Pituitary abscess is a rare but severe condition consisting of an infectious process with an accumulation of purulent material inside the sella turcica. Its symptoms are usually poorly specific, as are its radiographic characteristics. Diagnosis is often suspected at surgery, and is confirmed by pathological study.
We report the cases of two patients treated at our center for pituitary abscesses. Their clinical and radiographic characteristics are reported, and a literature review is provided.
Case 1This was a 44-year-old woman with persistent galactorrhea after the end of lactation in the setting of hyperprolactinemia which had started 10 years before. She was diagnosed with a non-functioning pituitary macroadenoma, and underwent a complete tumor resection through a transsphenoidal approach at another hospital. The histological diagnosis was pituitary adenoma. After surgery, the patient experienced secondary amenorrhea and diabetes insipidus, and was given chronic treatment with desmopressin.
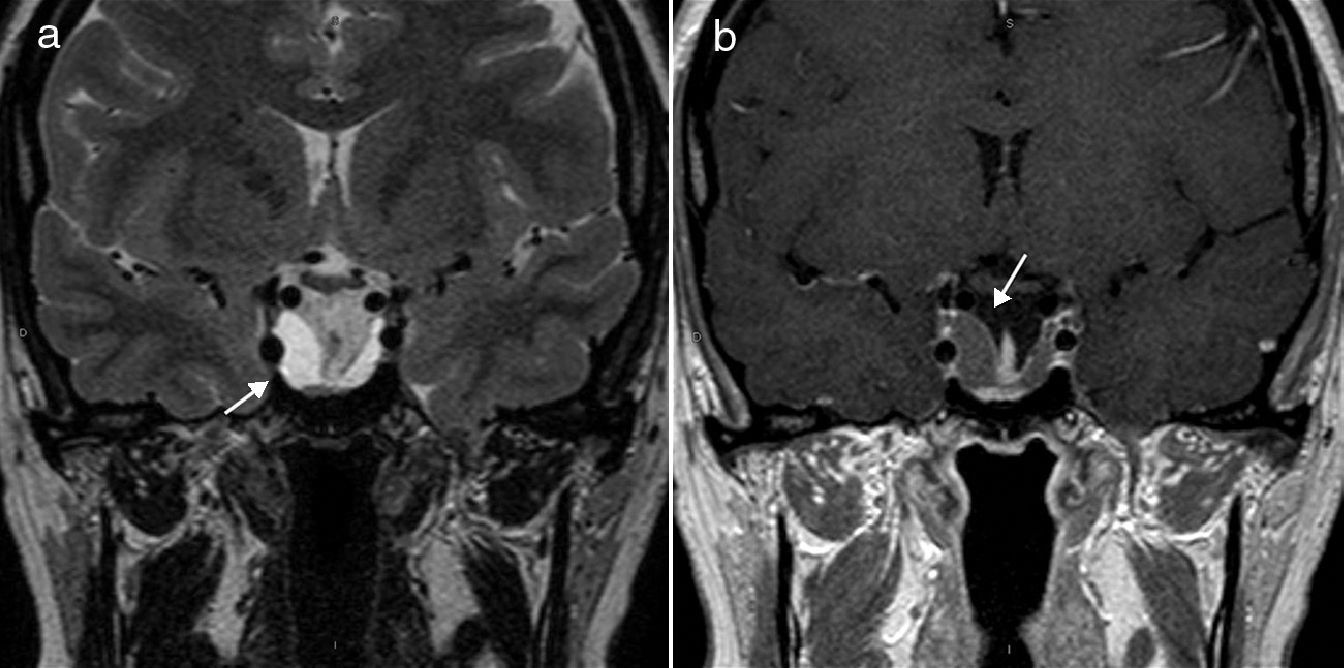
Early magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the pituitary gland showed no tumor remnant or recurrence. Ten years after surgery, a progressive increase was found in intrasellar tissue volume, which was diagnosed as a possible tumor recurrence (Fig. 1). The patient had no subjective symptoms, fever, new hormone deficiencies, or campimetric involvement.
Coronal T2-weighted spin-echo (a) and T1-weighted spin-echo (b) MRI sequences after intravenous administration of gadolinium. (a) A cystic lesion occupying the space of the sella turcica (arrow). (b) The same lesion appears well defined and hypointense in the pituitary gland, surrounded by a thin linear uptake (arrow).
Because of the findings in pituitary MRI, repeat surgery was performed through a transsphenoidal approach, which led to the exit of a creamy, yellowish, pus-like fluid, which filled the sellar space, through the dural opening. The fluid was drained, and sampled for culture and histological study. A pathological study found a pituitary abscess. The cultures were negative.
The patient was given intravenous antibiotic therapy (cefuroxime and vancomycin) for 2 weeks and oral antibiotic therapy (amoxicilin/clavulanate) to complete a total of 6 weeks of treatment. There were no postoperative complications or new pituitary hormone deficiencies. Subsequent postoperative MRI tests showed the usual changes after surgery and a significant decrease in sellar content volume. After 15 months of follow-up, the patient is symptom-free and on desmopressin replacement therapy.
Case 2This was a 53-year-old woman with a history of primary hypothyroidism on replacement therapy. She attended the hospital for severe headache and persistent vomiting with impaired general status, but no fever or other associated clinical signs of infection. The results of laboratory tests at admission included: WBC 17,000mm–3, severe hyponatremia (Na 120mmol/L) with normal volume, low plasma osmolarity, elevated urinary sodium, and hypocortisolism. The patient was diagnosed with syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion (SIADH) and adrenal insufficiency. Hydrocortisone replacement therapy and water restriction were started, and the patient experienced progressive improvement.
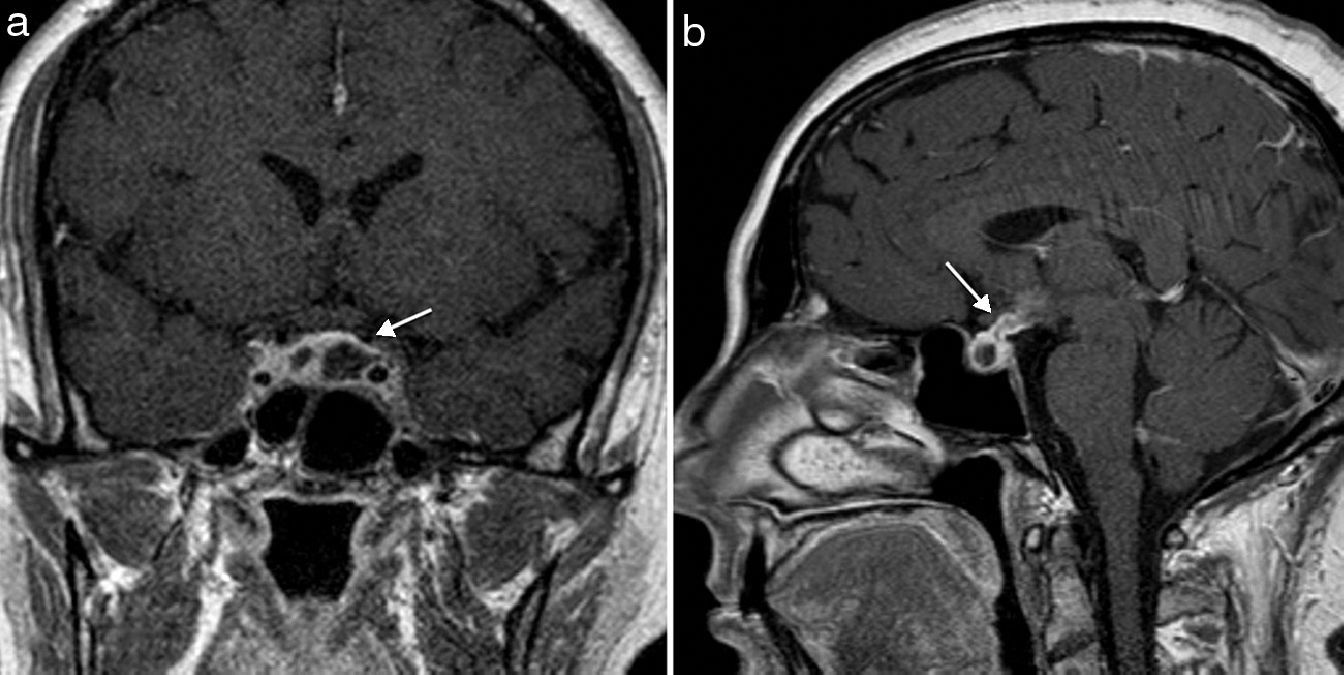
Computed tomography (CT) of the brain was normal, and MRI showed pituitary stalk thickening, mild hypothalamic uptake, and two cystic pituitary lesions with peripheral enhancement after contrast administration (Fig. 2). A possible cystic pituitary adenoma was initially diagnosed, and pituitary stalk and hypothalamic changes led to a differential diagnosis with sarcoidosis and histiocytosis X being considered (which, however, were subsequently ruled out after supplemental tests).
The patient was transferred to our hospital and underwent surgery through a transsphenoidal approach. Upon dural opening, a soft and yellowish tissue of a purulent appearance was found. A pathological study revealed a pituitary abscess. A culture of the sample was negative, despite no prior administration of antibiotic therapy.
After surgery, intravenous antibiotic therapy (ceftriaxone) was administered for 2 weeks. Oral antibiotic therapy (amoxicilin/clavulanate) was subsequently continued until 6 weeks of treatment were completed. No early postoperative complications occurred, and SIADH subsided, although the patient experienced diabetes insipidus which required the start of treatment with desmopressin. Subsequent MRI tests showed the disappearance of the lesion with normalization of pituitary stalk thickness. After 16 months of follow-up, the patient is symptom-free and on desmopressin and hydrocortisone replacement therapy.
Pituitary abscess is an uncommon condition accounting for less than 1% of pituitary lesions.1–5 Clinical and radiographic diagnosis is difficult because the condition has no characteristics that differentiate it from pituitary adenoma. Pituitary abscess may result from hematogenous dissemination or direct extension from an adjacent infectious site such as sphenoidal sinusitis, meningitis, or cavernous sinus thrombosis.1,3,5 A normal pituitary gland is most commonly affected, but abscess may also occur on a pre-existent lesion, such as adenoma, craniopharyngioma, or Rathke cleft cyst.1,2,6
Prior transsphenoidal surgery is the most significant risk factor.1,4 Immunosuppression and radiation are other predisposing factors. However, a significant number of cases occur in patients with no known risk factors.1–3
The clinical manifestations are non-specific, and the clinical course is usually chronic and indolent. Headache is the most common symptom. Other common symptoms include visual field changes (50%) and adenohypophysial hormone deficiencies (30–50%).2,4 Infectious manifestations only occur in one-third of the patients, and meningism in 25%,1–4,7 but when they occur, they support diagnostic suspicion. Diabetes insipidus may be helpful for differential diagnosis because it is an uncommon symptom in pituitary adenomas, while it is common in abscesses.1 There have, however, been very few cases reported of SIADH associated with a pituitary tumor,8 as occurred in case 2, in which SIADH initially occurred and subsided after abscess drainage, leaving diabetes insipidus as a sequela.
MRI is the radiographic diagnostic technique of choice.3 Pituitary abscess usually appears as a cystic sellar lesion with peripheral ring-shaped enhancement after intravenous contrast administration. Pituitary stalk thickening simulating infiltrative disease may also be seen.2 These findings are non-specific and suggest differential diagnosis with cystic adenoma, craniopharyngioma, or Rathke cleft cyst. Diffusion-weighted MRI may also help in differentiating the abscess, by showing a high diffusion signal with a low apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), from necrotic tumors, which show a low diffusion signal with high ADC.1,3
The final diagnosis is usually histological after surgical drainage. Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus is the most commonly isolated microorganism.2 According to the different series, the ratio between Gram stain and positive cultures ranges from 0% to 64%, which may first be explained by the low activity of bacteria in pituitary abscesses,5 and second, by preoperative antibiotic therapy.1,5
The treatment of choice consists of transsphenoidal surgical drainage and antibiotic therapy for 3–6 weeks.1,2,4–7 However, conservative antibiotic therapy may be useful for early pituitary abscesses.1 Visual deficiencies usually improve after treatment, but endocrine deficiencies may persist and require permanent replacement therapy. The recurrence rate is low, but MRI monitoring is advisable in order to detect recurrent abscess.
In conclusion, it can be said that preoperative diagnosis of pituitary abscess is difficult because of its insidious clinical signs and symptoms and poorly specific radiographic findings. Pituitary abscess should be suspected in a patient with a cystic sellar mass with ring-shaped enhancement,1 particularly when associated with clinical signs of infection and/or diabetes insipidus.
Because of the low frequency of pituitary abscess, we would like to see a multicenter study with a larger patient sample being conducted, with the aim of furthering our understanding of this condition.
Please cite this article as: Ramiro Gandia R, González Ibáñez SE, Riesgo Suárez PA, Fajardo Montañana C, Mollà Olmos E. Absceso hipofisario: presentación de 2 casos y revisión de la literatura. Endocrinol Nutr. 2014;61:220–222.