4th International Conference for Global Health (ICGH) in conjunction with the 7th Asian International Conference in Humanized Health Care (AIC-HHC)
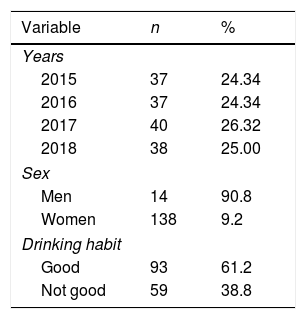
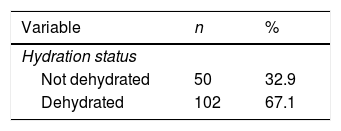
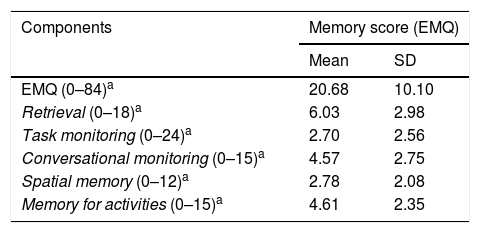
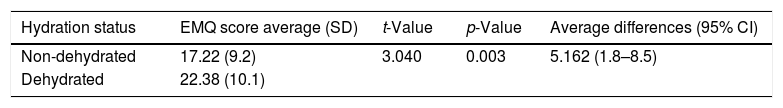
Más datosHydration status is a significant component to keep the functions of bodywork system. Memory is one of the cognitive brain functions which enables human to do daily activities optimally. The purpose of this study was to determine the correlation between hydration status and memory in nursing students. This research employed a comparative analytical method and involved 152 students. The measurement of hydration status was carried out by calculating urine specific gravity using a urinometer while the Everyday Memory Questionnaire (EMQ) was used to measure memory. The independent t-test employed to identify the relationship between hydration status and memory. This research reveals that there is a significant difference between the value of average memory score in students who do not suffer from dehydration and that in students who suffer from dehydration (p=0.003; t=3.040). Maintaining the balance of dehydration status is crucial to make the memory work optimally.