Post-cardiac surgery mediastinitis (PSM) is a serious, complex, and multifactorial complication of surgical procedures. Infectious diseases consultation (IDC) has demonstrated improvement in other complex infectious diseases. The objective of the study was to evaluate the impact of IDC in the management and outcome of patients with PSM.
MethodsObservational retrospective study, of adult patients with PSM between January 2010 and June 2021. After January 2016, IDC was performed in all the patients with PSM. The primary endpoint was clinical success, a composite variable of clinical cure, and absence of adverse events, or recurrence. Also, in-hospital stay, and clinical cure was evaluated in patients that received oral sequential therapy (OST).
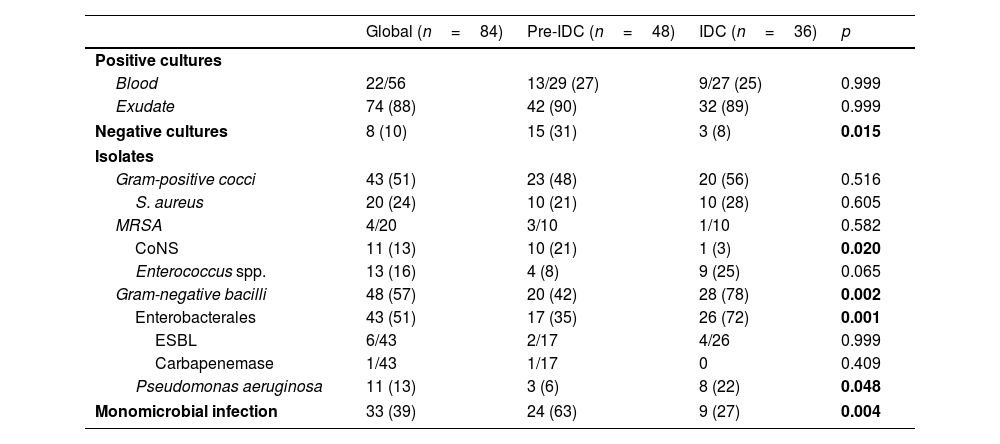
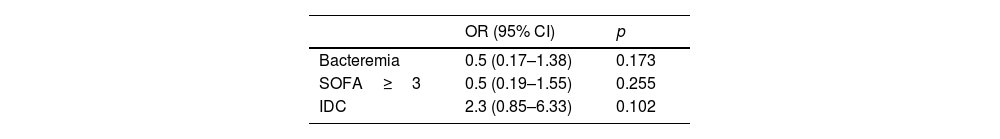
ResultsA total of 84 patients with PSM were included, 48 pre-IDC and 36 in IDC period. No differences in clinical success were observed between the two periods (pre-IDC 60% vs, IDC 77%, p=0.104). During the IDC period the rate of adequate targeted antibiotic treatment was higher (pre-IDC 71% vs. IDC 94%, p=0.016). Gram-negative bacilli infections (pre-IDC 42% vs. IDC 78%, p=0.002) and polymicrobial infections (pre-IDC 37% vs. IDC 63%, p=0.004) increased in the IDC period. Multivariate analysis did not show any variable associated with clinical success. OST was similar in both periods, and a shorter in-hospital stay was observed in the patients who underwent OST (no-OST, 70 days vs. OST, 44 days, p=0.003).
ConclusionsIDC was related with a higher adequate targeted antimicrobial therapy. We observed that OST offers a promising strategy in the management of this infection.
La mediastinitis poscirugía (MPQ) cardíaca es una complicación grave, compleja y multifactorial de la cirugía. La interconsulta de enfermedades infecciosas (IEI) mejora el manejo y evolución de otras enfermedades infecciosas. Evaluamos el impacto de la IEI en el manejo y evolución de esta dolencia.
MétodosEstudio observacional retrospectivo de pacientes adultos con MPQ entre enero de 2010 y junio de 2021. Después de enero de 2016, se realizó IEI en todos los pacientes. El objetivo principal fue el éxito clínico, variable compuesta de curación clínica y ausencia de eventos adversos o recurrencia. Además, se evaluó la estancia hospitalaria y la curación clínica en los pacientes que recibieron terapia secuencial oral (TSO).
ResultadosSe incluyeron 84 pacientes con MPQ, 48 pre-IEI y 36 en periodo post-IEI. No se observaron diferencias en el éxito clínico entre los 2 periodos (pre-IEI 60% vs. IEI 77%, p=0,104). Durante el periodo IEI, la tasa de tratamiento antibiótico dirigido adecuado fue superior (pre-IEI 71% vs. post-IEI 94%, p=0,016). Las infecciones por bacilos gramnegativos (pre-IEI 42% vs. post-IEI 78%, p=0,002) y las polimicrobianas (pre-IEI 37% vs. post-IEI 63%, p=0,004) aumentaron en el periodo post-IEI. El análisis multivariable no mostró ninguna variable asociada con el éxito clínico. El porcentaje de pacientes con TSO fue similar en ambos periodos, y en estos pacientes la estancia hospitalaria fue menor (sin TSO, 70 días vs. con TSO, 44 días, p=0,003).
ConclusionesLa IEI se relacionó con una mayor adecuación de tratamiento antimicrobiano dirigido. La TSO ofrece una estrategia prometedora en el manejo de esta infección.
Article
Socio de la Sociedad Española de Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiología Clínica

Para acceder a la revista
Es necesario que lo haga desde la zona privada de la web de la SEIMC, clique aquí
Para realizar los cursos formativos
La actividad estará abierta para socios de la SEIMC. IMPORTANTE, recuerde que requiere registro previo gratuito. Empezar aquí