Autoimmune haemolytic anaemia (AIHA) is an infrequent and heterogeneous disease in its pathophysiology and clinical behaviour, therefore it is generally managed empirically.
Patients and methodsWe conducted an observational, retrospective and multicentre study of 93 patients diagnosed with AHAI in 9 Spanish hospitals between 1987 and 2017, with a median follow-up of 28 months.
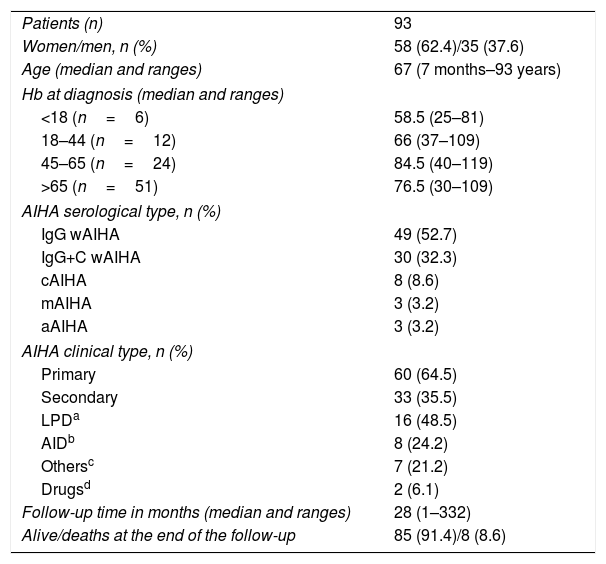
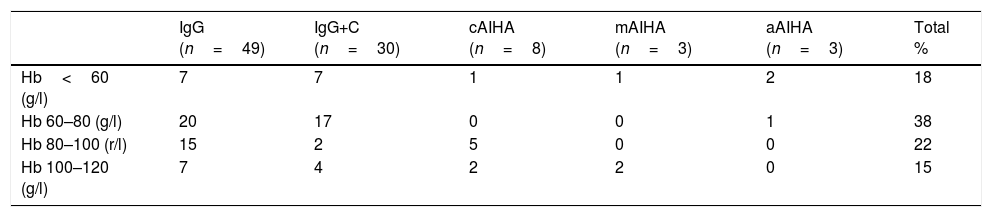
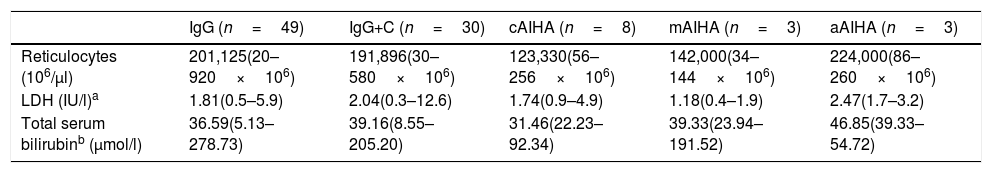
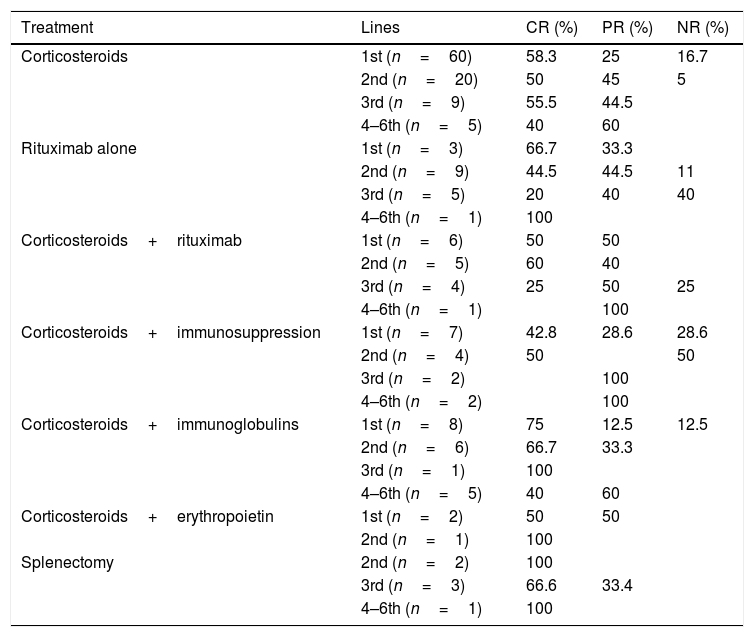
ResultsMedian age of 67 years; 85% AHAI for hot antibodies and 64% primary AHAI. The lowest haemoglobin values at diagnosis related to patients under 45 years of age and serological type IgG+C. Of the patients, 92% received first line treatment, 54% second line, and 27% third line. The warm AHAI were treated in first line with steroids, with overall responses of 83% and complete of 58%. Rituximab in monotherapy or in association with steroids was administered to 34 patients with overall responses close to 100% (complete responses 40–60%), relegating splenectomy to the third line. The immunosuppressive treatment was administered in patients with autoimmune diseases or in corticoid-dependent patients.
DiscussionWe found high rates of response to steroids, with very prolonged treatments that cause side effects and corticoid dependence in a third of patients. The combination of steroids with rituximab in the first line, could be indicated in patients with low levels of haemoglobin and serological type IgG+C. The high relapse rates make necessary the development of randomised studies with new drugs or the combination with existing ones, which allow longer response times and with fewer side effects.
Las anemias hemolíticas autoinmunes (AHAI) son enfermedades poco frecuentes y heterogéneas en su fisiopatología y comportamiento clínico, siendo el manejo de las mismas fundamentalmente empírico.
Pacientes y métodosRealizamos un estudio observacional, retrospectivo y multicéntrico de 93 pacientes diagnosticados de AHAI en 9 hospitales españoles entre 1987 y 2017, con una mediana de seguimiento de 28 meses.
ResultadosMediana de edad de 67 años; un 85% de AHAI por anticuerpos calientes y un 64% AHAI primarias. Los valores de hemoglobina más bajos al diagnóstico se relacionaron con edad<45 años y el tipo serológico IgG+C. Un 92% recibieron tratamiento de primera línea, un 54% de segunda línea y un 27% de tercera línea. Las AHAI calientes fueron tratadas en primera línea con esteroides, con respuestas globales del 83% y completas del 58%. El rituximab en monoterapia o asociado a esteroides se administró a 34 pacientes con respuestas globales cercanas al 100% (respuestas completas 40-60%), relegando la esplenectomía a tercera línea. El tratamiento inmunosupresor se administró en pacientes con enfermedades autoinmunes o en dependientes de corticoides.
DiscusiónEncontramos altas tasas de respuesta a esteroides, con tratamientos muy prolongados que provocan efectos secundarios y corticodependencia en un tercio de los pacientes. La asociación de esteroides con rituximab en primera línea podría estar indicada en pacientes con bajos niveles de hemoglobina y tipo serológico IgG+C. Las altas tasas de recaída hacen necesario el desarrollo de estudios aleatorizados con nuevos fármacos o la asociación con los ya existentes, que permitan mayor duración de las respuestas y con menores efectos secundarios.