Molecular changes in the CTLA-4 gene can modify the ability to control T lymphocyte proliferation, and promote the persistence or elimination of the hepatitis C virus (HCV). We aimed to investigate the frequency and association of −319 C/T and +49 A/G polymorphism in the CTLA-4 gene in patients infected with HCV.
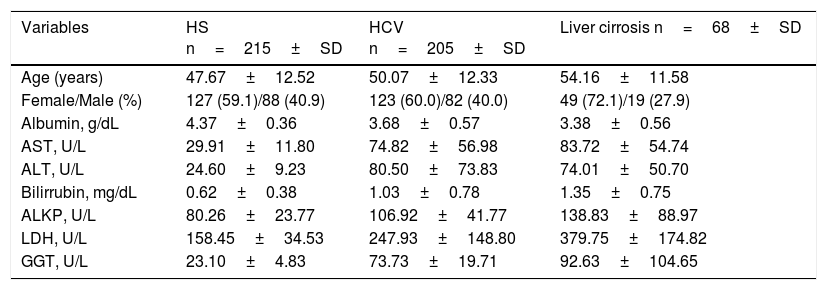
MethodsThe CTLA-4 gene polymorphisms (−319 C/T in the promoter region, and +49 A/G in exon 1) were analyzed by T-ARMS-PCR in 420 individuals, including 205 chronic HCV infected patients and 215 healthy subjects.
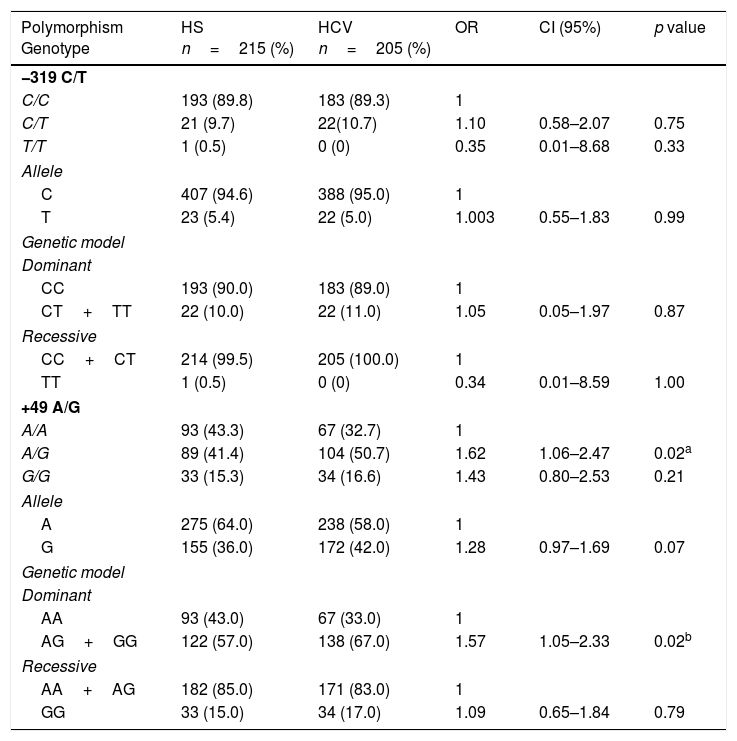
ResultsWe found a positive association of +49G allele with HCV infection (OR 1.48; 95% CI: 1.09–2.02; p=0.02), and with males (OR 1.80; 95% CI: 1.16–2.79; p=0.02), both in chronic disease (without cirrhosis). Also, significant differences in +49 A/G genotypes distribution between HCV infected patients and healthy subjects were shown in a dominant genetic model (GG+GA versus AA; OR 1.57; 95% CI: 1.05–2.33; p=0.04). No significant differences were observed in the −319 C/T polymorphism between HCV infected patients and healthy subjects. Moreover, −319C/+49G haplotype confers susceptibility to HCV genotype 3 infection (OR 10.68; 95% CI: 1.17–96.97; p=0.04).
ConclusionsThe +49G allele confers susceptibility to HCV infection and with male gender, both in chronic disease. In addition, the −319C/+49G haplotype confers susceptibility to HCV genotype 3 infection. Our results support an important role of the −319 C/T and +49 A/G polymorphisms in HCV infection.
Cambios moleculares en el gen CTLA-4 pueden modificar la habilidad para controlar la proliferación de los linfocitos T, y promover la persistencia o eliminación del virus de la hepatitis C (VHC). Nuestro objetivo fue investigar la frecuencia y asociación de los polimorfismos −319 C/T y +49 A/G del gen CTLA-4, en pacientes con infección por VHC.
MétodosLos polimorfismos del gen CTLA-4 (−319 C/T en la región promotora y +49 A/G en el exón 1) fueron analizados por T-ARMS-PCR en 420 individuos, incluidos 205 pacientes con infección crónica por VHC y 215 sujetos sanos.
ResultadosSe encontró una asociación positiva del alelo +49G con la infección por VHC (OR 1,48; IC 95% 1,09-2,02; p=0,02), y con el sexo masculino (OR 1,80; IC 95% 1,16-2,79; p=0,02), ambos en enfermedad crónica (sin cirrosis). Se observaron diferencias significativas en la distribución de los genotipos del polimorfismo +49 A/G, entre los pacientes con infección por VHC y los sujetos sanos en un modelo genético dominante (GG+GA frente a AA; OR1,57; IC 95% 1,05-2,33; p=0,04). No se observaron diferencias en las frecuencias del polimorfismo −319 C/T, entre pacientes con VHC y sujetos sanos. El haplotipo −319C/+49G confiere susceptibilidad a la infección por el genotipo 3 del VHC (OR 10,68; IC 95% 1,17-96,97; p=0,04).
ConclusionesEl alelo +49G confiere susceptibilidad a infección por VHC y a infección en el sexo masculino, ambos en enfermedad crónica. Además, el haplotipo −319C/+49G confiere susceptibilidad a la infección por el genotipo 3 del VHC. Nuestros resultados evidencian una implicación importante de los polimorfismos −319 C/T y +49 A/G en la infección por VHC.