To compare the nutritional status of a population of hospitalized patients, divided into 2 different groups, both at admission and hospital discharge, and to assess the influence of nutritional alteration during the hospital stay.
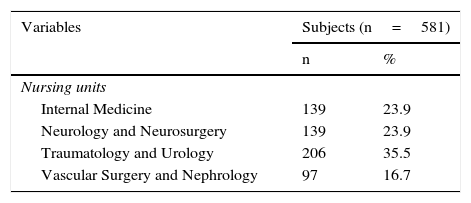
Material and methodsQuasi-experimental study comprising 2 groups of patients (N=581): an intervention group (n=303), in which nurses received specific training on managing care methodology, and a control group (n=278), in which nurses continued their usual dynamics. Each group was made up of 2 care units with patients from both surgical and medical specialties. Inclusion criteria: patients admitted to the selected units with a minimum stay of 5 days. The sample selection was performed prospectively and consecutively after implementing the training.
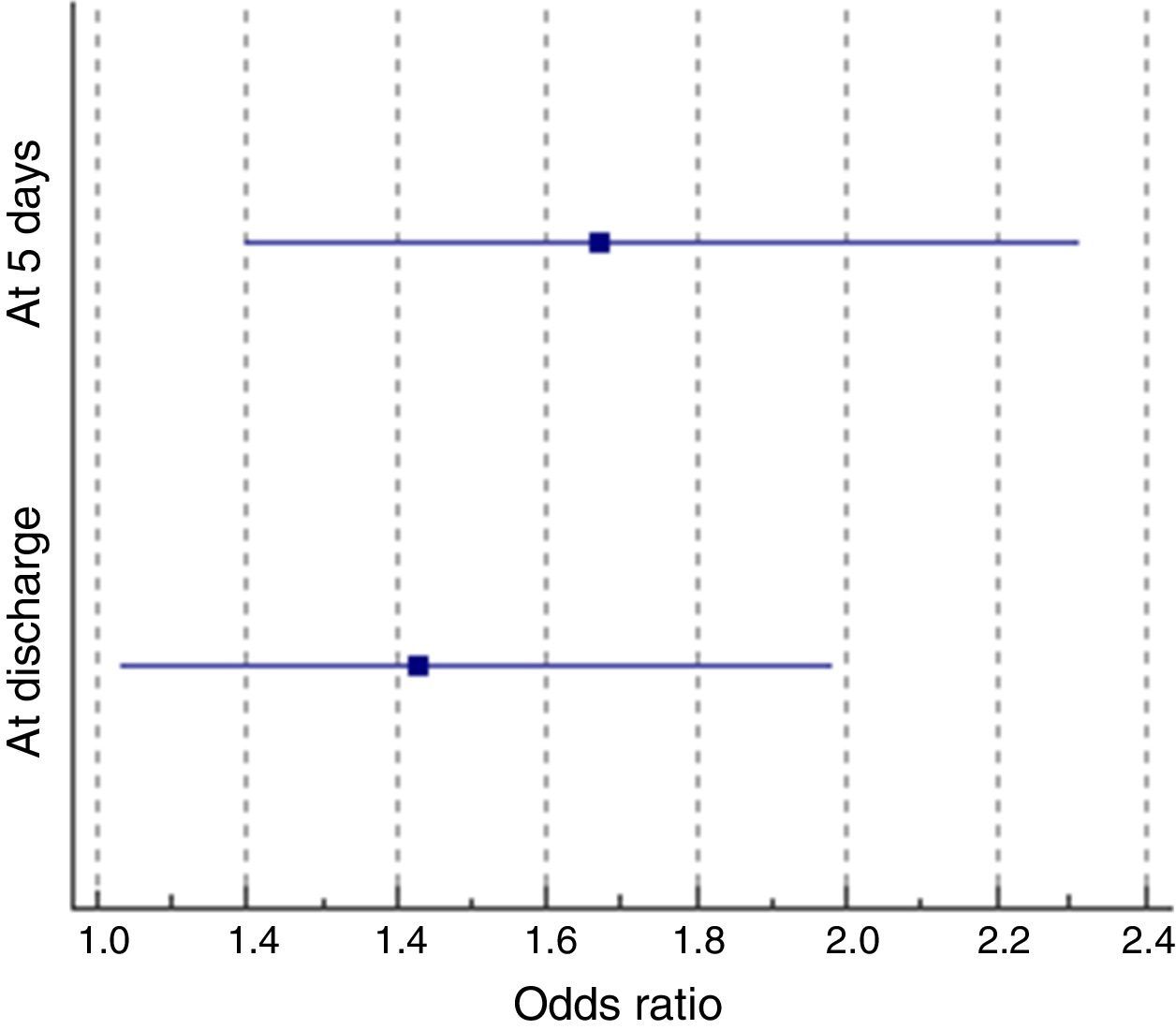
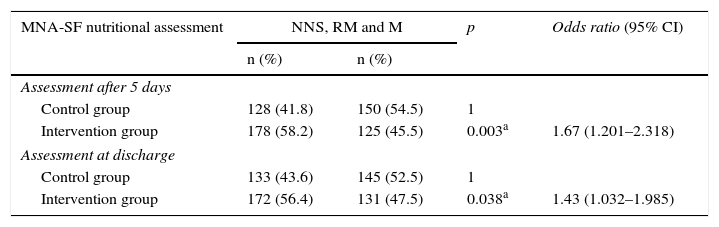
ResultsOf the 581 patients studied, 49.4% were women and 50.6% were men. Mean patient age was 68.29 (SD 16.23) years. In the intervention group, the odds ratio (OR) associated with good nutritional status was multiplied by 1.7 (OR=1.67) compared to the control group in the first evaluation and by 1.4 times (OR=1.43) at hospital discharge. The average stay in days was higher in the control group (13.71, SD 10.19) than in the intervention group (10.89, SD 7.49) (p<0.001).
ConclusionThe systematic methodology-based intervention in the chosen units was positive. Patients admitted to the intervention units had a lower nutritional alteration and a shorter hospital stay than those admitted to the control units.
Comparar el estado nutricional de una población de pacientes hospitalizados distribuidos en 2 grupos diferentes, tanto al ingreso como al alta hospitalaria y evaluar la influencia de la alteración nutricional en la estancia hospitalaria.
Material y métodosEstudio cuasiexperimental formado por 2 grupos de pacientes (N=581): un grupo de intervención (n=303), en el que las enfermeras responsables recibieron formación específica en metodología de cuidados y otro de control (n=278), en el que las enfermeras siguieron su dinámica habitual. Cada grupo estaba compuesto por 2 unidades de cuidados con pacientes tanto de especialidades médicas como quirúrgicas. Criterios de inclusión: pacientes ingresados en las unidades elegidas con una estancia mínima de 5 días. La selección de la muestra se realizó de manera prospectiva y consecutivamente tras realizar la acción formativa.
ResultadosDe los 581 pacientes estudiados, el 49,4% eran mujeres y el 50,6% hombres, con una edad media de 68,29 (DT 16,23) años. En el grupo intervención, la odds ratio (OR) asociada a un buen estado nutricional se multiplicaba por 1,7 veces (OR=1,67) respecto al grupo control en la primera evaluación y por 1,4 veces (OR=1,43) al alta. La estancia media en días resultó mayor en el grupo control (13,71, DT 10,19) que en el grupo intervención (10,89, DT 7,49) (p<0,001).
ConclusiónLa intervención basada en metodología sistematizada en las unidades intervenidas resultó positiva. Los pacientes ingresados en ellas presentaron una menor alteración nutricional y una menor estancia hospitalaria que los ingresados en las unidades control.