Serological diagnosis of infections due to measles and rubella viruses is done by IgM detection. The aim of this study was to comparatively evaluate commercial systems for detecting IgM against both viruses, including those of ELISA, in indirect and capture formats, chemiluminescence and electrochemiluminescence.
MethodsSeven (for rubella) and six (for measles) assays were studied. One hundred and sixty two samples were included in the study (from 90 rubella and 72 measles cases), and all were analyzed in all the assays.
ResultsThe ranges of sensitivity, specificity and agreement for rubella were 94.8–100%, 52.4–100% and 75.5–98.1%, respectively. The corresponding ranges for measles assays were 87.0–100%, 53.3–100%, and 73.0–99.4%.
ConclusionThe best-performing assays were chemiluminescence (for measles and rubella IgM), and electrochemiluminescence (for rubella IgM).
El diagnóstico serológico de las infecciones por los virus de la rubéola y del sarampión se realiza por detección de IgM específica. El objetivo de este estudio fue evaluar comparativamente sistemas comerciales para la detección de IgM frente a ambos virus, incluyendo ensayos de ELISA, tanto con metodologías indirectas como de captura, así como quimioluminiscencia y electroquimioluminiscencia.
MétodosSe estudiaron 7 ensayos para rubéola y 6 para sarampión. Se emplearon 162 muestras (de 90 casos de rubéola y de 72 de sarampión) que se analizaron en todos los ensayos.
ResultadosLos rangos de sensibilidad, especificidad y concordancia para los ensayos de rubéola fueron 94,8-100%, 52,4-100% y 75,5-98,1%, respectivamente. Los rangos correspondientes para los ensayos de sarampión fueron 87-100%, 53,3-100% y 73-99,4%, respectivamente.
ConclusiónLos mejores ensayos fueron quimioluminiscencia (para IgM frente a rubéola y a sarampión) y electroquimioluminiscencia (para IgM frente a rubéola).
Rubella and measles infections are usually diagnosed in the laboratory by RT-PCR detection of the virus genomes during the first four days of the disease. However, samples taken at the appropriate time for making a direct diagnosis are not always available, so the detection of IgM-class antibodies is used as a fundamental tool for correct case characterization.1 Using a combination of the two approaches greatly improves the performance of measles2,3 and rubella2 diagnosis. In a situation of elimination, such as the current one, serological tests with good sensitivity and specificity characteristics are required. Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics (Marburg, Germany) (ELISA-Siemens) currently supplies the reference methods (ELISA assays, Enzygnost®) for determining IgM against rubella (RuV) and measles (MeV) viruses. The Enzygnost® kits have been used by a large number of network laboratories for many years.4,5 However, they will soon be withdrawn from the market, so the identification of alternative methods with acceptable performance characteristics is a challenge for clinical laboratories.
The aim of this study is to assess the operating characteristics of ELISA assays, based on indirect or μ chain capture methodologies, and chemiluminescence (CLIA) (capture), all for the purpose of determining the levels of IgM against RuV and MeV, and of electrochemiluminescence (ECLIA) (capture), for determining IgM versus RuV. Seven assays were compared for RuV IgM and six for MeV IgM.
Materials and methodsSerological methodsThe following assays were studied (Table 1):
- 1.
Rubella assays
- i.
Enzygnost Rubella IgM, Siemens (Marburg, Germany) (RuV-ELISA-Siemens). The determinations were carried out in a Behring ELISA Processor III (BEPIII) (Siemens).
- ii.
Serion ELISA Classic Rubella IgM, Serion (Würzburg, Germany) (RuV-ELISA-Serion). The determinations were done in a BEPIII.
- iii.
Anti-Rubella IgM ELISA, EuroImmun (Lübeck, Germany) (RuV-ELISA-Euroimmun-1). The assay was done manually, and the plates were read in a BEPIII.
- iv.
Anti-Rubella IgM GP ELISA, EuroImmun (RuV-ELISA-Euroimmun-2). The tests were done manually, and the plates were read in a BEPIII.
- v.
Enzywell Rubella IgM, Diesse (Monteriggioni, Italy) (RuV-ELISA-Diesse). The tests were done manually, and the plates were read in a BEPIII.
- vi.
LIAISON® Rubella IgM, Diasorin (Saluggia, Italy) (RuV-CLIA). The determinations were done on a LIAISON® XL platform (Diasorin).
- vii.
ELECSYS® Rubella IgM, Roche Diagnostics (Penzberg, Germany) (RuV-ECLIA). The determinations were done in a Cobas e411 analyzer (Roche Diagnostics).
- 2.
Measles assays
- i.
Enzygnost Measles IgM, Siemens (MeV-ELISA-Siemens). The determinations were carried out in a BEPIII.
- ii.
Serion ELISA Classic Measles IgM, Serion (MeV-ELISA-Serion). The determinations were carried out in a BEPIII.
- iii.
Anti-Measles IgM ELISA, EuroImmun (MeV-ELISA-Euroimmun-1). The tests were done manually, and the plates were read in a BEPIII.
- iv.
Anti-Measles IgM NP ELISA, EuroImmun (MeV-ELISA-Euroimmun-2). Tests were done manually, and the plates were read in a BEPIII.
- v.
Enzywell Measles IgM, Diesse (MeV-ELISA-Diesse). Tests were done manually, and the plates were read in a BEPIII.
- vi.
LIAISON® Measles IgM (Diasorin) (MeV-CLIA). The determinations were done on a LIAISON® XL platform.
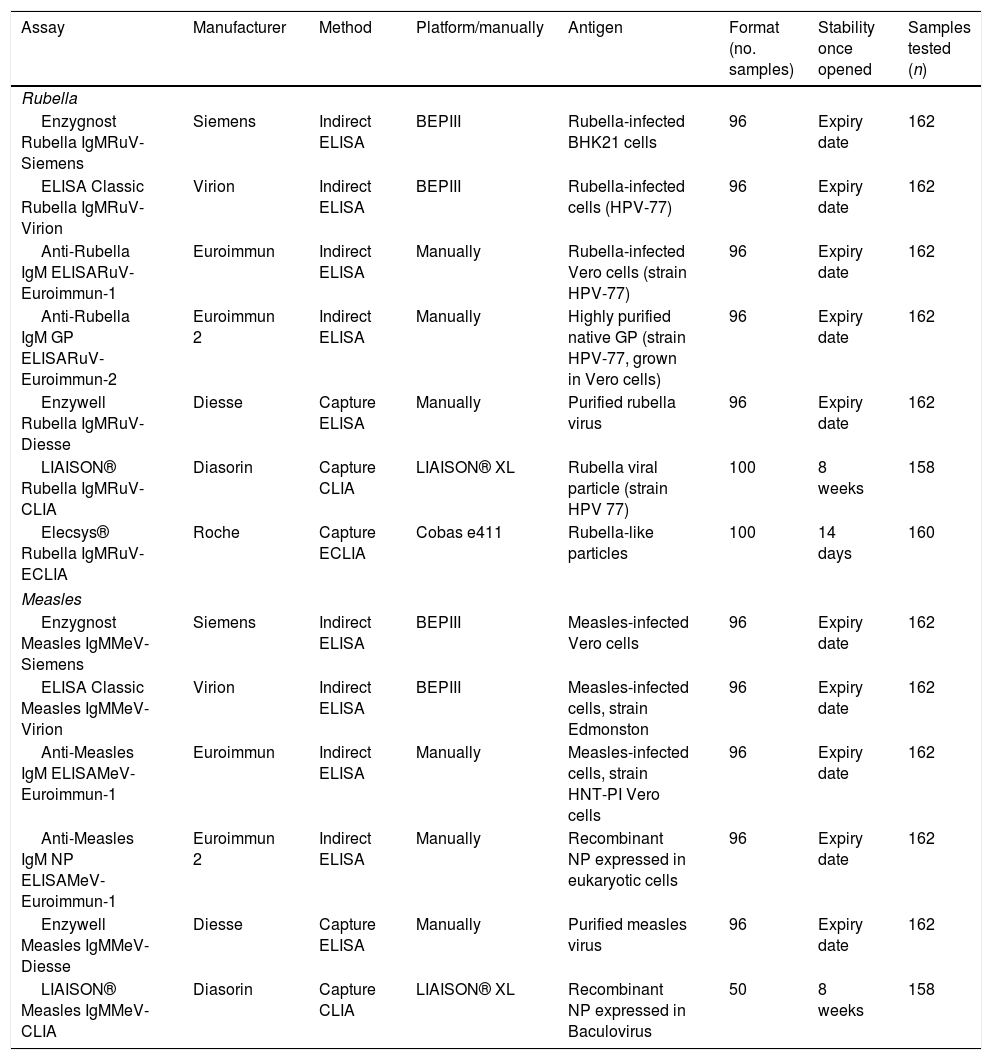
List of assays analyzed.
| Assay | Manufacturer | Method | Platform/manually | Antigen | Format (no. samples) | Stability once opened | Samples tested (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubella | |||||||
| Enzygnost Rubella IgMRuV-Siemens | Siemens | Indirect ELISA | BEPIII | Rubella-infected BHK21 cells | 96 | Expiry date | 162 |
| ELISA Classic Rubella IgMRuV-Virion | Virion | Indirect ELISA | BEPIII | Rubella-infected cells (HPV-77) | 96 | Expiry date | 162 |
| Anti-Rubella IgM ELISARuV-Euroimmun-1 | Euroimmun | Indirect ELISA | Manually | Rubella-infected Vero cells (strain HPV-77) | 96 | Expiry date | 162 |
| Anti-Rubella IgM GP ELISARuV-Euroimmun-2 | Euroimmun 2 | Indirect ELISA | Manually | Highly purified native GP (strain HPV-77, grown in Vero cells) | 96 | Expiry date | 162 |
| Enzywell Rubella IgMRuV-Diesse | Diesse | Capture ELISA | Manually | Purified rubella virus | 96 | Expiry date | 162 |
| LIAISON® Rubella IgMRuV-CLIA | Diasorin | Capture CLIA | LIAISON® XL | Rubella viral particle (strain HPV 77) | 100 | 8 weeks | 158 |
| Elecsys® Rubella IgMRuV-ECLIA | Roche | Capture ECLIA | Cobas e411 | Rubella-like particles | 100 | 14 days | 160 |
| Measles | |||||||
| Enzygnost Measles IgMMeV-Siemens | Siemens | Indirect ELISA | BEPIII | Measles-infected Vero cells | 96 | Expiry date | 162 |
| ELISA Classic Measles IgMMeV-Virion | Virion | Indirect ELISA | BEPIII | Measles-infected cells, strain Edmonston | 96 | Expiry date | 162 |
| Anti-Measles IgM ELISAMeV-Euroimmun-1 | Euroimmun | Indirect ELISA | Manually | Measles-infected cells, strain HNT-PI Vero cells | 96 | Expiry date | 162 |
| Anti-Measles IgM NP ELISAMeV-Euroimmun-1 | Euroimmun 2 | Indirect ELISA | Manually | Recombinant NP expressed in eukaryotic cells | 96 | Expiry date | 162 |
| Enzywell Measles IgMMeV-Diesse | Diesse | Capture ELISA | Manually | Purified measles virus | 96 | Expiry date | 162 |
| LIAISON® Measles IgMMeV-CLIA | Diasorin | Capture CLIA | LIAISON® XL | Recombinant NP expressed in Baculovirus | 50 | 8 weeks | 158 |
All the assays were carried out in strict accordance with the respective instructions for use. This includes the pretreatment with anti-human IgG to remove any interference from rheumatoid factors for the indirect methods.
SamplesA total of 162 samples from patients with exanthematic disease were included in the study; patients were diagnosed as having rubella or measles.
They were grouped into two panels.
- -
Panel 1. 90 samples from rubella cases from an outbreak that occurred in 1996.
- -
Panel 2. 72 samples from measles cases from an outbreak that occurred in 1991.
The samples were stored at −20°C until their use for this study.
All the samples were tested for both MeV- and RuV-IgM.
The samples were finally classified as positive or negative on the basis of the majority of results: in both cases, samples with four or more positive results were considered positive; samples with four or more negative results were considered negative. All other samples were considered indeterminate, and were excluded from subsequent analysis.
Ethical approvalThis study was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Institute of Health Carlos III (approval number: CEI PI 81_2019-v2_Enmienda 2019).
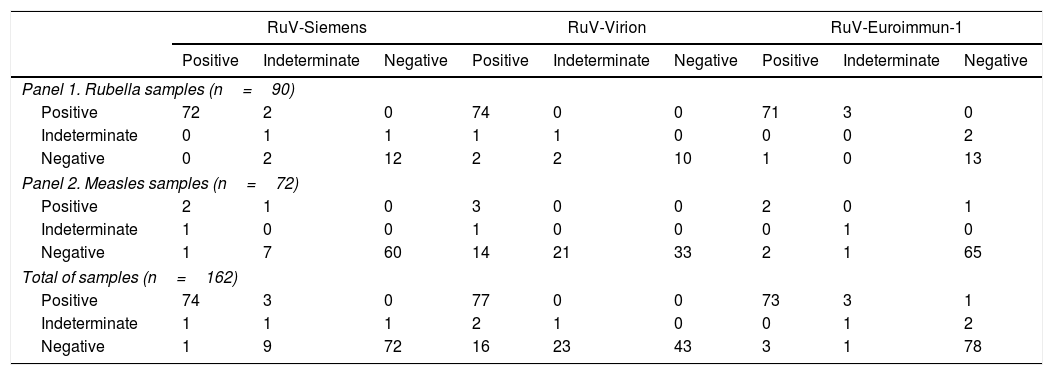
ResultsRubella assaysOf the rubella samples, 74 were classified as positive (≥4 positive results), 15 as negative (≥4 negative results), and one as indeterminate (Table 2). Of the positive samples, 67 were positive in all the assays, and six of the negative samples were negative in all the assays.
Comparison of rubella assays.
| RuV-Siemens | RuV-Virion | RuV-Euroimmun-1 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Indeterminate | Negative | Positive | Indeterminate | Negative | Positive | Indeterminate | Negative | |
| Panel 1. Rubella samples (n=90) | |||||||||
| Positive | 72 | 2 | 0 | 74 | 0 | 0 | 71 | 3 | 0 |
| Indeterminate | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Negative | 0 | 2 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 10 | 1 | 0 | 13 |
| Panel 2. Measles samples (n=72) | |||||||||
| Positive | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| Indeterminate | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Negative | 1 | 7 | 60 | 14 | 21 | 33 | 2 | 1 | 65 |
| Total of samples (n=162) | |||||||||
| Positive | 74 | 3 | 0 | 77 | 0 | 0 | 73 | 3 | 1 |
| Indeterminate | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Negative | 1 | 9 | 72 | 16 | 23 | 43 | 3 | 1 | 78 |
| RuV-Euroimmun-2 | RuV-Diesse | RuV-CLIAa | RuV-ECLIAb | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Indeterminate | Negative | Positive | Indeterminate | Negative | Positive | Indeterminate | Negative | Positive | Indeterminate | Negative | |
| Panel 1. Rubella samples (n=90) | ||||||||||||
| Positive | 71 | 3 | 0 | 73 | 0 | 1 | 69 | 0 | 1 | 70 | 1 | 1 |
| Indeterminate | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Negative | 0 | 2 | 12 | 1 | 3 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 14 |
| Panel 2. Measles samples (n=72) | ||||||||||||
| Positive | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Indeterminate | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Negative | 0 | 0 | 68 | 0 | 3 | 65 | 0 | 0 | 68 | 0 | 1 | 67 |
| Total of samples (n=162) | ||||||||||||
| Positive | 74 | 3 | 0 | 76 | 0 | 1 | 70 | 0 | 3 | 73 | 1 | 1 |
| Indeterminate | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Negative | 0 | 2 | 80 | 1 | 6 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 82 | 0 | 1 | 81 |
When analyzing the measles samples, three were identified as positive for RuV-IgM (confirmed as double infections) and one as indeterminate for rubella IgM, in a MeV IgM-positive case. Thirty-two samples were negative in all assays; the majority of discrepant results were obtained in RuV-Virion (14 positive and 21 indeterminate). The results from the RuV-IgM assays compared with the reference criterion are shown in Tables 2 and 3.
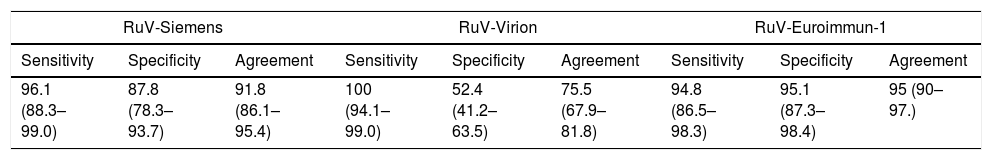
Performance characteristics of rubella assays.a
| RuV-Siemens | RuV-Virion | RuV-Euroimmun-1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | Specificity | Agreement | Sensitivity | Specificity | Agreement | Sensitivity | Specificity | Agreement |
| 96.1 (88.3–99.0) | 87.8 (78.3–93.7) | 91.8 (86.1–95.4) | 100 (94.1–99.0) | 52.4 (41.2–63.5) | 75.5 (67.9–81.8) | 94.8 (86.5–98.3) | 95.1 (87.3–98.4) | 95 (90–97.) |
| RuV-Euroimmun-2 | RuV-Diesse | RuV-CLIAb | RuV-ECLIAc | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | Specificity | Agreement | Sensitivity | Specificity | Agreement | Sensitivity | Specificity | Agreement | Sensitivity | Specificity | Agreement |
| 96.1 (88.3–99) | 97.6 (90.6–99.6) | 96.9 (92.4–98.8) | 98.7 (92–99.9) | 91.5 (82.7–96.2) | 95 (90–97.6) | 95.9 (87.7–98.9) | 100 (94.4–99.9) | 98.1 (94–99.5) | 97.3 (89.8–99.5) | 98.8 (92.5–99.9) | 98.1 (94.1–99.5) |
The best performances were obtained by RuV-CLIA (agreement: 98.1% [95% confidence interval (95% CI): 94.0–99.5%]; sensitivity: 95.9% [95% CI: 87.7–98.9%]; and specificity: 100% [95% CI: 94.4–99.9%]) and RuV-ECLIA (respectively, 98.1% [95% CI: 94.1–99.5%]; 97.3% [95% CI: 89.8–99.5%] and 98.8% [95% CI: 92.5–99.9%]). With the ELISA methods, the figures for agreement, sensitivity and specificity ranged from 96.9% [95% CI: 92.4–98.8%] (RuV-Euroimmun-2) to 75.5% [95% CI: 67.9–81.8%] (RuV-Virion); 100% [95% CI: 94.1–99.0%] (RuV-Virion) to 94.8% [95% CI: 86.5–98.3%] (RuV-Euroimmun-1); and 97.6% [95% CI: 90.6–99.6%] (RuV-Euroimmun-2) to 52.4% [95% CI: 41.2–63.5%] (RuV-Virion), respectively (Table 3).
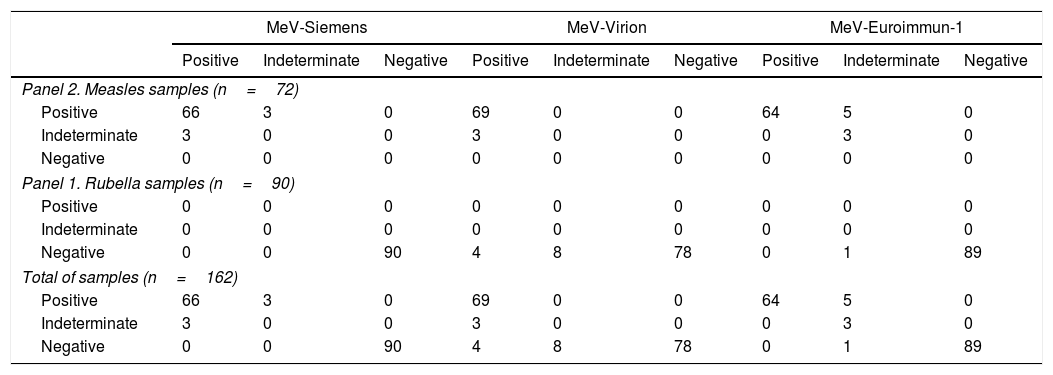
Measles assays69 samples from measles cases were classified as positive (≥4 positive results), and three as indeterminate. Amongst the positive cases, 57 samples gave positive result in all the assays.
Discrepant results were obtained mainly in MeV-Euroimmun-1 (5 samples with an indeterminate result) and MeV-Euroimmun-2 (7 indeterminate and 2 negative samples) (Table 4).
Comparison of measles assays.
| MeV-Siemens | MeV-Virion | MeV-Euroimmun-1 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Indeterminate | Negative | Positive | Indeterminate | Negative | Positive | Indeterminate | Negative | |
| Panel 2. Measles samples (n=72) | |||||||||
| Positive | 66 | 3 | 0 | 69 | 0 | 0 | 64 | 5 | 0 |
| Indeterminate | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Negative | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Panel 1. Rubella samples (n=90) | |||||||||
| Positive | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Indeterminate | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Negative | 0 | 0 | 90 | 4 | 8 | 78 | 0 | 1 | 89 |
| Total of samples (n=162) | |||||||||
| Positive | 66 | 3 | 0 | 69 | 0 | 0 | 64 | 5 | 0 |
| Indeterminate | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Negative | 0 | 0 | 90 | 4 | 8 | 78 | 0 | 1 | 89 |
| MeV-Euroimmun-2 | MeV-Diesse | MeV-CLIAa | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Indeterminate | Negative | Positive | Indeterminate | Negative | Positive | Indeterminate | Negative | |
| Panel 2. Measles samples (n=72) | |||||||||
| Positive | 60 | 7 | 2 | 68 | 1 | 0 | 67 | 1 | 0 |
| Indeterminate | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Negative | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Panel 1. Rubella samples (n=90) | |||||||||
| Positive | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Indeterminate | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Negative | 0 | 0 | 90 | 9 | 33 | 48 | 0 | 0 | 87 |
| Total of samples (n=162) | |||||||||
| Positive | 60 | 7 | 2 | 68 | 1 | 0 | 67 | 1 | 0 |
| Indeterminate | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Negative | 0 | 0 | 90 | 9 | 33 | 48 | 0 | 0 | 87 |
All samples from the rubella cases were identified as negative according to the final classification. No positive results were obtained in MeV-Siemens, MeV-EuroImmun-2 or MeV-CLIA.
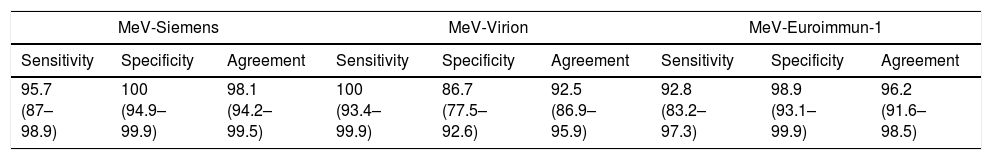
The results obtained in the compared assays are shown in Table 5. The best performances were obtained by MeV-CLIA (agreement: 99.4% [95%CI: 95.9–100%]; sensitivity: 98.5% [95% CI: 91.0–99.9%], and specificity: 100% [95% CI: 94.7–99.9%]). With the ELISA methods, the figures for agreement, sensitivity and specificity ranged from 98.1% [95% CI: 94.2–99.5%] (MeV-Siemens) to 73% [95% CI: 65.2–79.5%] (MeV-Diesse); 100% [95% CI: 93.4–99.9%] (MeV-Virion) to 87% [95% CI: 76.2–93.5%] (MeV-EuroImmun-2); and 100% [95% CI: 94.9–99.9%] (MeV-Siemens and MeV-EuroImmun-2) to 53.3% (MeV-Diesse) [95% CI: 42.6–63.8%], respectively.
Performance characteristics of measles assaysa.
| MeV-Siemens | MeV-Virion | MeV-Euroimmun-1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | Specificity | Agreement | Sensitivity | Specificity | Agreement | Sensitivity | Specificity | Agreement |
| 95.7 (87–98.9) | 100 (94.9–99.9) | 98.1 (94.2–99.5) | 100 (93.4–99.9) | 86.7 (77.5–92.6) | 92.5 (86.9–95.9) | 92.8 (83.2–97.3) | 98.9 (93.1–99.9) | 96.2 (91.6–98.5) |
| MeV-Euroimmun-2 | MeV-Diesse | MeV-CLIAb | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | Specificity | Agreement | Sensitivity | Specificity | Agreement | Sensitivity | Specificity | Agreement |
| 87 (76.2–93.5) | 100 (94.9–99.9) | 94.3 (89.2–97.2) | 98.6 (91.1–99.9) | 53.3 (42.6–63.8) | 73 (65.2–79.5) | 98.5 (91–99.9) | 100 (94.7–99.9) | 99.4 (95.9–100) |
In 2018, measles and rubella were eliminated in 35 (66%) and 39 (73%) of the Member States of the WHO European Region.6 This was made possible by adequate vaccine coverage and surveillance systems, and the availability of sensitive and specific diagnostic methods, using both direct detection by PCR and serological determination of specific IgMs. In recent years, the most commonly used methods for determining specific IgMs against RuV and MeV have been those of Enzygnost® Siemens. These methods have been used as reference.5 However, the company has ceased the production of these reagents, so the need to identify suitable alternative, sensitive and specific methods has become an important matter. Here, we compared seven methods for determining IgM against RuV and six methods for determining MeV-IgM, including Enzygnost® assays. Despite the consideration of the Siemens assays as reference5 we have used a consensus criterion for classification of the samples, due to the assay from Siemens may show negative results in very early samples at least for measles, as previously reported.7 Thus, we think that by using a consensus criterion, the case classification is strongly improved.
Given the lack of a gold standard, the criterion of the majority of results obtained in the compared assays was taken as the reference for classifying our results. For rubella, the best agreement, sensitivity and specificity figures were obtained by the RuV-CLIA and RuV-ECLIA methods, both of which are based on μ chain capture methods. Three of the ELISAs (RuV-Euroimmun-1, RuV-Euroimmun-2 and RuV-Diesse) yielded better values than those obtained by RuV-Siemens, the best of these being RuV-Euroimmun-2, which uses GP as the antigen, thereby making it a suitable alternative for detecting RuV IgM.
Several comparative studies have been published in recent years, some of which have involved the methods examined here. The RuV-ECLIA assay (Elecsys, Roche) shows good agreement (98.0%) with another CLIA (Architect, Abbott).8 RuV-EuroImmun-1 shows good comparability with RuV-Siemens in the diagnosis of suspected cases of congenital rubella syndrome, with an agreement of 94.7%.9 The RuV-ECLIA showed a sensitivity of 79.8–96.0% in a multicenter study, which is a lower range than that noted in the present study, with high specificity (98.7–99.0%).10
The best specificity values obtained in this study were those of RuV-CLIA and RuV-ECLIA. Moreover, RuV-EuroImmun-2 has been shown to be the most specific of the ELISA-based methods when compared with an ELISA method using whole-virus antigen.11 The majority of the discrepancies occurred in the RuV-Virion assay when measles samples were tested (35/72, 48%), resulting in a very low specificity for this method.
In relation to measles assays, the best values of sensitivity, specificity, and agreement were obtained with MeV-CLIA (98.5%, 100% and 99.4%, respectively). The only assay that produced low values for agreement and specificity (73.0% and 53.3%) was MeV-Diesse; the remaining assays yielded acceptable (MeV-Virion and MeV-Euroimmun-2) or excellent (MeV-Siemens and MeV-Euroimmun-2) overall values. The assays with more discrepant results were MeV-Diesse (33 indeterminate and 9 positive samples) and MeV-Virion (8 indeterminate and 4 positive samples) (Table 4), resulting in a very low value of specificity in both assays.
Recently published information is available from measles IgM assays. In general, capture ELISA methods are more sensitive than indirect ones.12
The MeV-CLIA method has been compared with the MeV-Siemens method in some reports, in which it showed sensitivity and specificity of 94.0% and 100%,13 and 93.8% and 98.8%,14 respectively. Compared with capture ELISA (Microimmune), MeV-CLIA showed 92.0% sensitivity and 100% specificity, with a small proportion of indeterminate results.15 In an additional report, MeV-CLIA showed improved corresponding values of a different CLIA (Vircell), although the difference was not statistically significant.16
Most assays for MeV IgM, except MeV-Diesse and, to a lesser extent, MeV-Virion, gave excellent specificity values. Therefore, it does not appear that the specificity of the assays is related to the antigen used (NP in the cases of MeV-Euroimmun-2 and MeV-CLIA, and extract from infected cells in the cases of MeV-Siemens and MeV-Euroimmun-1). In the current situation of elimination of measles and rubella, when the number of cases is declining, the positive predictive value of IgM determination decreases, so confirmatory methods are necessary. Detection of seroconversion or a significant increase in antibody titer in two paired samples indicates an acute infection.1 On the other hand, IgG avidity assays allow primary and secondary infections to be differentiated, this being applicable to measles cases in which the characterization of vaccine failure is possible,17 and to rubella,9 mainly to rule out primary infection in pregnancy, of devastating teratogenic effect. Commercial methods for characterizing IgG avidity against both viruses are available, including ELISA and CLIA.8,11,17,18 However, in the current circumstances, comparative elimination studies are necessary to ensure the quality of the serological methods used in clinical laboratories.5,19
Although the simultaneous reactivity against measles and rubella seems not be frequent,20 it can occur in subjects recently immunized by using measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine. In the present study no data about antecedents of recent vaccination was recorded. This situation could explain the finding of positive IgM to both viruses. According to our experience, in the context of measles and rubella outbreaks, MMR vaccination is implemented, as a Public Health measure. That is the reason why, in such situations, a number of vaccine related cases could be expected. To further explore this point, we have tested for mumps IgM the three samples classified as double infections, trying to confirm a recent MMR vaccination. One of them showed a positive result in the mumps IgM assay, confirming a recent vaccination, the remaining two being negative (results not shown).
The study has some weaknesses. First, samples were taken in 1991 and 1996, in an epidemic context. Although the medical doctors who sent the samples clinically characterized the patients, no additional information was available about the time of bleeding after the appearance of the exanthema. This information is important for the correct interpretation of discrepant results, which are mainly false negatives. Second, we tried to establish the performance characteristics of assays for RuV- and MeV-IgM, using samples from both diseases. However, samples of other infections that may cause differential diagnostic problems, mainly human parvovirus B19 (HPVB19), as well as cytomegalovirus and Epstein Barr virus, should also been included. This aspect is of great interest in the context of the elimination of measles and rubella, as is consistently evident for both RuV and MeV.1,21 The same occurs in travelers with cases acquired in countries with endemic circulation of arboviruses (Zika virus [ZikV], dengue and chikungunya). A certain degree of false-positive heterologous reactivity has recently been described, whereby the LIAISON assay for ZikV in cases of measles and HPVB19 gave positive results that were not confirmed in immunofluorescence assays.22 Finally, positive heterologous results due to polyclonal stimulation of B lymphocytes in both rubella and measles cases could not be excluded, which could compromise the specificity of measles and rubella assays. For these reasons, further studies are required to determine the importance of this phenomenon.
In conclusion, the information reported here will help clinical laboratories to improve the serological diagnosis of measles and rubella infections.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
This work was supported by the Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria (grant number FIS PI15CIII/00023).