This study aims to determine the effect of social media method intervention (Whats App) with the simulation game method (snake ladder) on increasing literacy in the form of knowledge and attitudes about HIV and AIDS in loading and unloading workkers at the Soekarno Hatta Port of Makassar.
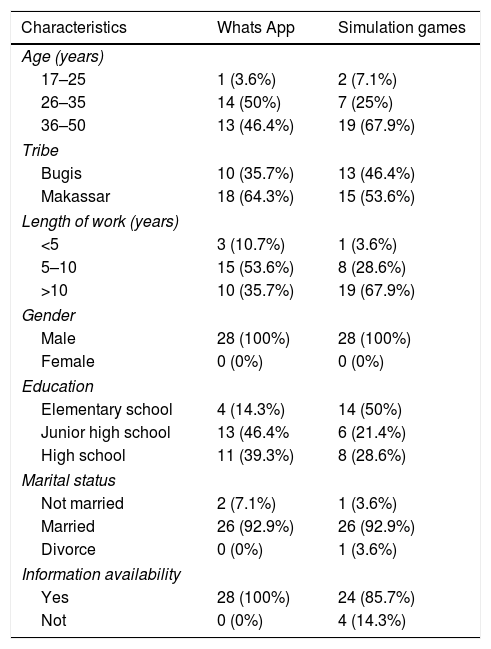
MethodsThis study uses a quasi-experiment. The population of the study were 776 people in loading and unloading workforce, 56 samples were selected by simple random sampling technique. Data are normally distributed and analyzed using repeated ANOVA test and unpaired sample t test.
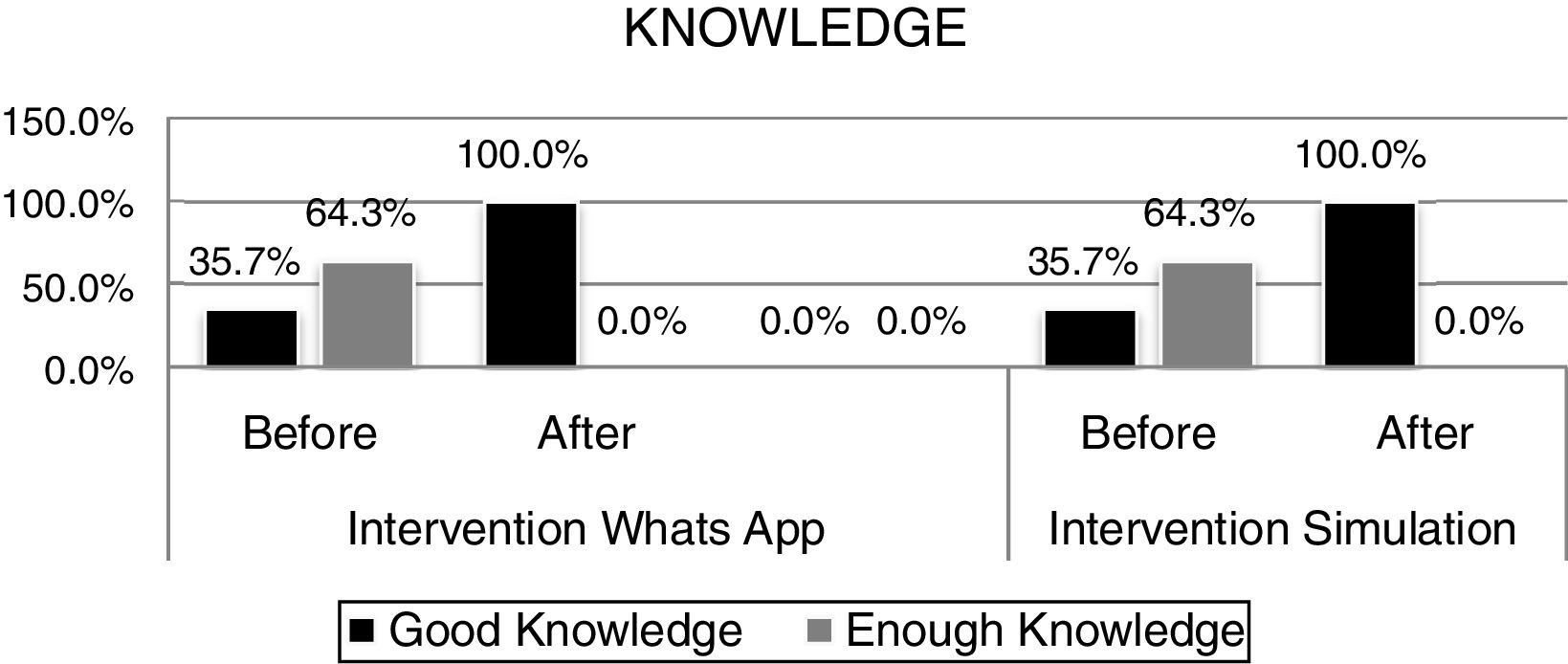
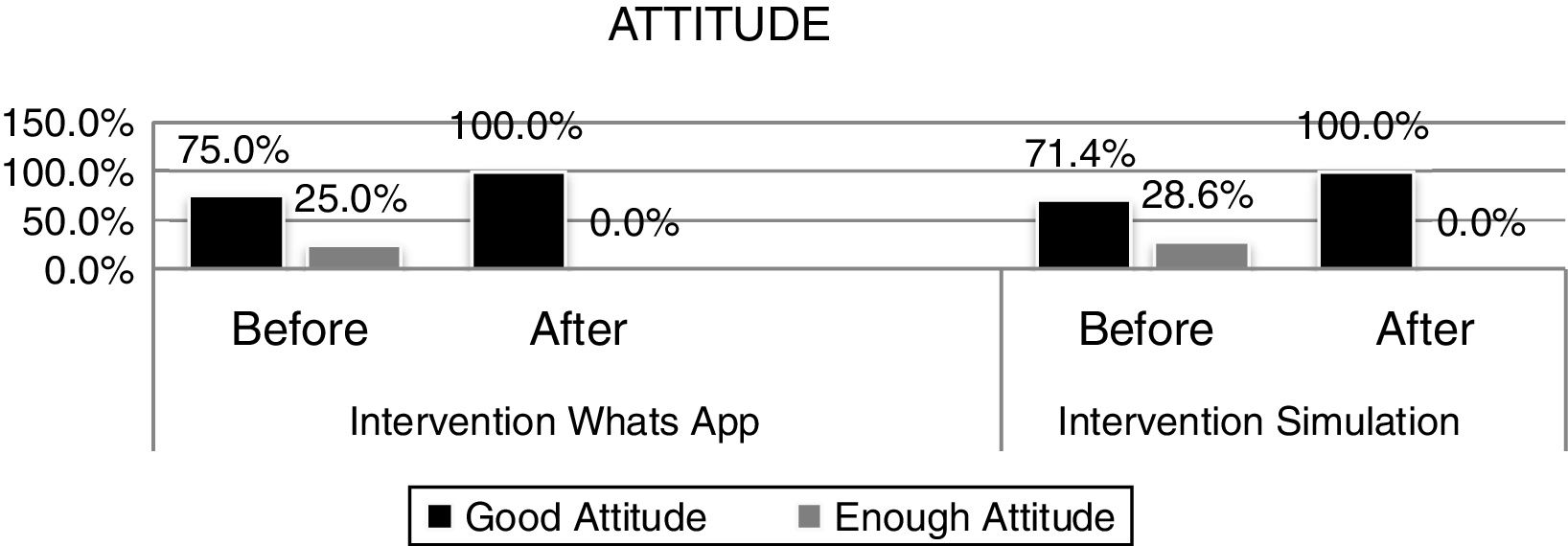
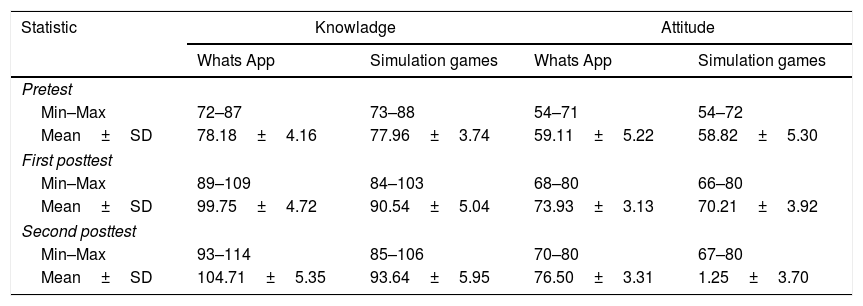
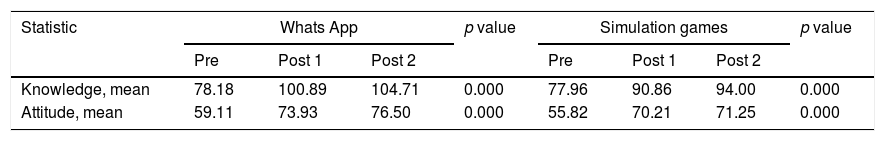
ResultsThe results showed that there were differences in the influence of social media methods with simulation games on increasing the increase in the literacy of HIV and AIDS in the unloading workforce of Makassar's Soekarno Hatta Port (p=0.000).
ConclusionSocial media interventions and simulation games have an affect on improving HIV and AIDS literacy.