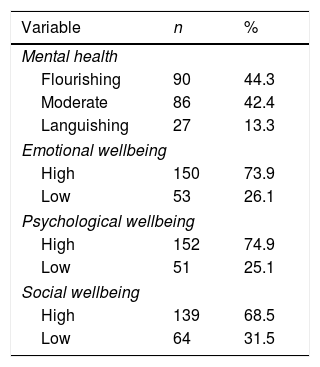
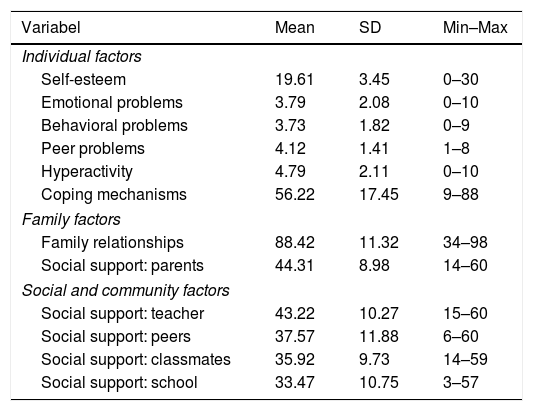
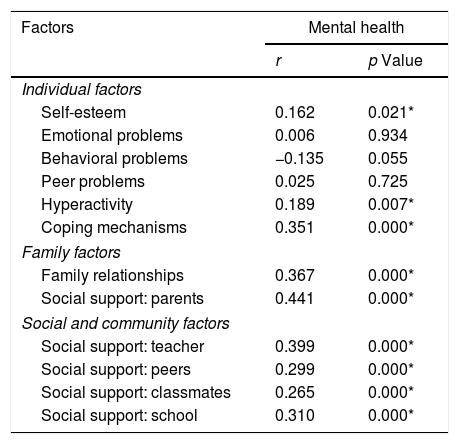
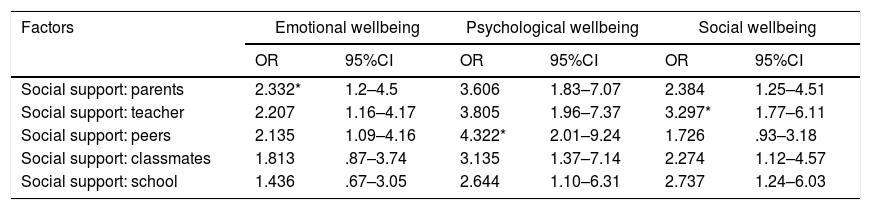
The aim of this study was to describe patterns and potential factors of mental health, including emotional, psychological, and social wellbeing among Indonesian adolescents. A descriptive, cross-sectional design was implemented. The sample consisted of 203 junior high school students from four schools (private and public schools) in Bali. Participants completed a one-time, self-report questionnaire on mental health and individual, family, and social community factors. Descriptive, pearson correlation, and logistic regression were used for the analysis. Approximately 44.3% of adolescents were flourishing, 42.4% had moderate mental health, and 13.3% were languishing. Almost all adolescents had high emotional, psychological, and social wellbeing. Self-esteem, behavioral problems, strength, hyperactivity, coping mechanisms, family relationships, social support from parents, teachers, peers, and classmates were perceived as contributing to adolescents’ mental health. Adolescents individuals need to develop adaptive coping abilities to deal with events positively. The involvement of parents and proximity between peers and school environments are needed to strengthen adolescent mental health. There needs to be a comprehensive between adolescents, family, and community as well as interventional strategies and policy directions to help adolescents maintain their mental health.
El factor de impacto mide la media del número de citaciones recibidas en un año por trabajos publicados en la publicación durante los dos años anteriores.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2025
SJR es una prestigiosa métrica basada en la idea de que todas las citaciones no son iguales. SJR usa un algoritmo similar al page rank de Google; es una medida cuantitativa y cualitativa al impacto de una publicación.
Ver másSNIP permite comparar el impacto de revistas de diferentes campos temáticos, corrigiendo las diferencias en la probabilidad de ser citado que existe entre revistas de distintas materias.
Ver más