This study aimed to investigate the impact of a multimodal exercise programme on the Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
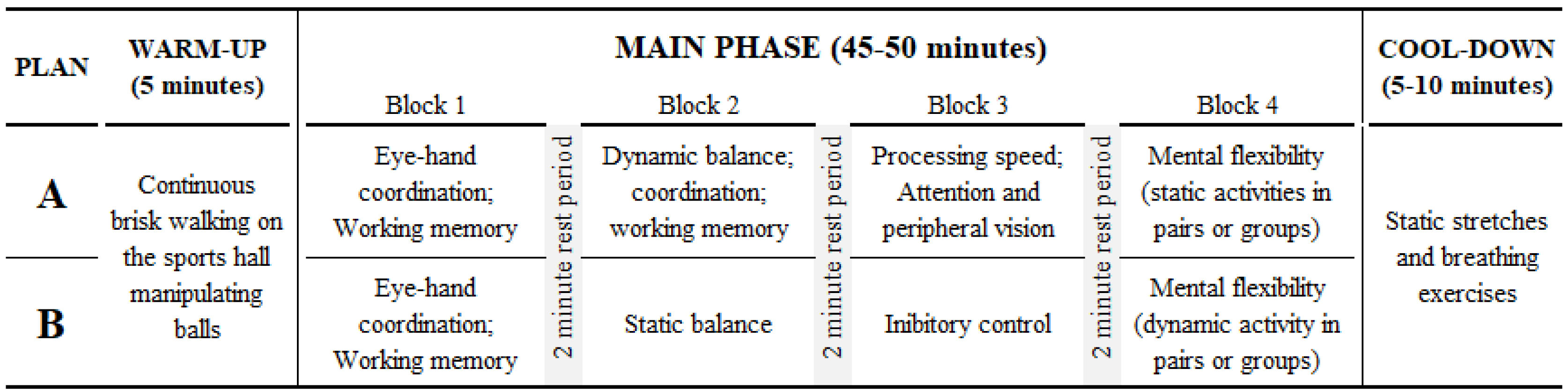
MethodsA quasi-experimental study with a single-group design and repeated measures was used. Twenty-six patients with T2DM (aged 68.58 ± 6.15 years, with a diabetes duration of 14.81 ± 8.35 years) participated in a motor-cognitive exercise programme that consisted of 60-minute sessions, three times per week for eight weeks. Data were collected at two baseline measurements (pretest 1 and pretest 2) and the final measurement (post-test). Health-related quality of life was assessed using the EuroQol five-dimensions-3-level questionnaire.
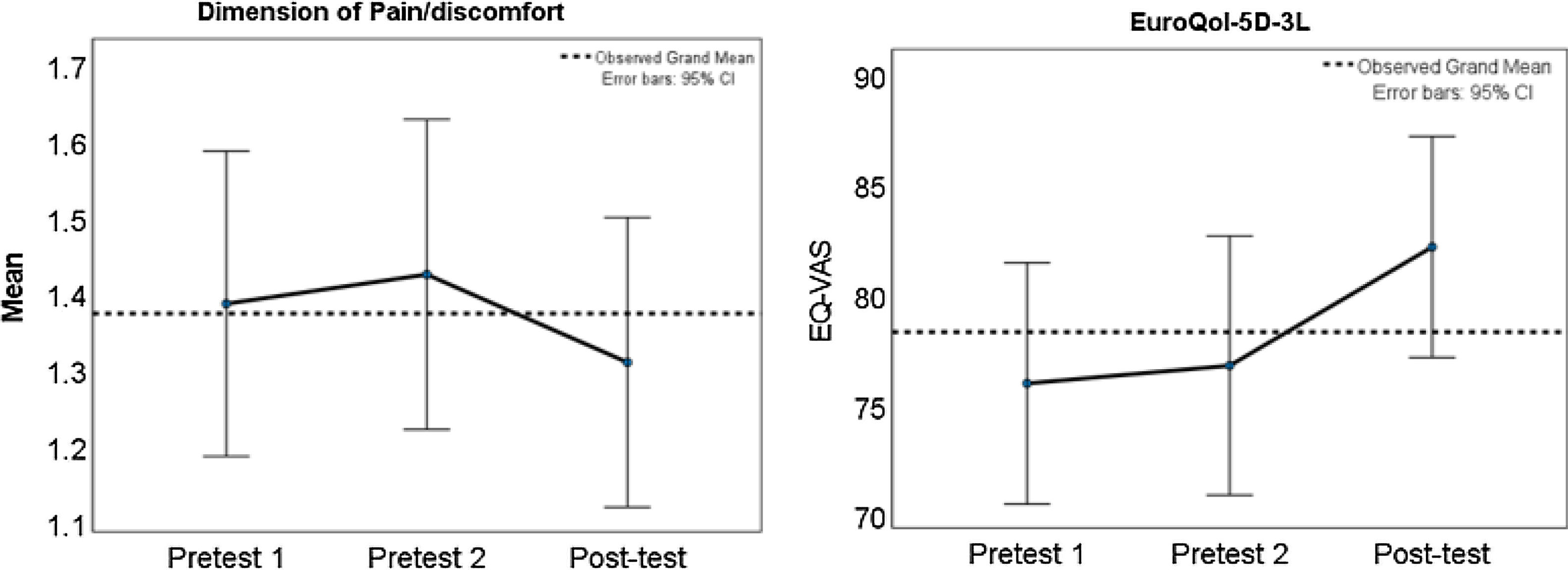
ResultsAlthough the repeated measure analysis showed no significant differences between measures at all time points, a small positive effect was found on the pain/discomfort domain and EuroQol visual analogue scale eight weeks after participating in the exercise programme.
ConclusionsThese results show promising effects of the motor-cognitive intervention on health-related quality of life in patients with T2DM. However, given the study's limitations, such as the small sample size and lack of a control group, further research is needed to investigate the intervention's efficacy.
Este estudio tuvo como objetivo investigar el impacto de un programa de ejercicio multimodal en la calidad de vida relacionada con la salud en pacientes con diabetes mellitus tipo 2 (DMT2).
MétodosSe utilizó un estudio cuasi-experimental con un diseño de un solo grupo y medidas repetidas. Veintiséis pacientes con DM2 (edad 68.58 ± 6.15 años, con una duración de la diabetes de 14.81 ± 8.35 años) participaron en un programa de ejercicios motor-cognitivos que consistió en sesiones de 60 minutos, tres veces por semana durante ocho semanas. Se recopilaron datos en dos mediciones iniciales (pretest 1 y pretest 2) y la medición final (post-test). La calidad de vida relacionada con la salud se evaluó utilizando el cuestionario EuroQol cinco dimensiones-3 niveles.
ResultadosAunque el análisis de medidas repetidas no mostró diferencias significativas entre las mediciones, se encontró un pequeño efecto positivo en el dominio de dolor/malestar y en la escala visual analógica del EuroQol ocho semanas después de participar en el programa de ejercicio.
ConclusionesEstos resultados muestran efectos prometedores de la intervención motor-cognitiva en la calidad de vida relacionada con la salud en pacientes con DMT2. Sin embargo, dadas las limitaciones del estudio, como el tamaño reducido de la muestra y la falta de un grupo de control, se necesita más investigación para estudiar la eficacia de la intervención.