Spondyloarthritis is a general term referring to a group of chronic rheumatic illnesses that share clinical, genetic, radiological and epidemiological features. The clinical presentation of spondyloarthritis is characterized by the compromise of both the axial and peripheral articular skeleton. We aimed to evaluate the efficacy of an aquatic exercise plus relaxation program in patients with spondyloarthritis.
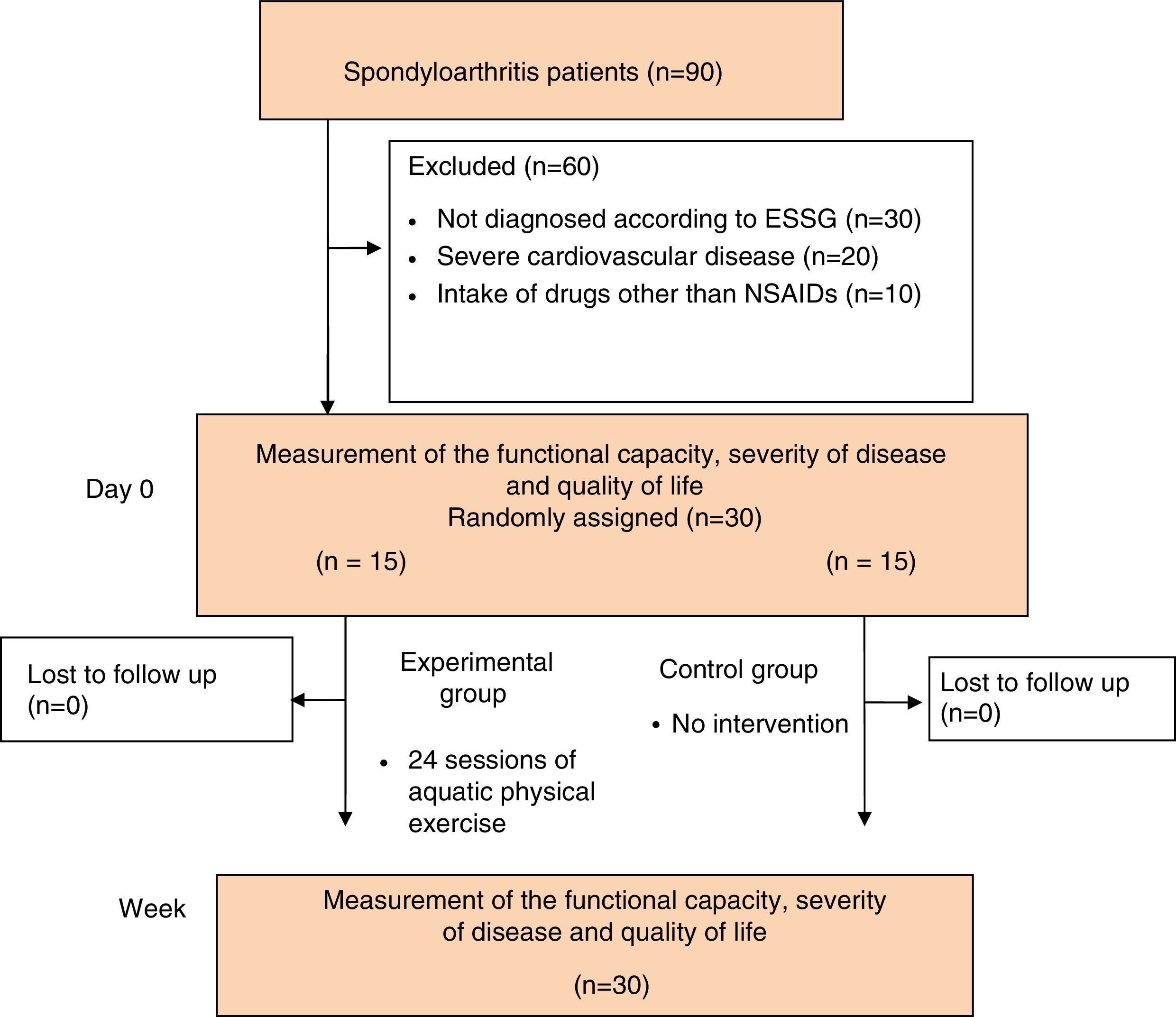
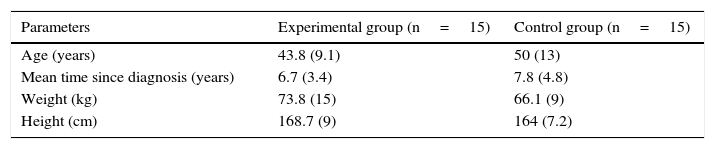
Patients and methodThis was a randomized single blind study including 30 patients with spondylitis who were randomly assigned to an experimental or control group. For 2 months, the experimental group underwent an aquatic fitness plus relaxation program (3 sessions per week). Evaluations were also performed in the control group the same days as the experimental group but they did not participate in any supervised exercise program. The following data were obtained at baseline and immediately after application of the last session: Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index, Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index, Health Questionnaire SF-12 and Sigma PC3® (Sigma-Elektro GmbH, Neustadt, Germany) Heart Rate Monitor.
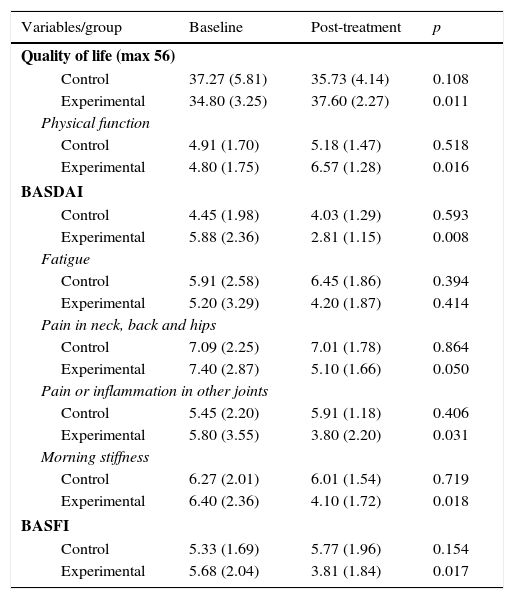
ResultsThe Mann–Whitney test showed statistically significant differences in the quality of life (physical function [p=0.05]), Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index (p=0.015), Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (fatigue [p=0.032], neck pain, back and hips [p=0.045], pain or swelling in other joints [p=0.032] and in waking morning stiffness [p=0.019]).
ConclusionsThe results of the present study suggest that therapy with physical exercise plus relaxation provides benefits to spondyloarthritis patients and these are advised as a part of their usual treatment.
La espondiloartritis hace referencia a un conjunto de enfermedades reumáticas crónicas que comparten diversas características clínicas, genéticas, radiológicas y epidemiológicas. La presentación clínica de las espondiloartritis se caracteriza por compromiso del esqueleto axial y articular periférico. El objetivo de este estudio fue evaluar la eficacia de un programa de entrenamiento físico más relajación en el medio acuático en personas con espondiloartritis.
Pacientes y métodoEstudio clínico aleatorizado de simple ciego en el que 30 personas con espondiloartritis fueron asignadas al azar a un grupo experimental o control. Durante 2 meses al grupo experimental se le aplicó un programa de entrenamiento físico en el medio acuático más relajación (3 sesiones por semana), y al grupo control se le realizaron las evaluaciones los mismos días que al experimental sin que participaran en ningún programa de ejercicio físico supervisado. Los datos obtenidos al inicio del estudio e inmediatamente después de la aplicación de la última sesión fueron: Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index («Índice de funcionalidad para las espondiloartritis»), Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index («Índice de actividad de la enfermedad del grupo de Bath»), Cuestionario de Salud SF-12 y pulsómetro Sigma PC3® (Sigma-Elektro GmbH, Neustadt, Aemania).
ResultadosLa prueba U de Mann-Whitney mostró diferencias estadísticamente significativas para la calidad de vida (función física [p=0,05]), Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index (p=0,015), Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (fatiga [p=0,032], dolor de cuello, espalda y caderas [p=0,045], dolor o inflamación en otras articulaciones [p=0,032] y rigidez matutina la despertar [p=0,019]).
ConclusionesLos resultados del presente estudio muestran que los tratamientos de ejercicio físico unidos a la relajación aportan beneficios a los pacientes con espondiloartritis y son recomendables como parte del tratamiento de la enfermedad.