Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are chronic conditions that may be accompanied by autoimmune liver disease (AILD), most commonly primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC). The objective of this study was to evaluate the behaviour of patients with IBD associated with AILD and compare a PSC group with a non-PSC group.
MethodsMedical records of patients with IBD associated with PSC, autoimmune cholangitis, primary biliary cholangitis, small-duct PSC, autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) and overlapping syndromes were assessed.
ResultsFifty-four patients were included: 48 (88.9%) had ulcerative colitis and six (11.1%) had Crohn's disease; 35 (64.8%) had PSC and 19 (35.2%) did not have PSC. There was no difference in outcomes (surgical treatment for IBD, liver transplantation or death) between the groups. Time since the diagnosis of IBD was associated with surgical treatment of IBD (p=0.041; OR: 1.139, 95% CI: 1.006–1.255). Time since the diagnosis of AILD (p=0.003; OR: 1.259, 95% CI: 1.1–1.396), as well as portal hypertension at diagnosis (p=0.014; OR: 18.22, 95% CI: 1.815–182.96), were associated with liver transplantation. In addition, previous diagnosis of AIH was associated with de novo IBD (p=0.012; OR: 7.1, 95% CI: 1.215–42.43).
ConclusionBoth groups had similar disease behaviour. A longer time since the diagnosis of IBD increased the risk for surgical treatment (13.9%/year). A 25.9%/year increase in liver transplantation was observed after the diagnosis of AILD, which was increased 18.22 times by the presence of portal hypertension. In addition, the diagnosis of AIH was associated with an increase in the number of diagnoses of de novo IBD (7.1).
Las enfermedades inflamatorias intestinales (EII) son afecciones crónicas que pueden ir acompañadas de enfermedad hepática autoinmune (EHA) o colangitis esclerosante primaria (CEP). El objetivo del estudio fue evaluar el comportamiento de pacientes con EII asociada a EHA y comparar un grupo con CEP con un grupo sin CEP.
MétodosSe evaluaron las historias clínicas de pacientes con EII asociadas con CEP, colangitis autoinmune, colangitis biliar primaria, CEP de conductos pequeños, hepatitis autoinmune (HAI) y síndromes superpuestos.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 54 pacientes. De ellos, 48 (88,9%) tenían colitis ulcerosa y seis (11,1%) tenían enfermedad de Crohn; 35 (64,8%) tenían CEP y 19 (35,2%) no tenían CEP. No hubo diferencias en los resultados (tratamiento quirúrgico para la EII, trasplante de hígado o muerte) entre los grupos. El tiempo transcurrido desde el diagnóstico de EII se asoció con el tratamiento quirúrgico de la EII (p=0,041). El tiempo desde el diagnóstico de EHA (p=0,003), así como la hipertensión portal en el momento del diagnóstico (p=0,014), fueron asociado con el trasplante de hígado. Además, el diagnóstico previo de HAI se asoció con EII de novo (p=0,012).
ConclusiónAmbos grupos tuvieron un comportamiento de enfermedad similar. Un mayor tiempo desde el diagnóstico de EII aumentó el riesgo de tratamiento quirúrgico (13,9%/año). Se observó un aumento del 25,9%/año en el trasplante de hígado después de diagnóstico de EIA, que se incrementó 18,22 veces por la presencia de hipertensión portal. Además, el diagnóstico de HAI se asoció con un aumento en el número de diagnósticos de EII de novo (7,1).
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are chronic recurrent diseases that include ulcerative colitis (UC), Crohn's disease (CD) and unclassified colitis. Although the aetiology of IBD remains unknown, it is suggested that an inappropriate inflammatory response to intestinal microbiota occurs in susceptible patients.1–3 Extraintestinal manifestations are frequent and are experienced by 21–47% of patients and most commonly involve the musculoskeletal system, skin, eyes and hepatobiliary tract.4,5 Although the prevalence is not high, the association between IBD and autoimmune liver diseases (AILD) has been described for several years, especially with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC).6 Other AILD may also be associated with IBD. These include autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), autoimmune cholangitis (AIC), primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), small-duct primary sclerosing cholangitis (small-duct PSC) and overlapping syndromes (or variant syndromes), when there is an association between two AILD.7
In general, AILD progress independently of IBD activity, but the presence of PSC is related to the altered behaviour of IBD.4,8,9 The pathophysiology of the association between IBD and AILD is not fully understood. Genetic, environmental, luminal and immunological factors related to the pathophysiology of IBD may contribute to these liver diseases. Enterohepatic circulation of lymphocytes from the intestine to the liver is a relevant alteration and could be associated with the genesis of these conditions.5
This association can also be present for the first time after liver transplantation. During the course of liver disease, some patients will need liver transplantation and can develop IBD after transplantation, which is defined as de novo IBD. Some studies suggest that the incidence of de novo IBD is even more frequent in solid-organ recipients than in other patients.10
Little is known about the association between IBD and non-PSC AILD. Only a few series of clinical cases have been published.11,12 The aim of the present study was to study clinical features and disease progression in patients with IBD and AILD and to compare the group of patients with IBD associated with PSC and the group of patients with IBD associated with non-PSC AILD.
MethodsThis observational, retrospective, historical cohort study was based on data obtained from the patients’ medical records. The study included individuals of both sexes, over 18 years of age, with a diagnosis of IBD (UC or CD) associated with AILD (PSC, AIH, overlapping syndromes, small-duct PSC, AIC or PBC) from the Hospital das Clínicas of Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais. The variables were analysed in the sample as a whole and separately in the groups of patients with IBD and PSC and IBD associated with non-PSC AILD. The included variables were age, sex, smoking, time since the diagnosis of IBD and liver disease, the occurrence of de novo IBD after liver transplantation, clinical and endoscopic phenotype of IBD based on the Montreal classification, the severity of IBD (assessed according to the need for corticosteroid therapy), drugs being used in the treatment of IBD and AILD, portal hypertension at diagnosis (evaluated through indirect measures, such as the presence of oesophageal varices, presence of ascites, increase in the diameter of portal system veins associated with splenomegaly, reversal of portal vein blood flow and presence of portosystemic collateral circulation), liver biochemical profile at the diagnosis of liver disease, cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection, colon cancer, the need for surgical treatment of IBD, liver transplantation and death.
The diagnosis of IBD was made based on clinical, laboratory, radiological, endoscopic, histological and surgical findings.13,14De novo IBD was defined as the development of IBD after liver transplantation in patients who were excluded for the presence of IBD before the transplantation and other causes of colitis after transplantation.15 All patients, independent of when they developed IBD, were included in the study to assess the nature of the association of IBD with AILD.
In relation to the characterization of AILD, the diagnosis of PSC required the presence of clinical and/or laboratory findings of cholestasis associated with abnormal imaging findings either on endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) or magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP), namely, multifocal narrowing and segmental dilatations of the bile ducts.16,17 Histologically, obliterative fibrosis and mononuclear inflammatory infiltrate involving interlobular bile ducts (i.e., pericholangitis) were considered anatomopathological criteria for the diagnosis of PSC when liver biopsy was performed to stage the disease.18
The diagnosis of small-duct PSC, a chronic AILD of undefined aetiology, was based on cholestatic and histological changes similar to those of PSC and the absence of changes in imaging tests (ERCP or MRCP).19,20 Patients with small-duct PSC were included in the non-PSC group because small-duct PSC has a clinical evolution different from that of PSC.
The diagnosis of PBC was confirmed by changes in the hepatic biochemical profile that suggested cholestasis associated with the presence of antimitochondrial antibody (AMA).21 Liver biopsy was performed when it was not possible to confirm the diagnosis using the two previous criteria. The histological parameters were the presence of chronic inflammation of the bile ducts, characterized by chronic nonsuppurative cholangitis, and destruction of interlobular ducts (according to Ludwig's classification), defined as a florid ductular reaction.22
The diagnosis of AIH, a chronic liver disease characterized by hepatitis associated with hypergammaglobulinemia and autoantibody reactivity, was based on the simplified score established by the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group in 2008.23,24
The diagnosis of AIC was established based on elevated canalicular enzymes associated with the presence of antinuclear antibodies and elevated gamma globulins, without the presence of AMA or abnormal imaging findings suggestive of other cholestatic diseases.25,26 In addition, histologically, only lymphocyte infiltrates that permeated ductal cells or ductopenia were observed, with no obliterative fibrosis or florid ductular reaction that would indicate PBC. At the time of diagnosis, sp100 or gp210 antibody screening, which could help in the differential diagnosis of PBC, was not performed.21,27
A diagnosis of overlapping syndromes was established when two AILD occurred concomitantly or at different times during follow-up. In patients with overlapping syndromes, there were laboratory and histological changes typical of cholestatic disease associated with diagnostic criteria for autoimmune hepatitis.28
Follow-up time was defined as the duration of outpatient follow-up until the patient was included in the study or died.
The study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais (CAAE 65962817.2.0000.5149).
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS for Windows version 21.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Numerical variables were evaluated for normality using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test for the selection of the presented data. Categorical variables are expressed as absolute and percentage values. The numerical variables were compared using Student's t-test or the Mann–Whitney test (according to the distribution of the data), and the chi-square test (or Fisher's exact test, when appropriate) was used for the qualitative variables. Variables with p<0.2 obtained through univariate analysis were included in the linear regression analyses. The Hosmer and Lemeshow test was used to evaluate the goodness of fit of the regression model. The significance level was set at p<0.05.
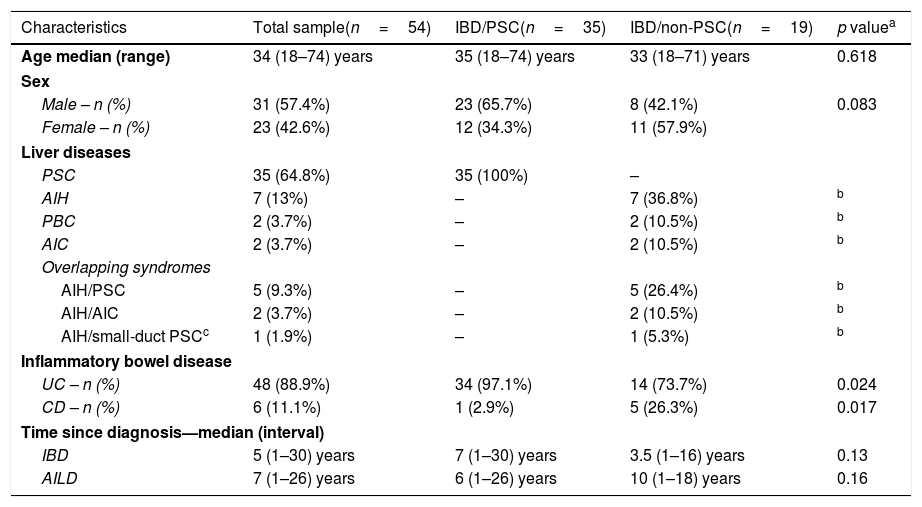
ResultsInitially, 58 patients were included in the study. Four patients were excluded during the review of the medical records. The diagnosis of IBD was not confirmed for three individuals, and one patient attended just one appointment, which did not allow an evaluation of the outcomes. Therefore, 54 patients with IBD associated with AILD were included in the study. Forty-eight patients (88.9%) had a diagnosis of UC, and six (11.1%) had CD. Thirty-five patients (64.8%) had an IBD/PSC association, and 19 (35.2%) belonged to the IBD/non-PSC group. The median age of the patients was 34 (18–74) years; 57.4% patients were men. Among the patients with PSC, 34 had a diagnosis of UC and just one had a diagnosis of CD (p=0.017). Of the 35 patients with IBD/PSC, 23 were male, and among the 19 patients with IBD/non-PSC, 8 were male (p=0.083). The median time since the diagnosis of IBD was 5 (1–30) years, and the median time since the diagnosis of liver disease was 7 (1–26) years.
The diagnosis of AILD preceded the diagnosis of IBD in 45% of patients, and the diagnosis of IBD preceded the diagnosis of AILD in 40% of patients. The two diseases were diagnosed concomitantly in 15% of patients. None of the patients were smokers; there was no CMV infection during the follow-up period, and regular screening was performed for up to 3 months in liver transplantation patients. The clinical and demographic data of the entire sample of patients and of the IBD/PSC and IBD/non-PSC groups are listed in Table 1.
Demographic and clinical data of patients.
| Characteristics | Total sample(n=54) | IBD/PSC(n=35) | IBD/non-PSC(n=19) | p valuea |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age median (range) | 34 (18–74) years | 35 (18–74) years | 33 (18–71) years | 0.618 |
| Sex | ||||
| Male – n (%) | 31 (57.4%) | 23 (65.7%) | 8 (42.1%) | 0.083 |
| Female – n (%) | 23 (42.6%) | 12 (34.3%) | 11 (57.9%) | |
| Liver diseases | ||||
| PSC | 35 (64.8%) | 35 (100%) | – | |
| AIH | 7 (13%) | – | 7 (36.8%) | b |
| PBC | 2 (3.7%) | – | 2 (10.5%) | b |
| AIC | 2 (3.7%) | – | 2 (10.5%) | b |
| Overlapping syndromes | ||||
| AIH/PSC | 5 (9.3%) | – | 5 (26.4%) | b |
| AIH/AIC | 2 (3.7%) | – | 2 (10.5%) | b |
| AIH/small-duct PSCc | 1 (1.9%) | – | 1 (5.3%) | b |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | ||||
| UC – n (%) | 48 (88.9%) | 34 (97.1%) | 14 (73.7%) | 0.024 |
| CD – n (%) | 6 (11.1%) | 1 (2.9%) | 5 (26.3%) | 0.017 |
| Time since diagnosis—median (interval) | ||||
| IBD | 5 (1–30) years | 7 (1–30) years | 3.5 (1–16) years | 0.13 |
| AILD | 7 (1–26) years | 6 (1–26) years | 10 (1–18) years | 0.16 |
AIH: autoimmune hepatitis; PSC: primary sclerosing cholangitis; PBC: primary biliary cholangitis; AIC: autoimmune cholangitis; UC: ulcerative colitis; CD: Crohn's disease; IBD: inflammatory bowel disease.
Among the patients diagnosed with UC, 40 (83.4%) had pancolitis, four (8.3%) had left colitis and four (8.3%) had proctitis upon diagnosis. There was no change in UC behaviour during the follow-up period. At diagnosis, according to the Montreal classification of CD, five patients (83.3%) were between 17 and 40 years (A2), and one patient (16.7%) was older than 40 years (A3); five patients (83.3%) had ileocolonic disease (L3), and one patient (16.7%) had ileal disease (L1). In relation to the behaviour of the disease, four patients (66.7%) had the inflammatory phenotype (B1), one patient (16.7%) had the stenosing phenotype (B2), and one patient (16.7%) had complex fistulizing perianal and anovaginal disease (B3p). Similar to UC, there was no change in the CD profile over the outpatient follow-up time.
Among the 54 patients, 11 had a diagnosis of IBD after liver transplantation, which was defined as de novo IBD. The other 43 had a diagnosis of IBD before liver transplantation. Among the patients with de novo IBD, 10 (90.9%) had a diagnosis of UC, and one (9.1%) had a diagnosis of CD. Of these 11 patients, five had a prior diagnosis of PSC, four had AIH, one had PBC and one had AIH/PSC overlap. Eight of these 11 patients underwent colonoscopy before liver transplantation, and there were no alterations suggestive of IBD. The other three patients did not undergo colonoscopy; they all had a diagnosis of AIH and had no symptoms to suggest the presence of IBD. Under 50 years, without a diagnosis of PSC, there was no need to perform colonoscopy based on the institutional protocol.
At the time of AILD diagnosis, 19 patients presented with portal hypertension. Twenty-three patients met the portal hypertension criteria when they were included in the study (p=0.063 – difference between the number of patients with portal hypertension at diagnosis and the number with portal hypertension at the end of the follow-up period).
Regarding the need for corticosteroid therapy in the initial stage of IBD treatment, 37 patients (68.5%) started prednisone at diagnosis. At the end of the follow-up period, eight out of 48 patients (16.6%) were on corticosteroids (6 patients died). There was no difference between the PSC and non-PSC groups in relation to the use of corticosteroids in the treatment of IBD (p=0.99). The other drug classes that were used for IBD treatment, in order of frequency, were 5-aminosalicylic acid derivatives (81.2%), immunosuppressants (41.6%), and biological therapy with anti-TNF alpha (20.8%). There was no difference between the PSC and non-PSC groups regarding the drugs used in the treatment of IBD (p=0.722; p=0.831, and p=1.0, respectively). The use of anti-TNF in patients diagnosed with IBD before liver transplantation was not related to the need for surgical treatment of IBD, colon cancer or death (p=1.0; p=0.417, and p=0.32, respectively).
Five patients (9.25%) underwent surgery for the treatment of IBD, of whom four were diagnosed with UC. In three of these four patients, the disease was refractory to clinical treatment, and one patient exhibited sigmoid colon perforation due to the complication of infectious colitis. A patient diagnosed with CD, also not transplanted, had a diagnosis of colon adenocarcinoma and underwent colectomy.
Of the 54 patients, 22 (40.7%) underwent liver transplantation. The mean time since the diagnosis of liver disease until transplantation was 5.64±4.03 years in the studied sample.
Thirteen of the 22 patients were transplanted because of PSC. The mean time between PSC diagnosis and transplantation was 4.77±4.18 years. Nine patients underwent transplantation due to other AILD, and their mean time between diagnosis and transplantation was 6.89±3.65 years. There was no difference between this group and the IBD/PSC group (p=0.12). The mean follow-up time after transplantation was 6.73±3.93 years. Tacrolimus was the calcineurin inhibitor used in 20 out of 22 patients.
Of the 54 patients, 6 (11.1%) died, of whom four died in the post-transplantation period. The other two deaths were not associated with liver transplantation. One patient died due to decompensated cirrhosis (acute kidney injury and infection), and the other died of metastatic invasive colon adenocarcinoma. When the outcomes surgical treatment for IBD, liver transplantation and death were evaluated separately in both groups, there was no difference regarding any of the events (p=1.0, p=0.727, and p=0.655, respectively). The patients with a diagnosis of de novo IBD were not included in this analysis.
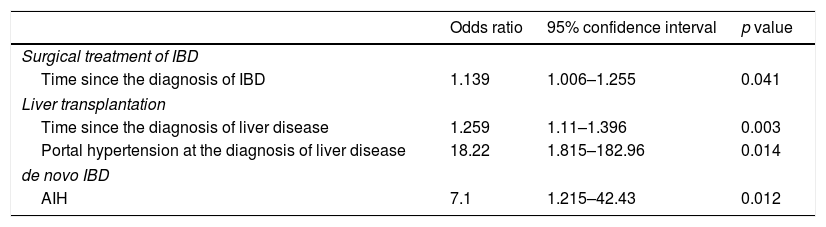
To analyse factors that could explain outcomes (surgical treatment of IBD, liver transplantation and death) and the incidence of de novo IBD, multivariate analysis (linear regression) was performed, and variables with p values<0.2 in the initial model were included. Once again, de novo IBD was not included as an outcome. Regarding the outcome need for surgical treatment of IBD, age (p=0.18) and time since the diagnosis of IBD (p=0.041) were included in the initial model, but only the variable time since the diagnosis of IBD remained in the final model (p=0.041; OR: 1.139, 95% CI: 1.006–1.255). Regarding the outcome liver transplantation, time since the diagnosis of AILD (p=0.0001), AIH/PSC overlap (p=0.059) and portal hypertension at the diagnosis of liver disease (p<0.0001) were present in the initial phase of analysis; however, just time since the diagnosis of liver disease (p=0.003; OR: 1.259, 95% CI: 1.1–1.396) and portal hypertension at diagnosis (p=0.014; OR: 18.22, 95% CI: 1.815–182.96) remained in the final model. Regarding the outcome death, the initial multivariate analysis model included the type of IBD (p=0.092), current CD behaviour (p=0.15), surgical treatment of IBD (p=0.03), overlapping syndrome of AILD (p=0.023), time since the diagnosis of AILD (p=0.054) and liver transplantation (p=0.14). However, none of the variables had a p value<0.05 in the final model.
Finally, multivariate analysis was also performed for de novo IBD. Age (p=0.122) and previous diagnosis of AIH (p=0.012) were included, and only the diagnosis of AIH remained in the final model (p=0.012; OR: 7.1, 95% CI: 1.215–42.43). Table 2 shows the results of the final linear regression model for surgical treatment of IBD, liver transplantation and de novo IBD.
Final logistic regression model for surgical treatment of IBD, liver transplantation and de novo IBD.
| Odds ratio | 95% confidence interval | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical treatment of IBD | |||
| Time since the diagnosis of IBD | 1.139 | 1.006–1.255 | 0.041 |
| Liver transplantation | |||
| Time since the diagnosis of liver disease | 1.259 | 1.11–1.396 | 0.003 |
| Portal hypertension at the diagnosis of liver disease | 18.22 | 1.815–182.96 | 0.014 |
| de novo IBD | |||
| AIH | 7.1 | 1.215–42.43 | 0.012 |
IBD: inflammatory bowel disease; AIH: autoimmune hepatitis.
The association between IBD and AILD has been described for several years, especially the association between UC and PSC, and this group of patients has some particular features. UC usually has more quiescent behaviour and courses with fewer episodes of recurrence. The rectum tends not to be affected, and reflux ileitis is more frequent. There is also a higher prevalence of bolsitis among patients who undergo proctocolectomy. Due to these characteristics, some studies suggest that these patients with UC/PSC may be classified as having a distinct disease phenotype.4,29 However, little is known about the association with other AILD.
In this study, 64.8% of patients had an IBD/PSC association, and 35.2% were IBD/non-PSC patients. In fact, PSC is the most specific liver disease in patients with IBD, being present in 4–5% of cases. Approximately 70% of patients diagnosed with PSC have associated IBD, and approximately two-thirds of patients with IBD/PSC have UC.3,4,30 In the present study, there was an even higher prevalence of PSC associated with UC (97%), with most patients being men; the analysis of the proportion of patients with CD and PSC showed that the prevalence of this association was significantly lower (p=0.017).
Boonstra et al., in a retrospective study involving 380 patients with IBD/PSC, showed that UC affected 75% of patients, mostly men.31 Similarly, Sørensen et al. conducted a population study with 257 patients with IBD/PSC and reported that 72% had UC, the majority being men.32
In the present study, there was a higher proportion of male individuals in the IBD/PSC group (although the p value was 0.083). In the IBD/non-PSC group, UC was also more prevalent, but the patients were predominantly women (57.9%). In this group, AIH alone or as a component of overlapping syndromes was the most prevalent autoimmune liver disease.
Regarding the extent of UC involvement, pancolitis was the most prevalent form of UC (83.4%). In the study by Boonstra et al., involvement in the form of pancolitis was present in 83% of patients.31 Similarly, Sørensen et al. reported that 78% of patients had involvement beyond the splenic flexure.32 In patients with CD, ileocolonic and nonstricturing/nonpenetrating forms were predominant, as described in the two cited case series.31,32
There were no differences between the IBD/PSC and IBD/non-PSC groups in terms of age, follow-up time or the kind of treatment, including the initial need for corticosteroid therapy. The results of the outcomes need for surgical treatment of IBD, liver transplantation and death were also similar between the two groups. No data were found in the literature for comparison with our results.
Regarding the need for surgical treatment of IBD, a longer time since the diagnosis of IBD was associated with the need for colectomy. Each additional year after diagnosis increased the risk of surgery by 13.9%. This means that the risk was 13.9 times higher within 10 years. Literature data referring to the need for surgical treatment in patients with IBD associated with AILD are conflicting. Two studies suggest that these patients are more likely to require colectomy than patients with UC alone.33,34 However, Boonstra et al. did not show an increased risk of colectomy when comparing patients with UC/PSC and patients with UC alone.31 Regardless of AILD occurrence, approximately 30% and 80% of patients with UC and CD, respectively, will need some form of surgical treatment during the course of the disease.1,3,13,14 The rate was 12.5% in the follow-up period for this sample of patients.
Another outcome studied through multivariate analysis, the need for liver transplantation, was associated with time since the diagnosis of AILD. Each additional year after the diagnosis of AILD increased the likelihood of liver transplantation by 25.9%. Another variable associated with this outcome was portal hypertension at the time of the diagnosis of the disease. The presence of portal hypertension increased the likelihood of liver transplantation by 18.22 times. Approximately 65% of patients diagnosed with PSC will require liver transplantation within 10 years.17,18 Among patients with PBC, 33% are expected to progress to needing transplantation within 10 years,35 and 70% of patients with AIH who do not receive adequate treatment or have no therapeutic response will progress to the cirrhosis stage that will require transplantation within 10 years.24 There are no reports in the literature about the other AILD evaluated in this sample. In the present study, patients in the IBD/PSC group underwent liver transplantation earlier than patients in the IBD/non-PSC group (4.77±4.18 vs 6.89±3.65 years), but this difference was not significant.
Regarding death, some studies suggest that patients with IBD/PSC are at increased risk of death compared with patients with IBD alone. Sørensen et al., in a retrospective study in the Danish population with 257 patients with IBD/PSC, observed a fourfold higher mortality rate in these patients (OR: 4.39, 95% CI: 3.22–6.00).32
It is known that patients with UC/PSC have a higher risk of developing colorectal cancer than patients with UC alone.30 In relation to patients with CD/PSC, it is not known whether their risk of colorectal cancer is higher than that of patients with CD alone. In this sample, colorectal cancer was diagnosed in only one patient (1.8%), a 29-year-old individual with ileocolonic Crohn's disease. A study conducted in England included 166 patients with IBD/PSC – 120 patients with UC/PSC, 35 patients with CD/PSC, and 11 patients with indeterminate colitis/PSC. The occurrence of nondysplastic adenomas and colorectal cancer was more frequent in patients with UC/PSC than in patients with CD/PSC (p=0.07).36 Another study conducted in Sweden compared 28 patients with CD/PSC with 46 patients with CD alone. A higher frequency of colorectal dysplasia/cancer was observed in the patients with CD/PSC (p=0.007).37
A significant portion of the present sample consisted of patients with de novo IBD (20.4%). According to the literature, the incidence of de novo IBD after organ transplantation is higher than that in the general population (206 vs 20 new cases/100,000/year).10 The explanation for this finding is probably related to the profile of these patients. The presence of AILD possibly acts as a predisposing factor to other autoimmune diseases. Moreover, the graft may cause changes in the regulation of the immune system. More recently, the type of immunosuppressant used has also been implicated in the increase in the number of cases of de novo IBD.10,15,38 In the present study, which is the largest sample evaluated in the country to date, all 11 patients with de novo IBD received tacrolimus as a calcineurin inhibitor. According to some authors, the use of tacrolimus is more associated with de novo IBD because it is more potent than cyclosporine.10,38 Tacrolimus is a potent inhibitor of interleukin-2, and this cytokine plays an important role in the development of regulatory T cells responsible for immunological homeostasis in the intestine. A reduction in serum interleukin-2 levels could lead to a decrease in the concentration of regulatory T cells, and this event could be associated with the development of de novo IBD.10,15
Finally, in the evaluation of de novo IBD, a previous diagnosis of AIH was associated with a 7.1 times higher probability of a diagnosis of de novo IBD, which strengthens the hypothesis of immune-mediated phenomena being involved in the genesis of this process, as previously mentioned. There are some case-series studies about the incidence of de novo IBD in liver transplantation patients described in the literature. Nepal et al., in a review that evaluated IBD and de novo IBD in transplantation patients, identified 22 studies with 80 cases of de novo IBD in liver transplantation patients from 1970 to 2012, with the largest sample among the evaluated studies comprising 12 patients.39 In another retrospective study conducted by Loftus et al., which included 373 patients transplanted as a result of PSC and without a prior diagnosis of IBD, 22 patients developed de novo IBD, and the use of mycophenolate mofetil was identified as a risk factor for de novo IBD.15 Intestinal microbiota alterations secondary to the use of immunosuppressants, which expose the intestinal mucosa to different antigens, probably act as a pathophysiological mechanism underlying this association.40 Another theory implies the role of infections in the genesis of the disease.29,38 In a study conducted at the University of Nebraska with 91 patients transplanted due to PSC or AIH, eight patients had de novo IBD, seven of whom developed UC, and one developed unclassified colitis. CMV infection was the only risk factor identified for de novo IBD, p=0.045 (OR: 4.42, 95% CI: 1.03–18.87).38 In our sample, no patient reported CMV infection after transplantation despite antigen testing being performed routinely in the first 3 months after transplantation.
ConclusionPSC was more frequent among patients with UC, whereas only one patient with CD had PSC. There was no difference regarding disease progression features between the two groups of patients. The analysis of the outcomes in the entire sample showed that the need for surgical treatment was increased by 13.9% for each additional year after the diagnosis of IBD. In relation to liver transplantation, there was a 25.9% increase in the likelihood of a need for liver transplantation for each additional year after the diagnosis of liver disease, and the presence of portal hypertension at AILD diagnosis increased this likelihood 18.22 times. Finally, regarding the incidence of de novo IBD, a previous diagnosis of AIH increased the likelihood of developing de novo IBD after liver transplantation by 7.1 times. This information is important for future comparisons, with the aim of better understanding the phenotypes of these groups of patients.
Financial supportThis research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflicts of interestNone declared.
We are grateful to the patients of Hospital das Clínicas da Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais.