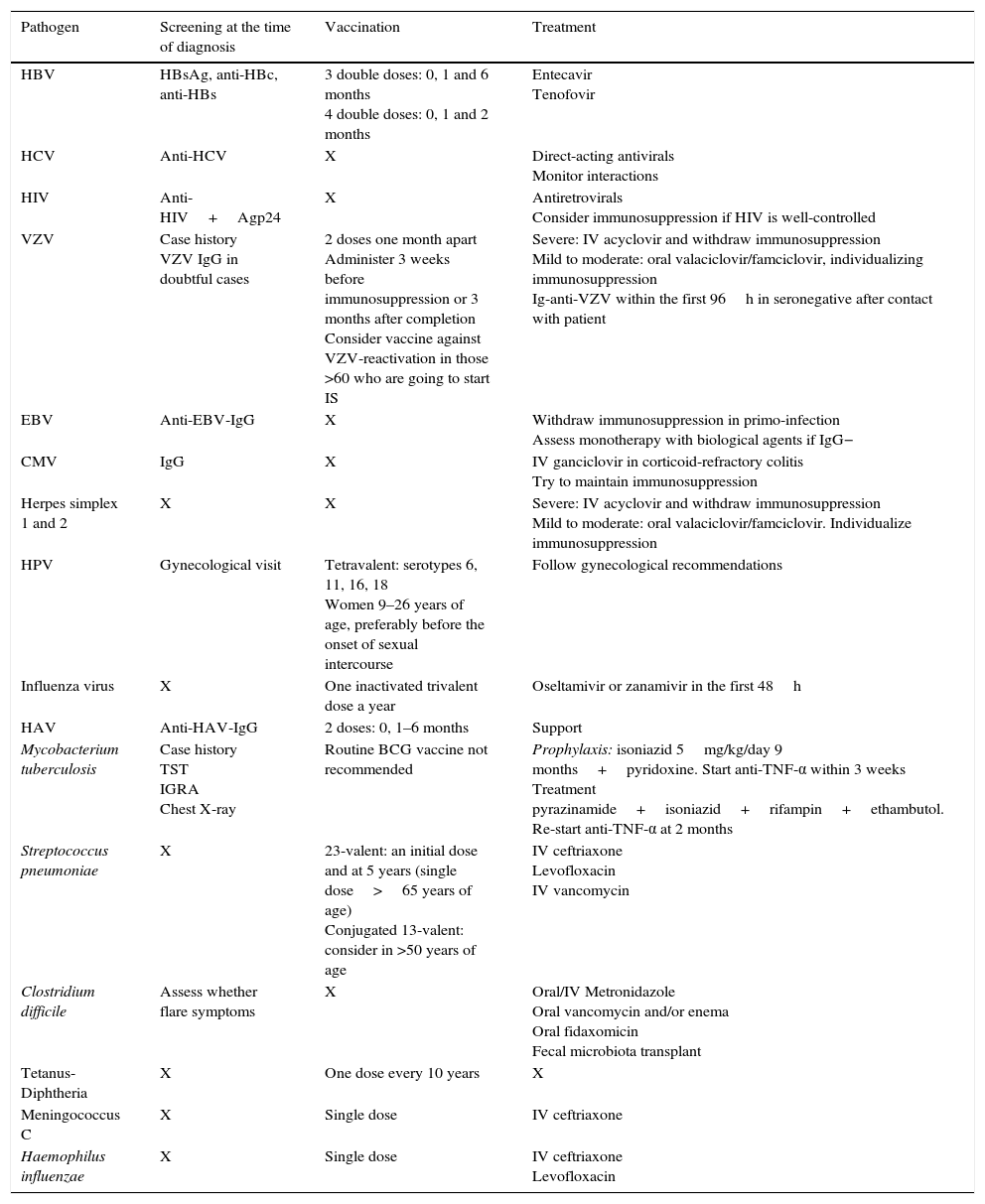
Patients with inflammatory bowel disease constitute a population with a special predisposition to develop bacterial, viral and fungal infections. Iatrogenic immunosuppression, frequent contact with healthcare facilities and surgical interventions are some of the risk factors that explain why these infections are one of the main causes of morbi-mortality in this disease. Some of these infections follow a subtle and paucisymptomatic evolution; their diagnosis and management may become a real challenge for the attending physician if their screening is not systematized or they are not considered in the differential diagnosis.
The objective of this review is to provide an update from a practical and concise perspective on the knowledge regarding the epidemiology, prevention, diagnosis and treatment of the most common infections.
Los pacientes con enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal son una población con especial predisposición a presentar infecciones bacterianas, víricas y fúngicas. La inmunosupresión iatrogénica, el contacto frecuente con el medio hospitalario y las intervenciones quirúrgicas son algunos de los factores de riesgo que explican el que las infecciones sean una de las principales causas de morbimortalidad en esta enfermedad. Algunas de estas infecciones cursan de forma larvada y paucisintomática en muchas de las fases de su historia natural; su diagnóstico y tratamiento suponen un verdadero reto si no se sistematiza su detección o no se tienen presentes en el diagnóstico diferencial.
El objetivo de esta revisión es actualizar desde una perspectiva práctica y concisa el conocimiento sobre la epidemiología, la prevención, el diagnóstico y el tratamiento de las infecciones más comunes.