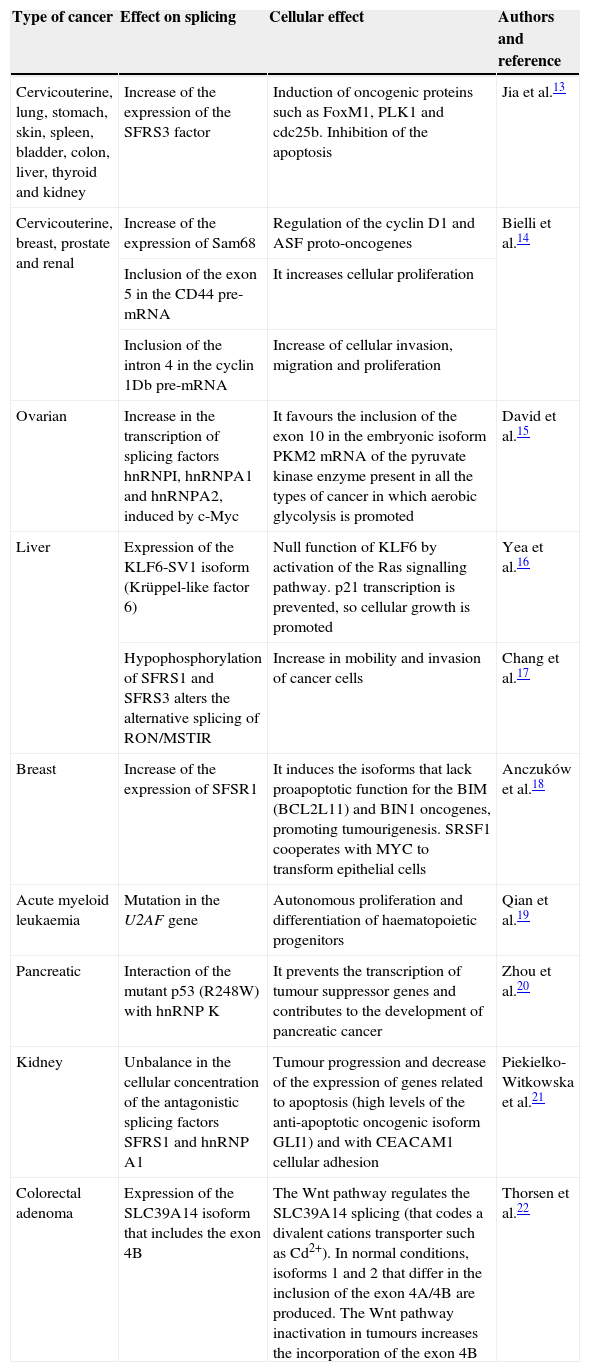
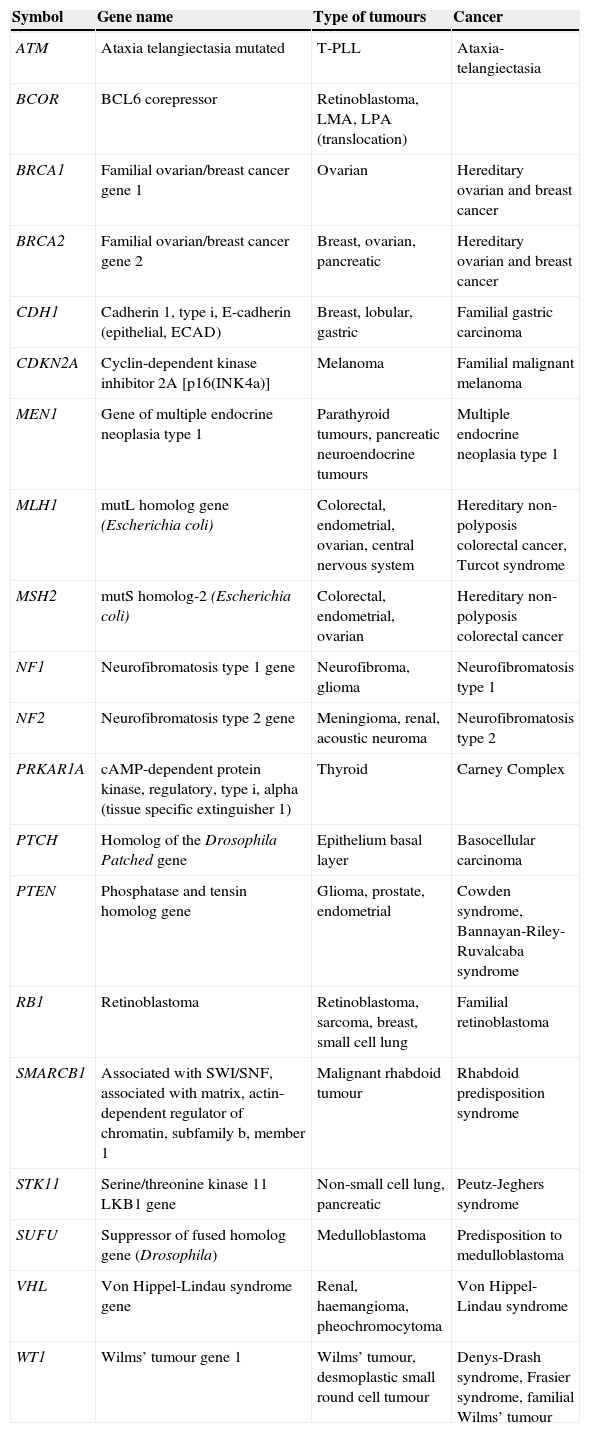
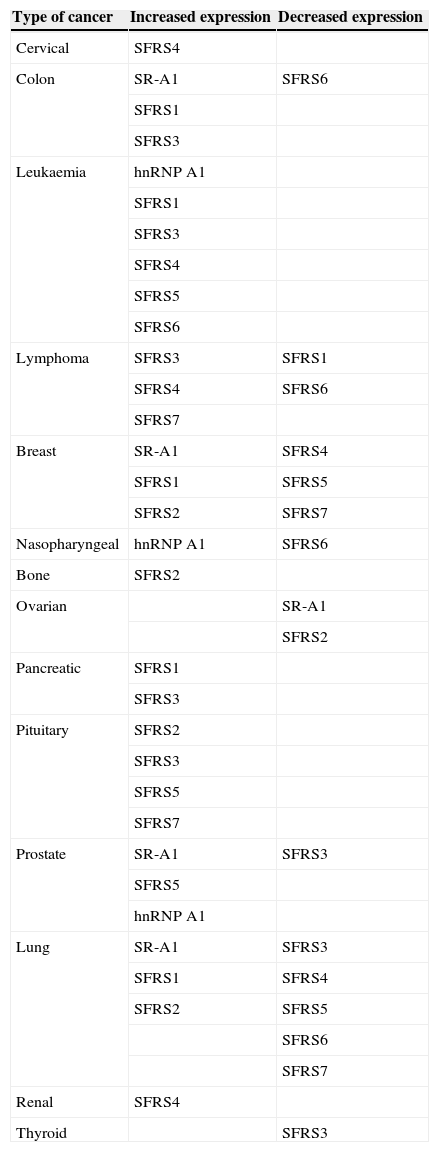
The accurate expression of the genetic information is regulated by processes like mRNA splicing, proposed after the discoveries of Phil Sharp and Richard Roberts, who demonstrated the existence of intronic sequences, present in almost every structural eukaryotic gene, which should be precisely removed. This intron removal is called “splicing”, which generates different proteins from a single mRNA, with different or even antagonistic functions. We currently know that alternative splicing is the most important source of protein diversity, given that 70% of the human genes undergo splicing and that mutations causing defects in this process could originate up to 50% of genetic diseases, including cancer. When these defects occur in genes involved in cell adhesion, proliferation and cell cycle regulation, there is an impact on cancer progression, rising the opportunity to diagnose and treat some types of cancer according to a particular splicing profile.
La expresión de la información genética es regulada por procesos como el splicing del ARN mensajero, mecanismo propuesto por Phil Sharp y Richard Roberts, quienes demostraron la existencia de secuencias intrónicas, las cuales interrumpen a la mayoría de los genes estructurales en eucariotes y deben ser removidas con gran precisión. Dicha remoción de intrones se denomina splicing, y permite generar variantes proteicas a partir de un solo gen, cada una con funciones diversas y, a menudo, antagónicas. Actualmente se sabe que el splicing es la principal fuente de diversidad proteica, ya que el 70% de los genes humanos lo sufren, y defectos en este proceso originan hasta el 50% de las enfermedades genéticas, incluido el cáncer. Cuando estos defectos se presentan en genes involucrados en adhesión, proliferación y ciclo celular, repercuten en la progresión de procesos cancerosos cuyo diagnóstico, tratamiento y prognosis puede determinarse en base a su perfil de splicing.