This study aims to determine the risk of education of parents with the incidence of sexual violence in children in Palopo city.
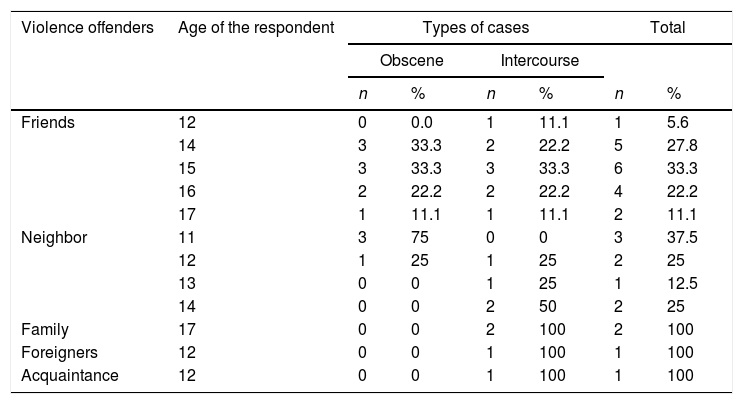
MethodsThe design of this study was analytic observational with a case control study. The technique of determining the sample in this study used a total sampling technique. Thirty people involved as a sample study. Data collection techniques in this study used primary data obtained through observation and interviews using questionnaires, as well as secondary data obtained from the Palopo Police Women's and Child Protection Unit about the number of cases of sexual violence in children from 2016 to 2018 years.
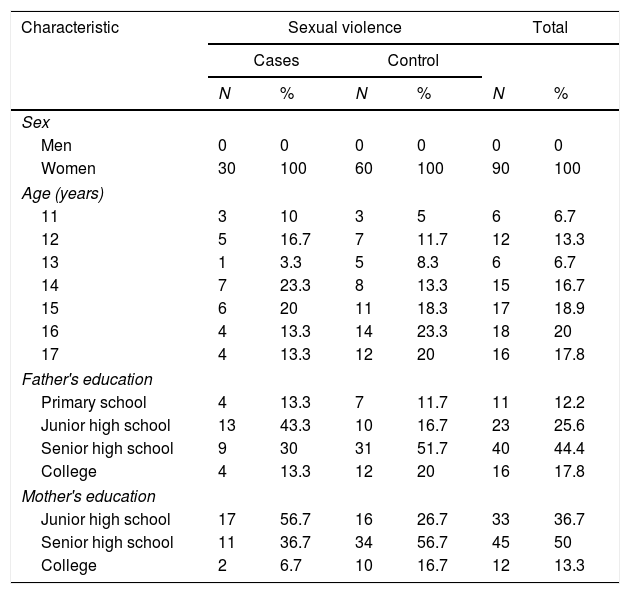
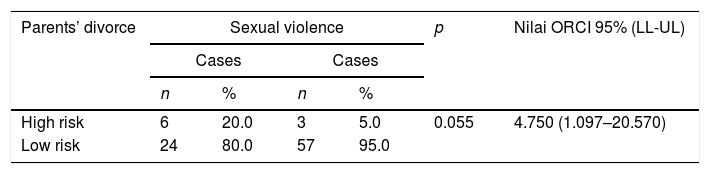
ResultsThe analysis in this study consisted of univariate analysis and bivariate analysis, using SPSS version 20. The Results showed that parental divorce (OR 4.750; CI 95% 1.097–20.570) and parental education level (OR=3.596; CI 95% 1.431–9.036) are risk factors for sexual violence in children.
ConclusionsParental divorce and parental education level are risk factors for sexual violence events, in which children with parental divorce have a risk of 4.750 times compared to children whose parents are not divorced while the low education level of parents is 3.596 compared to high parents education level.