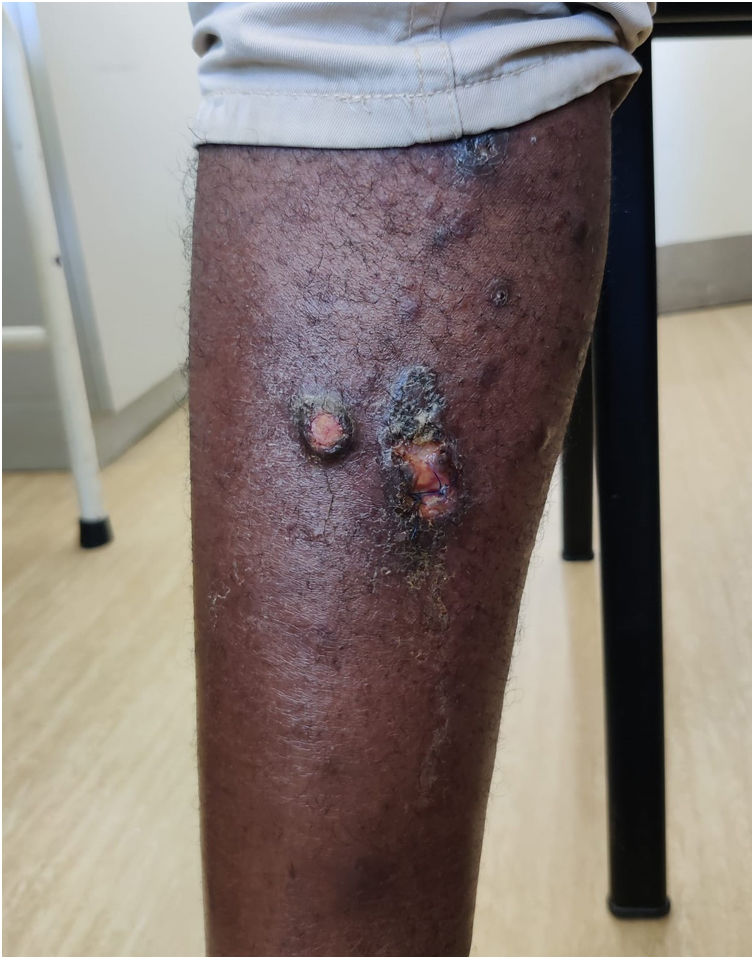
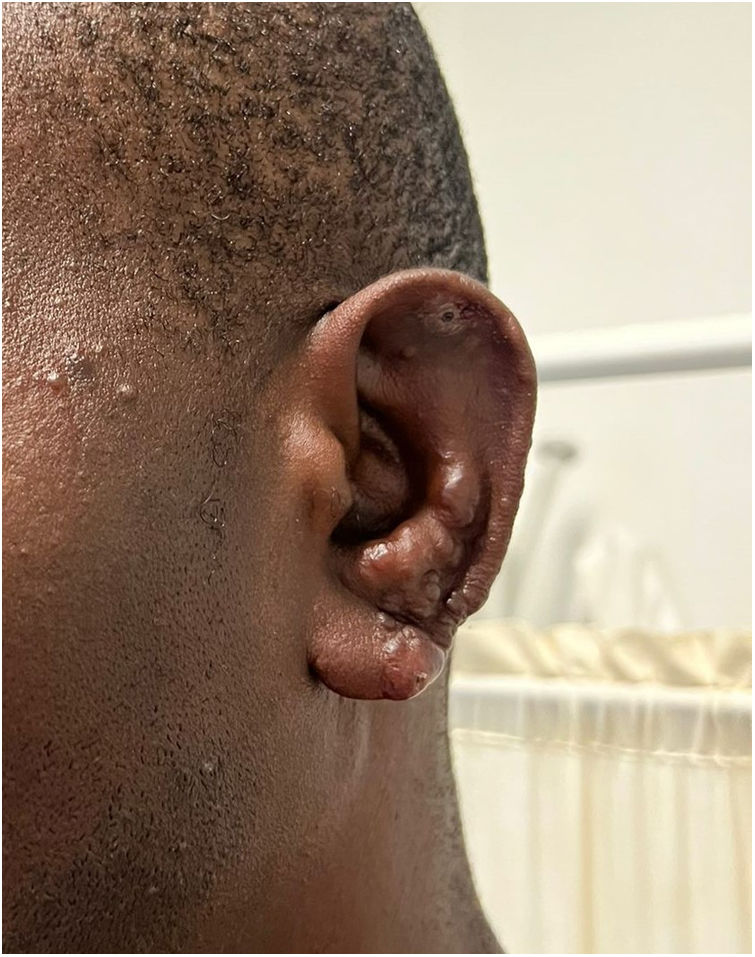
We report a case of a 44-year-old man, with no notable medical history, originally from Nigeria, living in Portugal for about 1 month, who went to the Emergency Department complaining of hypoesthesia and itching in his right leg for about 9 months. He reported the appearance of multiple nodules approximately 3 months ago, initially on the lower limbs (Fig. 1), with subsequent spread to the trunk, upper limbs, face, and auricular pavilion (Fig. 2). On physical examination, the patient presented with multiple nodules, some with a central crust, on the face, left auricular pavilion, upper limbs, and right lower limb. Salmon-colored conjunctivitis was also noted. Laboratory tests were notable for normocytic normochromic anemia and leukopenia.
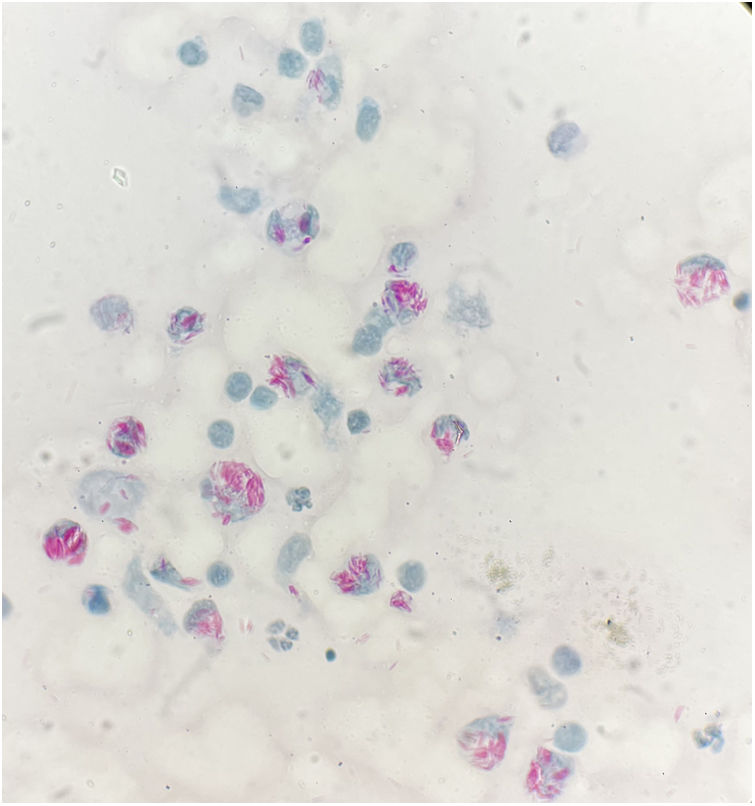
He was referred to outpatient Dermatology and Infectious Diseases consultations and underwent skin biopsies of the lesions for direct examination to search for mycobacteria. Direct examination (Ziehl-Neelsen staining) revealed the presence of multiple clusters of intracellular acid-fast bacilli (Fig. 3).
He initiated a triple therapy with dapsone, rifampicin, and clofazimine, with no significant adverse effects. Upon clinical reevaluation after 1 month of treatment, an improvement in skin lesions was observed, with no rhinitis or conjunctivitis.
We did not perform any exams to evaluate whether the patient had neurological involvement because sensitivity improved with antibiotic therapy. The patient is currently (December 2023) on the ninth month of antibiotherapy, and the plan is to complete twelve months. We will perform skin slits at the end of the course of therapy.
The described case illustrates the presentation of lepromatous leprosy with more than six disseminated lepromas, rhinosinusitis, and salmon-colored conjunctivitis. It is important to do an early diagnosis, as prompt treatment is effective and can prevent long-term neurological damage.
Leprosy, or Hansen's disease, is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium leprae and Mycobacterium lepromatosis, involving the skin and peripheral nerves. It predominantly occurs in developing countries, with higher prevalence in India, Brazil, Indonesia, Bangladesh, and Nigeria. With the increase of international traveling, it is a possible diagnosis anywhere in the world. Contrary to popular belief, leprosy is not highly contagious, and the treatment is quite effective.
FundingThis article received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflicts of interestNone declared.
We are grateful to the patient for providing permission to publish the case.