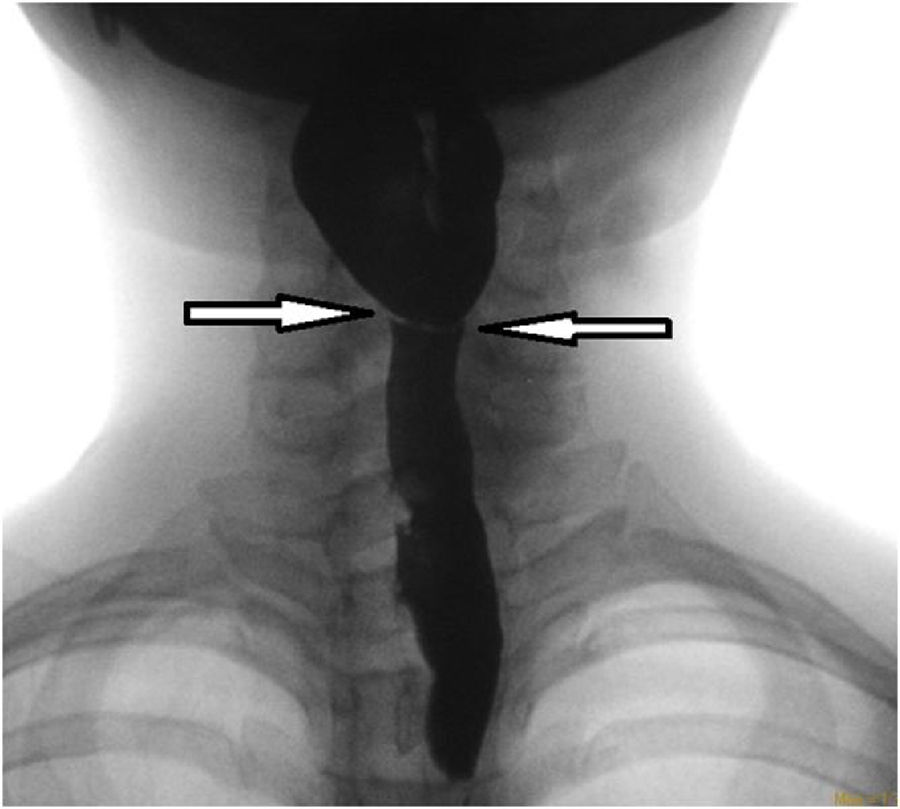
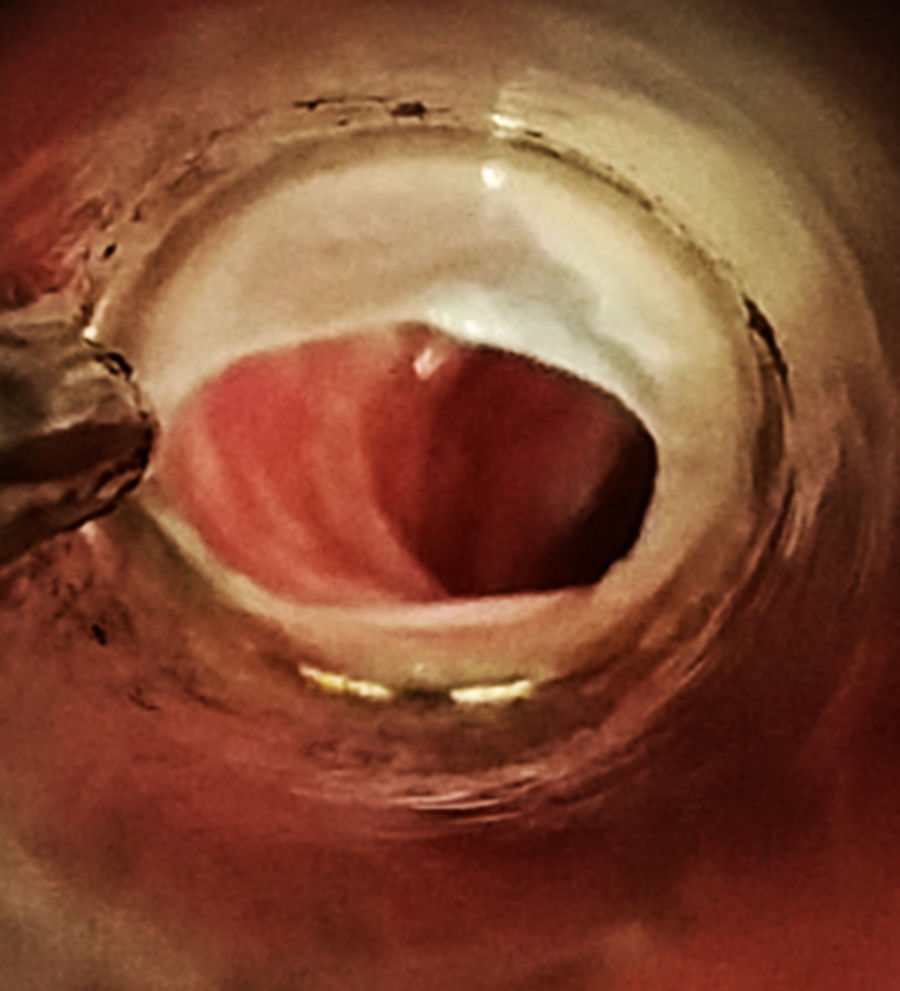
A 21-year-old woman presented with gradually progressive dysphagia for 4 months. On examination she was pale and had glossitis, cheilitis and koilonychia. The Barium swallow revealed a 8mm web in the post cricoid region (Fig. 1) and blood smear showed microcytic hypochromic anemia with anisocytosis. Other values were Hemoglobin of 4g/dL (12–14), MCV 63fL (80–95), MCH 17pg/dL (27–32), Serum Iron 20μg/dL (50–140), Serum Ferritin 13ng/mL (25–250), and total iron binding capacity 480μg/dL (245–450). A provisional diagnosis of Paterson Brown Kelly syndrome was made and the patient was treated with dilatation of the web (Fig. 2). The anemia was corrected with 2 units of packed cell transfusion and oral hematinics and it improved to 10g/dL. Paterson Brown Kelly Syndrome or Sideropenic dysphagia consists of a triad of dysphagia, iron deficiency anemia and esophageal webs. The exact etiology is unknown although nutritional deficiencies and some genetic factors have been implicated. It is more common in females and patients usually present with progressive dysphagia along with symptoms of iron deficiency anemia like easy fatigability. The prognosis is good however since it is thought to be a premalignant condition and regular surveillance with annual endoscopy should be done.
The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2025
SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact.
See moreSNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field.
See more