Academic help-seeking for students is the process of interaction between students and others in order to obtain solutions to their problems. Help-seeking can prevent the possibility of failure, and increase independent learning to improve learning achievement.
Objectiveto determine the relationship of academic help-seeking with student achievement in Nursing Study Program STIKes Muhammadiyah Palembang.
Research methodsThe research design used was cross-sectional with a total sampling technique and a total sample of 116 respondents. Data collection tools such as questionnaires and data analysis using the chi-square test (α=0.05).
Research resultsThere is a relationship between academic help-seeking and student achievement in Nursing Science Study Program STIKes Muhammadiyah Palembang (p value 0.000).
Students are part of the academic community at a tertiary institution where they are future leaders. A student is expected to have a good perspective, have a soul and also a healthy and strong personality. In the learning process a student must be able to master the problem and have a positive way of thinking about each problem or obstacle he faces.1
The learning process of students follows the learning response in accordance with the applicable curriculum that offers a variety of new insights and ways of thinking. A student has his own problems in the learning process at each development. Problems owned by these students can be sourced from various factors such as the learning process in class, family, self, and also the environment around the student.2
In every problem solving related to the learning process, students tend to have a strong ego orientation, therefore the goal of each problem solving tends to influence them to use self-protection strategies in their learning situations with the tendency to use learning aids.3 Help-seeking can be a strategy that can contribute to student learning. This behavior not only has the potential to solve student learning problems directly but can also provide sustainable acquisition of skills and knowledge.4
Activities seeking learning assistance or academic help-seeking for students can be a process of social interaction between students and others as a way to find solutions to each of their learning problems. Students can take advantage of the search for help when finding difficulties in each learning, students can seek learning assistance to friends, lecturers or others who are considered to be able to help solve their learning problems.5,6 In his research stated that academic help-seeking behavior is critical behavior that will help students in achieving their learning goals. Help-seeking can be a strategic resource used by students to maximize each learning process. In this research, help-seeking behavior is strongly related to a student's perception of academic competence.
Researchers conducted a preliminary study by interviewing 10 Kindergarten Nursing Study Program students. III STIKes Muhammdiyah Palembang. From the results of the preliminary study, it was found that they tend to do academic help-seeking behavior if they have learning problems. 8 students prefer to ask friends rather than lecturers and 2 students ask lecturers and classmates if they do not understand the subject of learning. They assume by doing academic help-seeking they can understand the material and can do tasks that they cannot do alone.
Academic help-seeking behavior can be said as a form of self-regulation that can be done by every student in solving his learning difficulties by utilizing other people as a medium of learning assistance. Help-seeking behavior can occur when a student needs learning assistance or they cannot solve the problems faced related to learning. Help-seeking can prevent the possibility of failure, and increase the likelihood of long-term mastery and independent learning to improve learning achievement7,8 said learning achievement is a result that has been obtained or achieved from activities that have been carried out or done. By knowing student achievement, it can be known the position of students who are smart, moderate or lacking. In student learning activities in tertiary institutions, assessment of learning achievement can be seen with the parameters of student success in learning using the results of academic grades or achievement index (IP).9
From the data obtained at the BAAK STIKes Muhammadiyah Palembang Semester Achievement Index (IPS) of the fourth semester Nursing Study Program, there were 89 students who had a GPA>3.00 and 27 student of Nursing Study Program had a GPA of<3.00. In addition, the reason researchers took samples of Nursing Study Program students because the sample is a student who has been through a lot of lecture processes and official schedule activities so that it may have a higher level of learning problems and difficulties.
Based on this description, researchers are interested in conducting research on the relationship of academic help seeking with student learning achievement in the Nursing study program at STIKes Muhammadiyah Palembang.
Research methodsThis type of research is quantitative research, using analytic survey research design with cross sectional approach with total sampling method, the independent variable is academic help-seeking and the dependent variable is learning achievement. The sample in this research was 116 students.
Results and discussionResult of this research regarding the relationship of academic help-seeking with learning achievement as follows:
Based on Table 1 frequency distribution analysis of 116 respondents in Nursing Science Study Program students at STIKes Muhammadiyah Palembang, the results showed that most respondents were 85 female students (73.3%) and 31 male students (male students) 26.7%).
Based on Table 2 analysis of the frequency distribution of 116 respondents regarding academic help-seeking which is categorized in two categories, namely good and not good, it is found that 75 respondents (64.7%) with academic help-seeking behavior are in the good category and 41 respondents (35.3%) in the bad category.
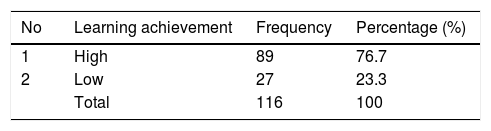
Based on Table 3 analysis of the frequency distribution of 116 respondents regarding learning achievement which is categorized in two categories namely high and low it is found that 89 respondents (76.7%) with learning achievement are in the high category and 27 respondents (23.3%) with learning achievements in low category (Table 4).
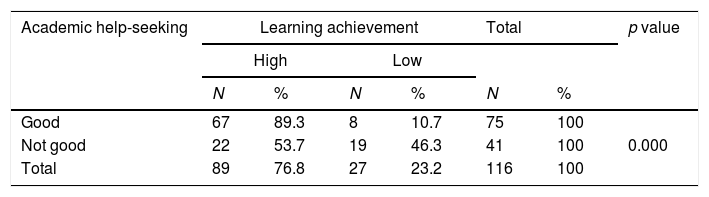
Based on the results of research conducted to students of Nursing Science Study Program STIKes Muhammadiyah Palembang, STIKes found that 67 respondents (89.3%) did academic help-seeking behavior in the good category with high learning achievement results, 8 respondents (10.7%) did good academic help-seeking behavior with low learning achievement and as many as 22 respondents (53.7%) did poor academic help-seeking behavior with high learning achievement results, 27 other respondents (46.3%) did poor academic help-seeking with learning outcomes in the low category.
Statistical test results using the Chi Square test method with a table (2×2) and significance level α=0.05 obtained p value (0.000)≤α (0.05). So that Ho is rejected means there is a significant relationship between academic help-seeking and student learning achievement in the Nursing Science Study Program III STIKes Muhammadiyah Palembang.
This research is supported by the results of5 study which states that there is a relationship between academic help-seeking and the success of one's learning. Academic help-seeking behavior in students can help students in gaining knowledge, building goals, building learning communities, and experiencing growth in their work and daily life.
This research is also in line with research conducted by,10 which states that academic help-seeking one of the factors that influence it is the existence of individual perceptions and beliefs, these perceptions and beliefs include the beliefs held by individuals in their ability to regulate, and act to solve a problem in achieving goals during the learning process. While Nelson-Le Gall11 explains that when individuals who have good cognitive abilities in monitoring strategies that can support their progress, these individuals will be able to realize when they experience problems and need help in the learning process, in other words these individuals will bring up academic help-seeking behavior to solve the difficulties that are being faced.
Academic help-seeking is not only a self-organizing learning strategy, but also social interaction.6 There are two types of social relationships in the learning process: horizontal relationships between peers This is in line with research conducted by12 on boarding students who have learning difficulties tend to ask friends and seniors for assistance in conducting learning. There is also a vertical relationship with the lecturer. Because they might seek help from lecturers and peers, both the social benefits felt with peers and with lecturers are significantly and independently associated with their academic assistance.
From the viewpoint of nursing students at STIKes Muhammadiyah Palembang, it can be said that students play an active role in conducting the learning process and optimizing their learning activities. They conduct academic help-seeking activities with the aim of understanding the material or also to help in dealing with learning difficulties in class. They tend to do academic help-seeking activities informally and instrumentally where they are more seeking help learning with classmates with the aim of solving problems or achieving the goals in question in the learning process on him.
This is supported by5 which states that in academic help-seeking activities students use more interaction with other students in terms of solving the learning difficulties experienced.4 also states that in academic help-seeking activities not only also has the potential to help deal with the learning difficulties encountered, but also these activities can contribute in obtaining skills and knowledge that can be used in learning or subsequent situations.
Based on the results of research, theory and literary studies, the researcher believes that there is a relationship between academic help-seeking and learning achievement. This is because academic help-seeking behavior in students can help students understand the learning process that is not yet understood by a student by using the help of friends, lecturers or learning structures. Students can be more interactive outside class hours because they can learn with the help of others outside the classroom.
Academic help-seeking with 116 respondents found that 75 respondents (64.7%) in the good category, Learning Achievement with 116 respondents found that 89 respondents (76.7%) with learning achievement in the high category. there is a relationship between Academic help-seeking with learning achievement with a p value of 0.000.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Peer-review under responsibility of the scientific committee of the 3rd International Conference on Healthcare and Allied Sciences (2019). Full-text and the content of it is under responsibility of authors of the article.