Human papilloma virus (HPV) is one of the main risk factors associated with the development of cervical cancer and its precursor lesions. It has been reported that HPV16 and 18 types cover approximately 70% of cervical cancer worldwide; however, significant variation in percentages of HPV infections could be related to specific populations.
Materials and methodsPurified DNA of 67 cervical samples were analyzed by Linear Array® HPV genotyping kit. These analyzed samples correspond to 19 cervical tumours, 15 high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions, 20 low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions, and 13 cervical samples without injury were studied, all of them previously diagnosed.
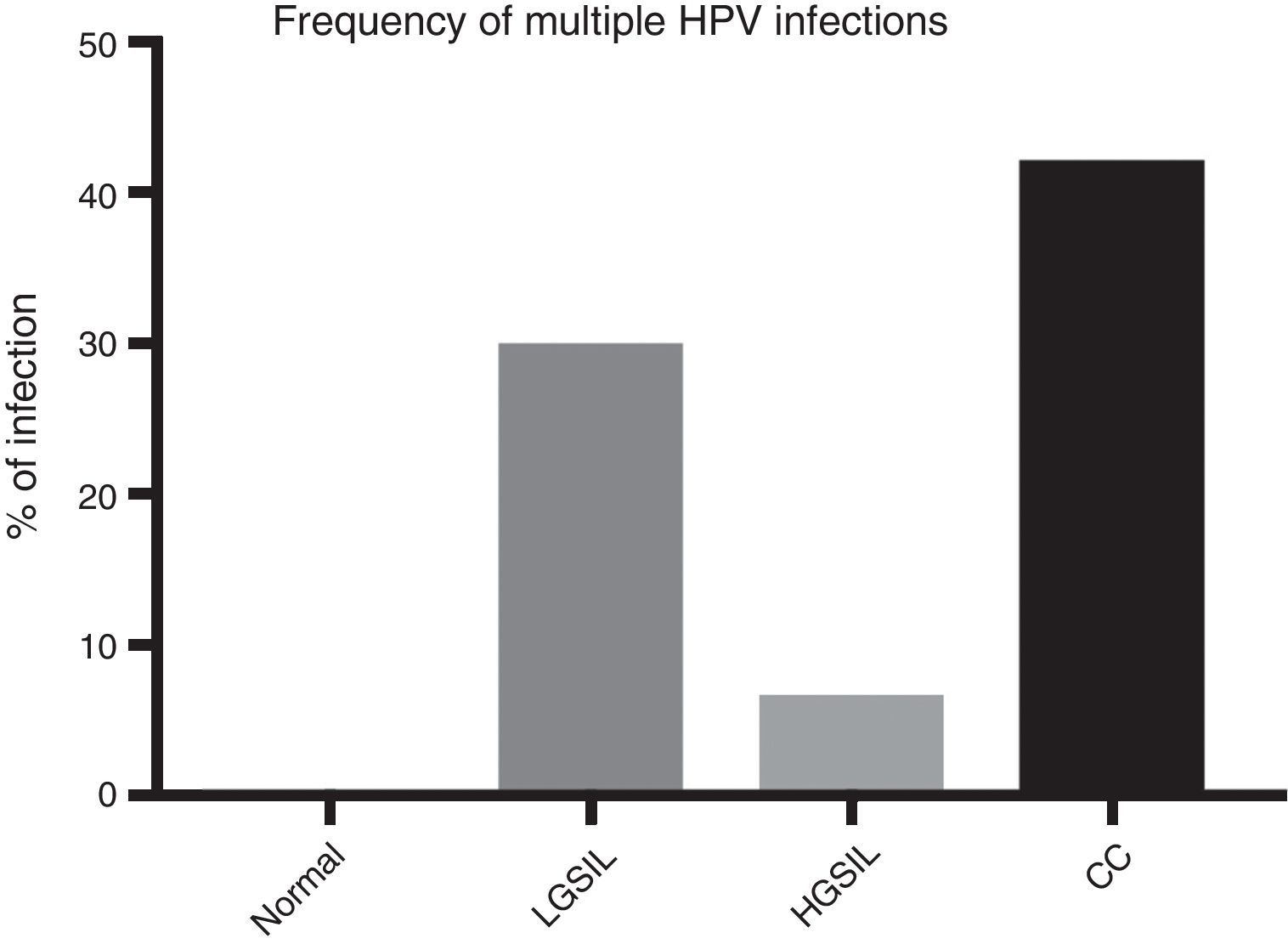
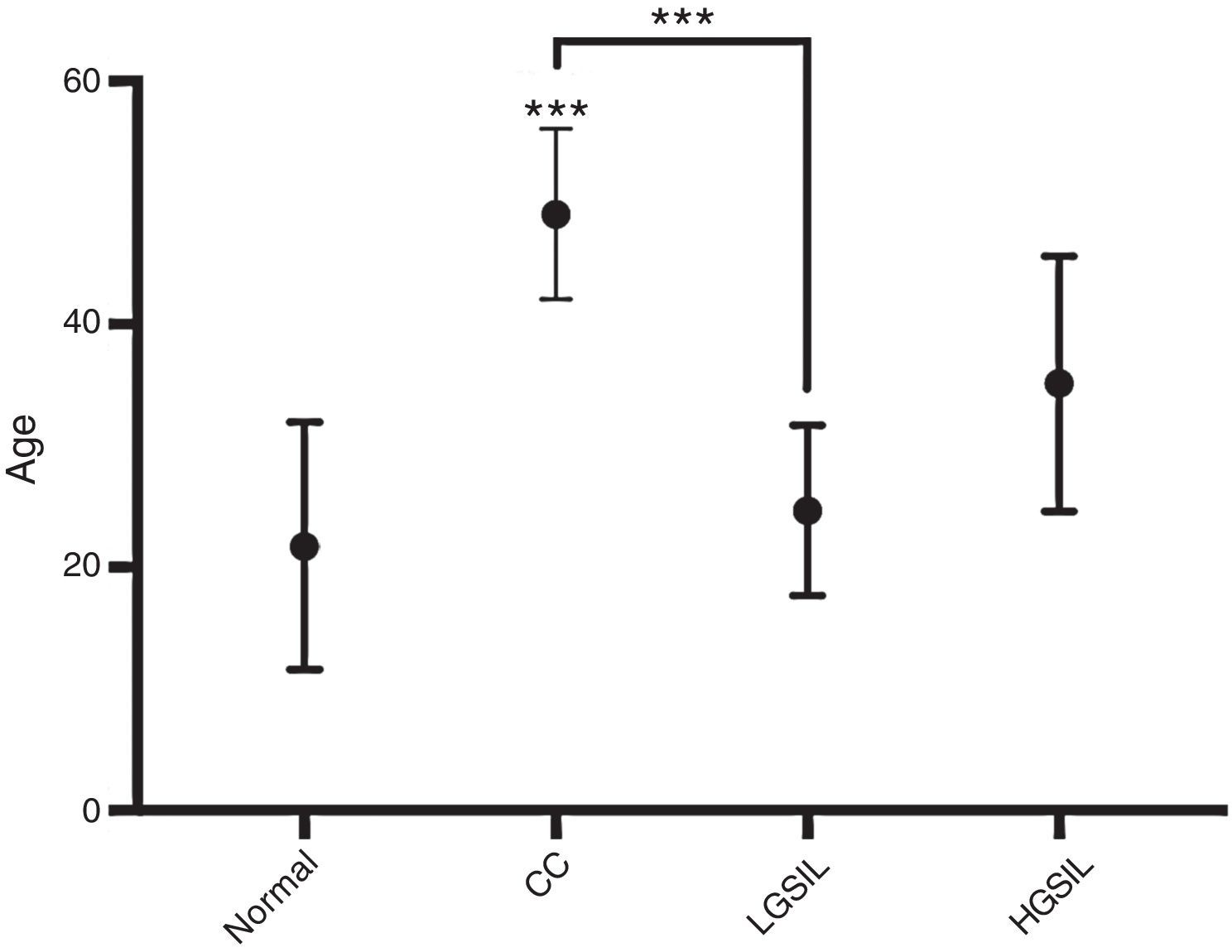
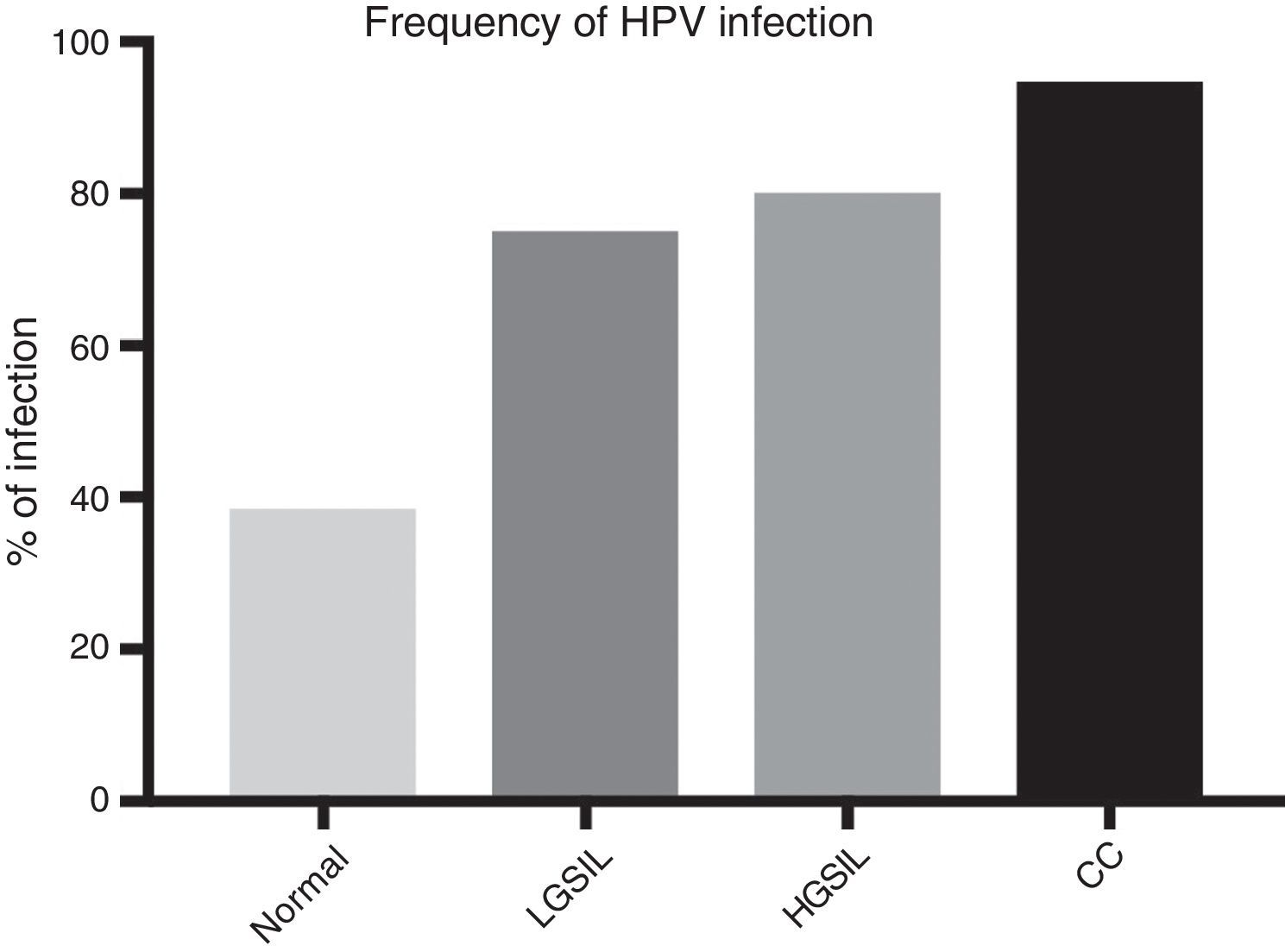
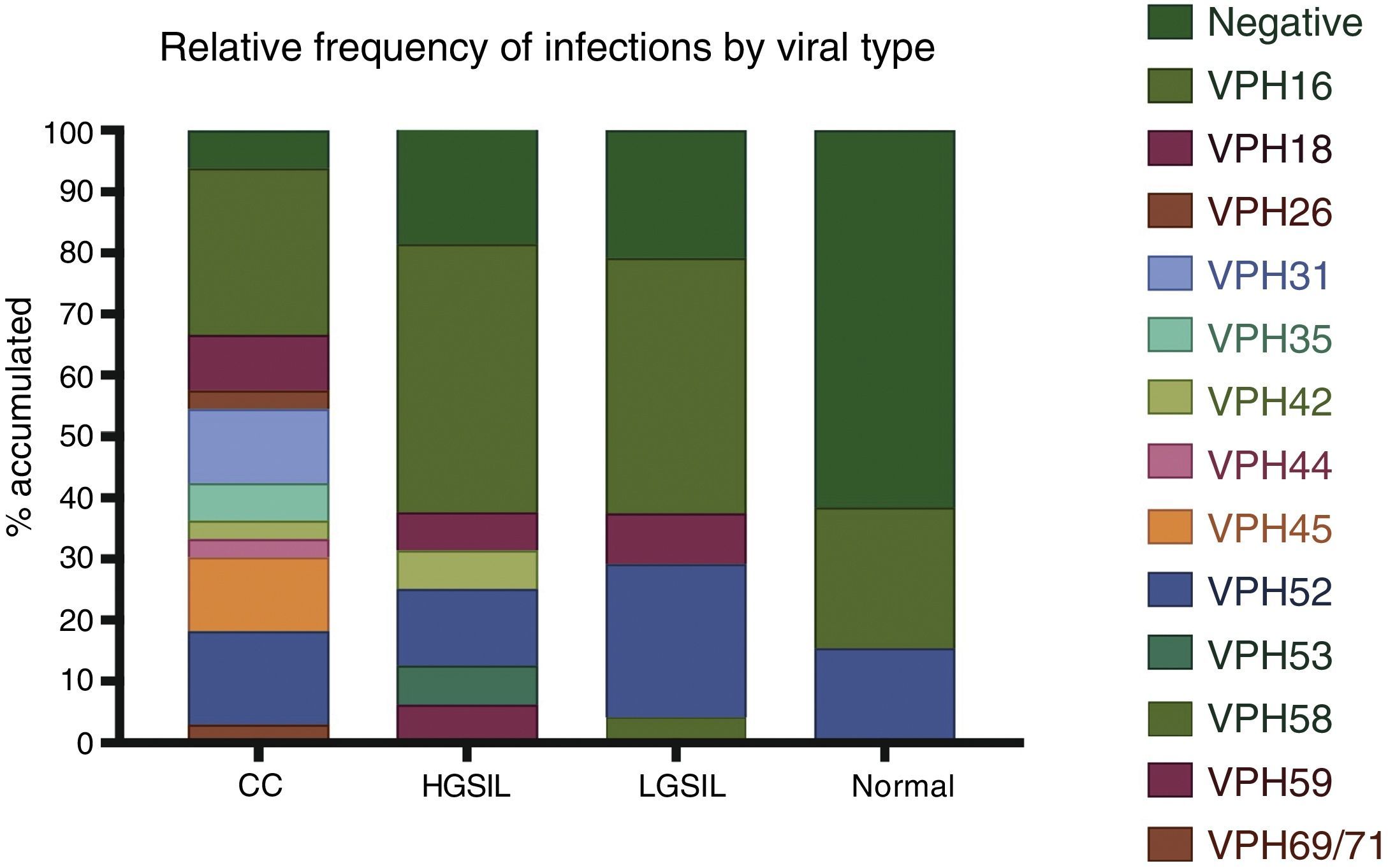
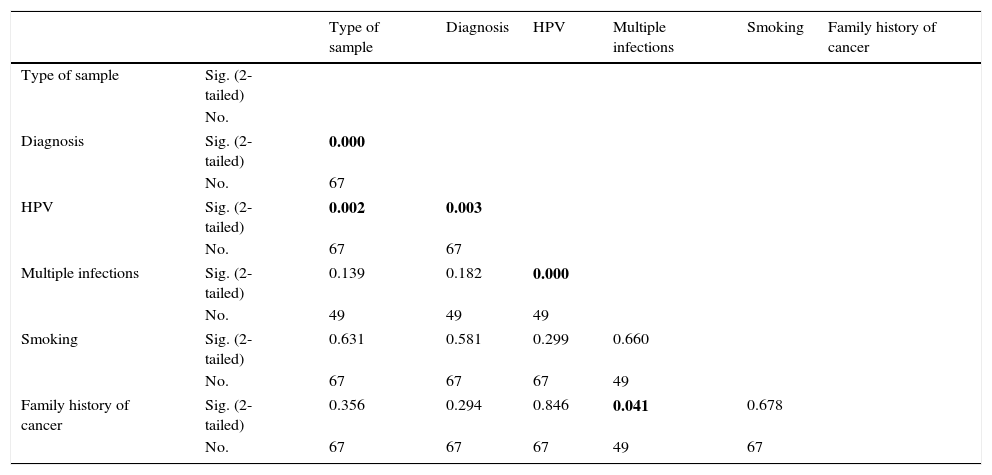
ResultsIn general, 16 different HPV types were found with differences in their frequencies, cervical invasive cancer being the richest in HPV sequences, followed by the low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions and then high-grade lesions. HPV16 was the most frequently distributed type in neoplastic lesions of the cervix, followed by the HPV52, suggesting viral type variability, probably associated to the geographical region studied.
ConclusionsThe results could indicate variability in HPV presence in Mexico, underlining the important role for HPV52 among others in the Mexican population. This would also potentially have an impact on the current anti-HPV vaccination schemes.
El virus del papiloma humano (VPH) es uno de los principales factores de riesgo para el desarrollo del cáncer cervicouterino y sus lesiones precursoras. Se ha mencionado que a nivel mundial los tipos VPH16 y 18 cubren aproximadamente el 70% del cáncer de cérvix; sin embargo, se ha reportado que estos porcentajes varían significativamente dependiendo de la población en estudio.
Materiales y métodosSe estudió el ADN de un grupo de 67 muestras de tejidos cervicales mediante el kit HPV Linear Array® que detecta 37 tipos diferentes de VPH, y que correspondieron a 19 lesiones escamosos invasivas del cérvix, 15 lesiones intraepiteliales escamosas de alto grado, 20 lesiones intraepiteliales escamosas de bajo grado y 13 muestras de cérvix uterino sin lesión, todas ellas previamente diagnosticadas.
ResultadosEn general, se encontraron 16 tipos distintos de VPH con una clara diferencia en sus frecuencias, siendo en el cáncer invasivo donde se encontró mayor variedad de VPH, seguido por las lesiones intraepiteliales escamosas de bajo grado y, posteriormente, las de alto grado. El VPH16 fue el tipo más frecuentemente distribuido en las lesiones estudiadas, seguido por el VPH52, evidenciando una variabilidad de tipos virales dependiendo de la zona geográfica de referencia.
ConclusionesLos resultados indicarían variabilidad en la presencia de los VPH en México, resaltando la importancia del VPH52, entre otros, en nuestra población. Estos datos, además, tendrían un potencial impacto en la actual campaña de vacunación anti-VPH.