To determine the incidence and risk factors of infection in liver transplant recipients immediately post-transplant, during admission to a liver transplant unit during the immediate post-transplant admission.
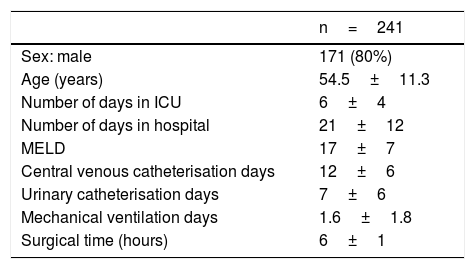
MethodologyDescriptive, prospective study performed in the Liver Transplant Unit of Hospital Clínic, Barcelona. All liver transplant recipients between January 2012 and August 2015 (n=241) were included. Statistical analysis was performed with R Commander. Variables were compared with Chi-square and Student's t-test. A value of p≤.05 was considered significant.
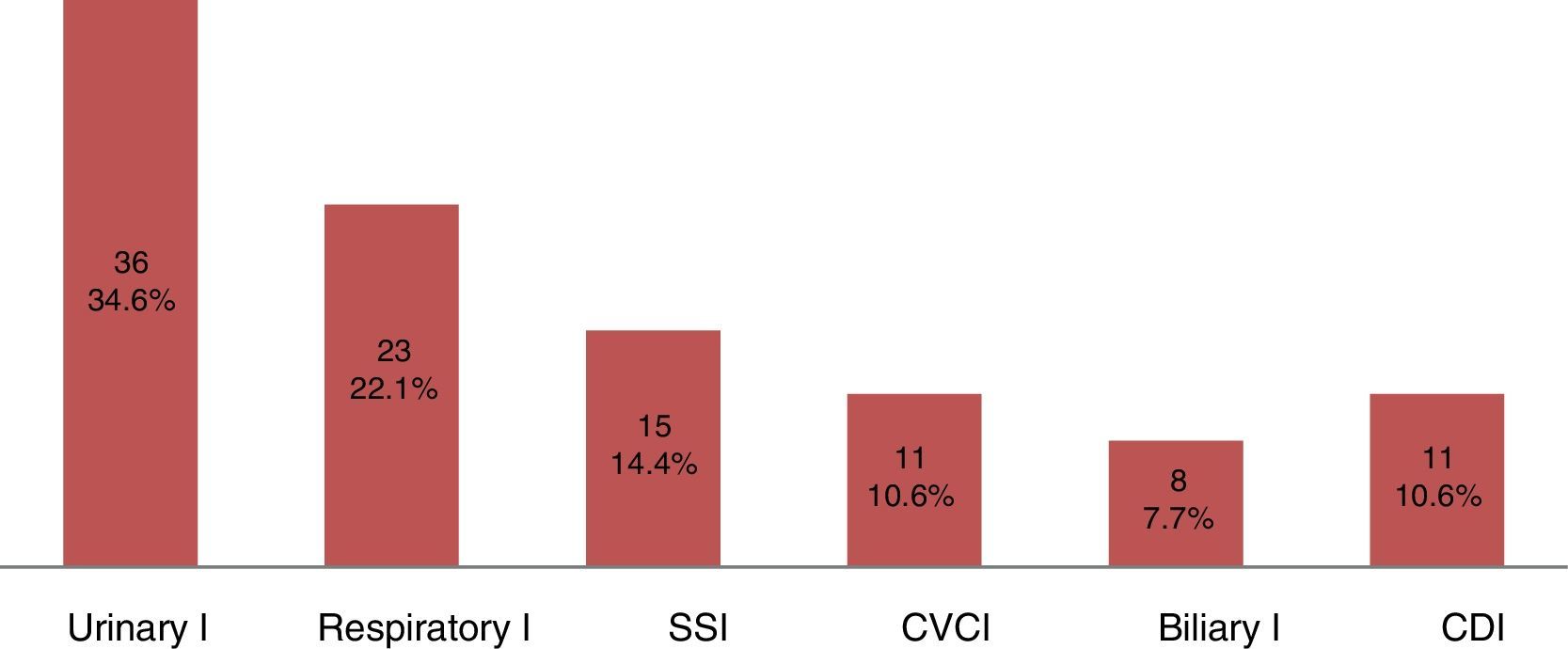
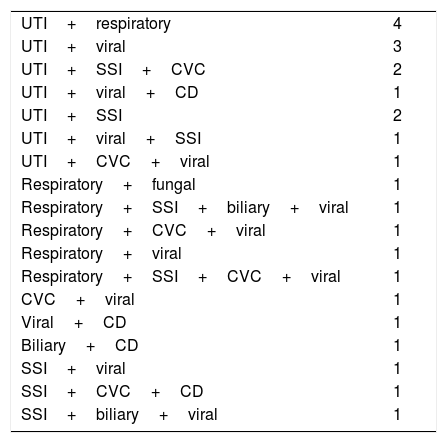
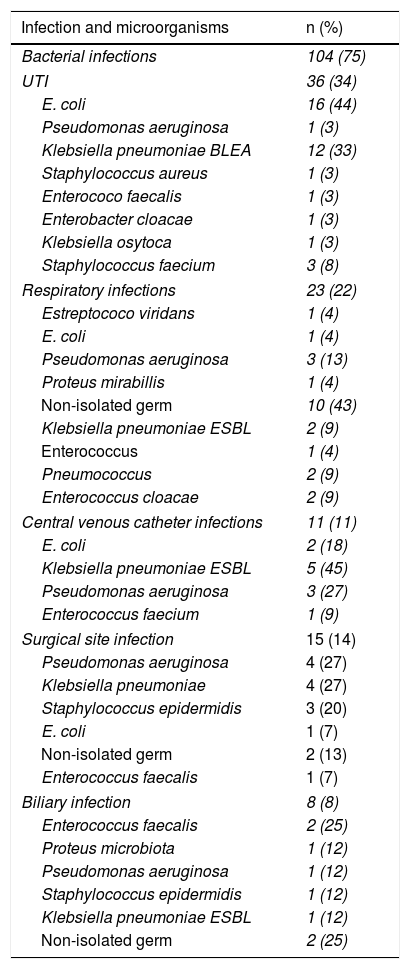
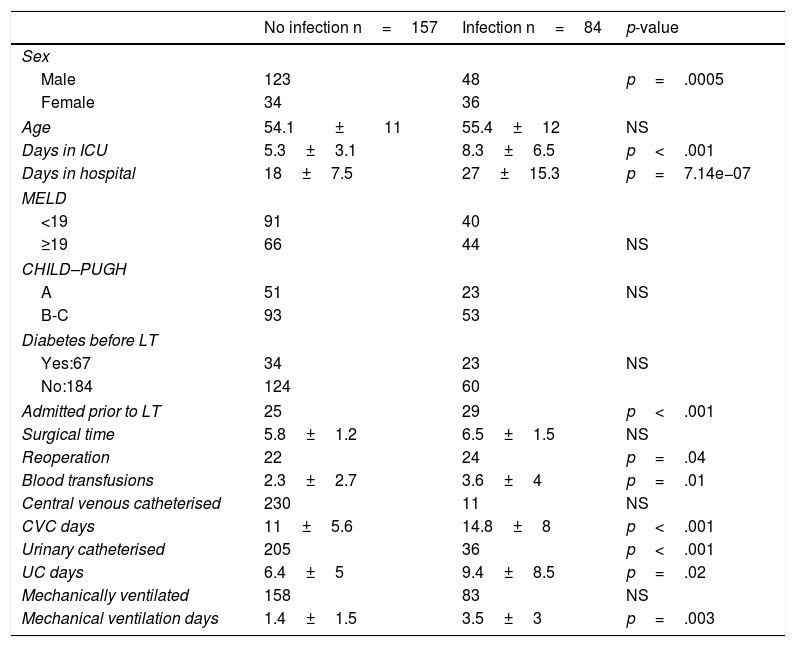
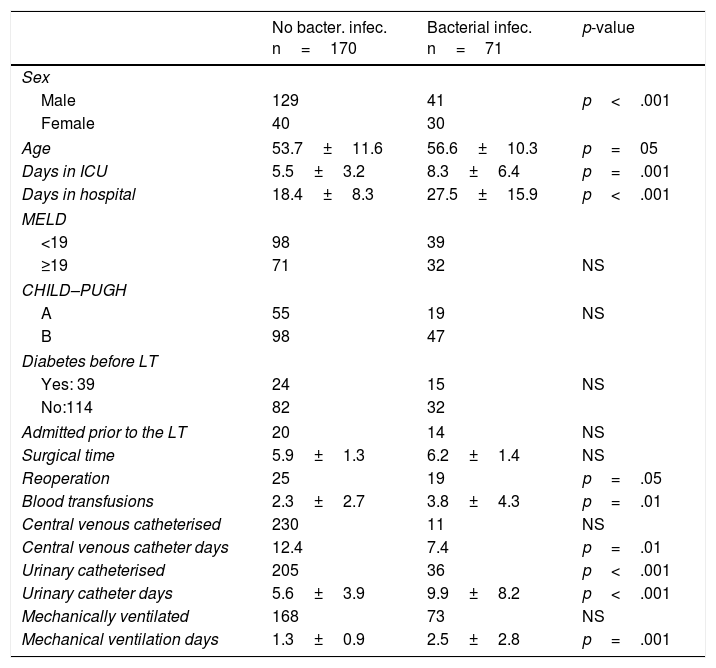
ResultsThe incidence of infection was 34.8%. The most frequent infections were bacterial (75.3%), particularly urinary infections (34.6%) caused by Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Independent risk factors for the development of bacterial infections according to multivariate analysis were sex, age and length of hospital stay.
ConclusionsInfections are a significant problem in the early post-transplant period, and are associated with longer hospitalisation periods. The role of nursing in preventing infections, by identifying risk factors, correctly applying nursing protocols in insertion, maintenance and early withdrawal of medical devices and fulfilling hand hygiene, is essential.
Conocer la incidencia de infección en pacientes trasplantados hepáticos, en el postrasplante inmediato y los factores de riesgo de infección, durante el ingreso en una unidad de trasplante hepático.
MetodologíaEstudio descriptivo, prospectivo realizado en la Unidad de trasplante hepático del Hospital Clínic que incluyó a todos los pacientes que fueron trasplantados entre enero de 2012 y agosto de 2015 (n=241). Se realizó el análisis de datos con el paquete estadístico R Comander. Las variables cualitativas se compararon con el chi2 y las cuantitativas con la t de Student, considerándose significativa una p ≤ 0,05.
ResultadosLa incidencia de infección fue de 34,8% (n = 241). Las bacterianas fueron las más frecuentes (75,3%) y dentro de estas las urinarias (34%) causadas por Escherichia coli y Klebsiella pneumoniae. Realizado el análisis multivariado en las infecciones bacterianas, se observó que el sexo, la edad y los días de estancia en hospital fueron los factores predictivos independientes.
ConclusionesLa infección bacteriana en el postrasplante inmediato es común y repercute en la recuperación del paciente, implicando más días de estancia hospitalaria y más procesos invasivos. El personal de enfermería debe conocer los factores de riesgo relacionados con la infección para extremar medidas de prevención. La correcta aplicación de las recomendaciones publicadas en la bibliografía sobre la inserción, mantenimiento y retirada precoz de dispositivos médicos y el cumplimiento de la higiene de manos son fundamentales.