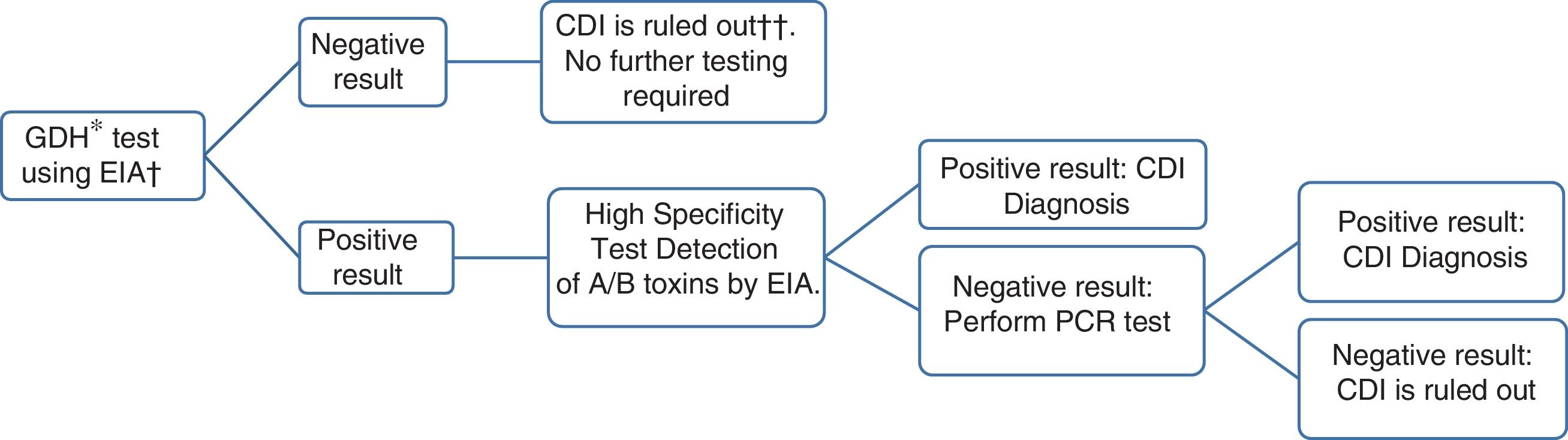
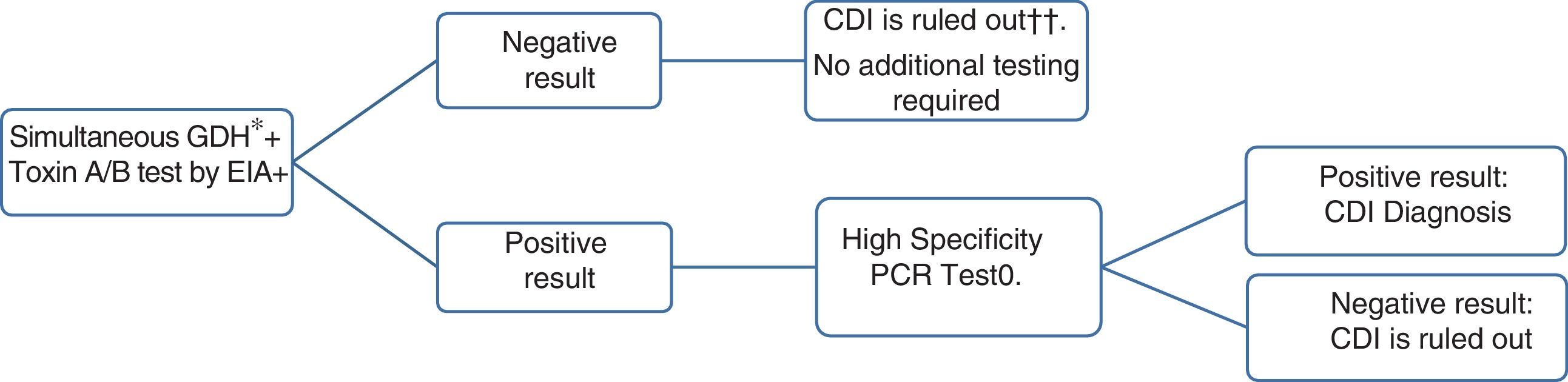
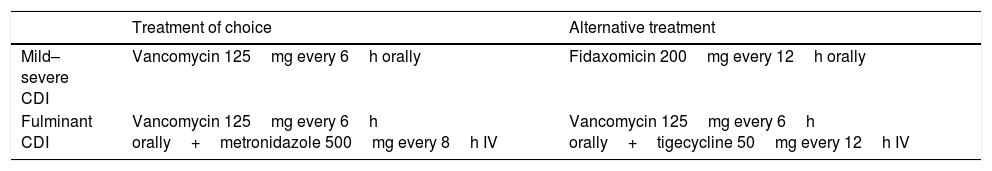
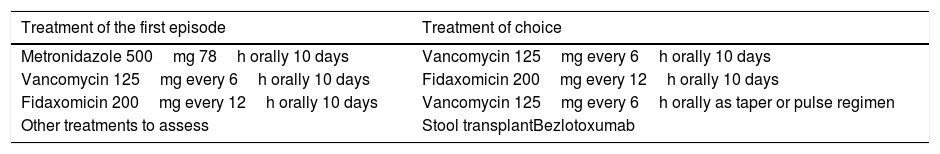
Clostridioides difficile is the main cause of healthcare-associated diarrhoea in adults. The incidence of C. difficile infection (CDI) has increased in recent years. The risk of recurrence of CDI is 15–25% in a first episode and this risk is increased in subsequent episodes. Toxigenic culture and cytotoxicity tests are the reference techniques for the microbiological diagnosis of CDI. These are laborious and slow techniques and therefore they have been replaced in clinical practice by the application of a multi-step algorithm that includes the detection of glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH), toxins and molecular techniques. The treatment of choice for CDI is vancomycin. In recent years, new drugs and new treatment strategies have appeared that are especially useful in the treatment of relapses of CDI.
Clostridioides difficile es el principal responsable de la diarrea asociada con la atención sanitaria en adultos. La incidencia de la infección por C. difficile (ICD) ha aumentado en los últimos años. El riesgo de recidivas de la ICD es del 15-25% en un primer episodio, y este riesgo se incrementa en los posteriores episodios. Las técnicas de referencia para el diagnóstico microbiológico de la ICD son el cultivo toxigénico y el ensayo de citotoxicidad. Son técnicas laboriosas y lentas, por lo que han sido sustituidas en la práctica clínica por la aplicación de un algoritmo de varios pasos que incluye la detección de glutamato deshidrogenasa (GDH), toxinas y técnicas moleculares. El tratamiento de elección de la ICD es la vancomicina. En los últimos años han aparecido nuevos fármacos y nuevas estrategias especialmente útiles en el tratamiento de las recidivas de la ICD.