Detection of Neisseria gonorrhoeae (NG) and Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) is periodically indicated in asymptomatic patients with risky sexual practices. The objective of this study was to assess the efficacy of employing a rapid polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test in a combined pool of three samples from the same patient and compare it with the standard PCR performed in the three different samples separately.
MethodsSamples were collected from asymptomatic patients at risk of sexually transmitted infections (STI). Urine samples, two pharyngeal swabs, and two rectal swabs were collected from each patient. Two PCR techniques were performed: standard PCR (Allplex CT/NG/MG/TV®, Seegene) in each of the three samples separately, and rapid PCR (Xpert CT/NG®, Cepheid) in a pool of three samples.
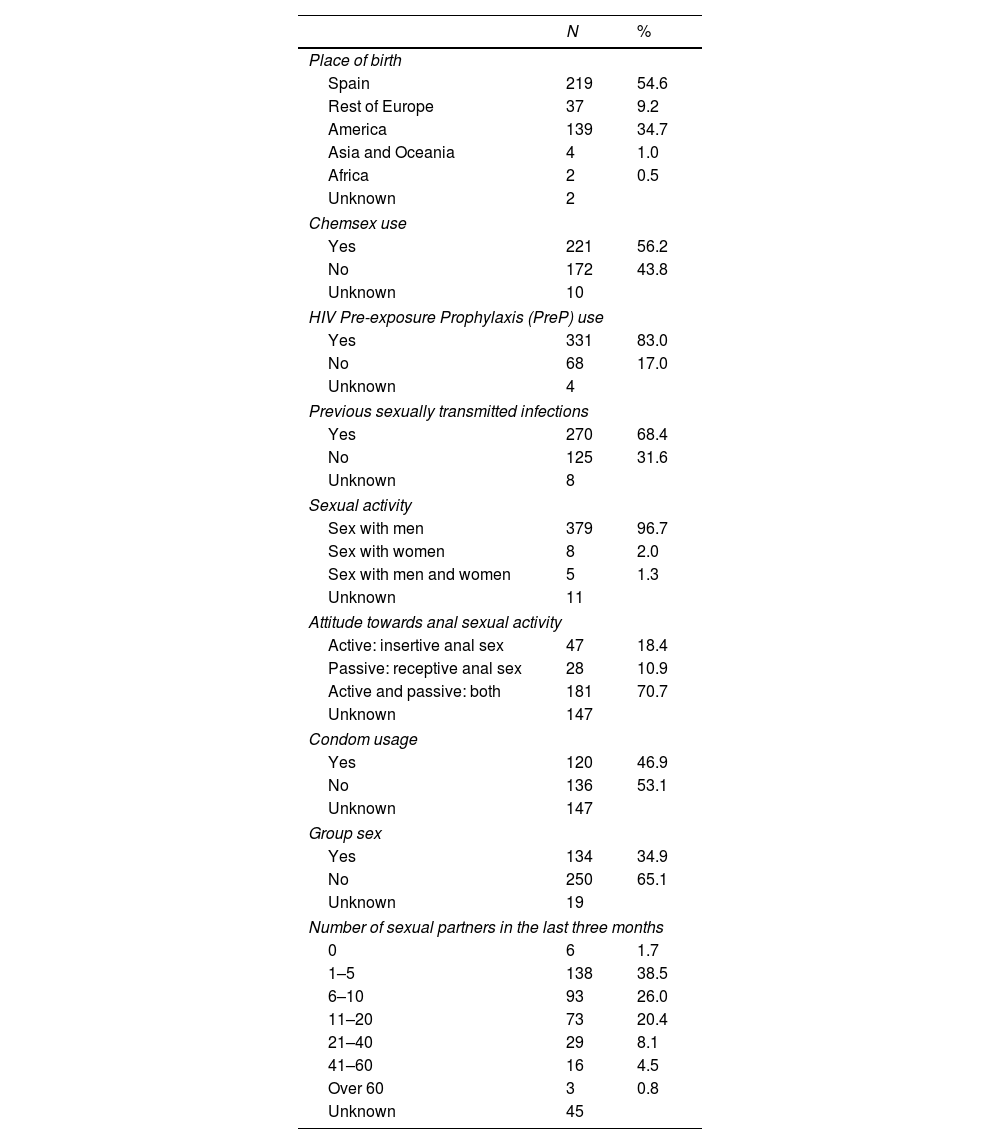
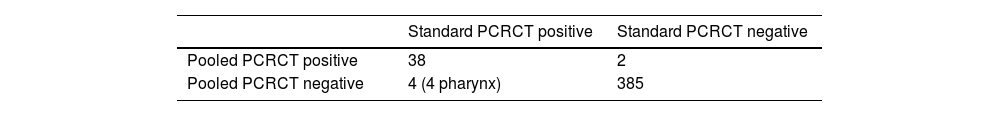
ResultsA total of 429 pooled samples from 403 patients were included in the study, and 426 urine samples, 412 rectal swabs and 426 pharyngeal swabs were also processed. Concordances between pooled and individual PCRs for both CT and NG identification were 94.17%, with 77 (17.9%) positive samples. The concordance for CT was 98.60%, with 38 positive samples (8.88%), being 95.33% for NG, with 51 positive samples (11.88%).
ConclusionThe use of a pool of three samples (urine, rectum and pharynx) for the detection of NG and CT using rapid PCR can be a cost-effective alternative to performing conventional PCR in the three samples separately in asymptomatic patients at risk of developing STI.
La detección de Neisseria gonorrhoeae (NG) y Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) está indicada periódicamente en pacientes asintomáticos con prácticas sexuales de riesgo. El objetivo de este estudio fue evaluar la eficacia de emplear una prueba rápida de reacción en cadena de la polimerasa (PCR) en una agrupación de tres muestras del mismo paciente y compararla con la PCR estándar realizada en las 3 muestras diferentes por separado.
MétodosSe recolectaron muestras de pacientes asintomáticos con riesgo de padecer infecciones de transmisión sexual (ITS). De cada paciente se recogieron muestras de orina, 2 hisopos faríngeos y 2 hisopos rectales. Se realizaron dos técnicas de PCR: PCR estándar (Allplex CT/NG/MG/TV®, Seegene) en cada una de las 3 muestras por separado, y PCR rápida (Xpert CT/NG®, Cepheid) en la agrupación de las 3 muestras.
ResultadosSe incluyeron en el estudio un total de 429 muestras agrupadas de 403 pacientes y también se procesaron 426 muestras de orina, 412 hisopos rectales y 426 hisopos faríngeos. La concordancia entre las PCR combinadas e individuales para la identificación de CT y NG fue del 94,17%, con 77 (17,9%) muestras positivas. La concordancia para CT fue del 98,60%, con 38 muestras positivas (8,88%), siendo del 95,33% para NG, con 51 muestras positivas (11,88%).
ConclusiónEl uso de una agrupación de 3 muestras (orina, recto y faringe) para la detección de NG y CT mediante una PCR rápida puede ser una alternativa coste/efectiva a la realización de una PCR convencional en las 3 muestras por separado en pacientes asintomáticos con riesgo de desarrollar ITS.
Article
Socio de la Sociedad Española de Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiología Clínica

Para acceder a la revista
Es necesario que lo haga desde la zona privada de la web de la SEIMC, clique aquí
Para realizar los cursos formativos
La actividad estará abierta para socios de la SEIMC. IMPORTANTE, recuerde que requiere registro previo gratuito. Empezar aquí