Peribulbar anesthesia is currently considered the regional anesthetic technique of choice for various ophthalmic surgical procedures because of its effectiveness and low incidence of complications. Recent techniques have reduced the number of injections from two to one and are undergoing evaluation.
ObjectivesTo measure the efficacy and safety of the caruncular single injection peribulbar technique for various surgical procedures performed at an ophthalmic clinic in Popayan city, Colombia.
MethodsPatients undergoing various ophthalmic procedures were included. The anesthetic technique used was based on a caruncular single peribulbar injection. The anesthetic agent used contained 0.5% bupivacaine 2.5ml, 2% lidocaine 2.5ml with hyaluronidase 7IU/ml. Patients were evaluated at 10, 15, and 20min. The motor functionality of the four extra ocular muscles and the upper and lower eyelid motor control was measured.
Results137 patients were included; 54% were females and 77% ASA II. 10minutes into the evaluation, 92% of the patients achieved an adequate level of anesthesia to proceed with surgery. 36 patients (26.3%) required a booster dose of an additional peribulbar injection. Twenty-two patients (16%) reported mild pain during the anesthetic procedure. There were four cases of chemosis (3%).
ConclusionsUsing the caruncular single peribulbar injection, most patients achieved an appropriate ocular block for multiple ophthalmic surgical procedures. As time elapses, this block becomes stronger and the incidence of complications is low.
En la actualidad la anestesia peribulbar se considera la técnica de anestesiaregional de elección para diversos procedimientos quirúrgicos oftalmológicos debido a su efectividad y a su baja incidencia de complicaciones. Técnicas recientes reducen las 2 punciones a una sola y se encuentran en proceso de evaluación.
ObjetivosMedir la eficacia y la seguridad de la técnica de punción única peribulbar caruncular para distintos procedimientos quirúrgicos llevados a cabo en una clínica oftalmológica en la ciudad de Popayán (Colombia).
MétodosSe incluyeron pacientes sometidos a diversos procedimientos oftalmológicos. La técnica anestésica empleada consistía en una punción única peribulbar caruncular. El anestésico utilizado fue bupivacaína 0,5% 2,5ml, lidocaína 2% 2,5 ml con hialuronidasa 7UI/ml. Los pacientes fueron evaluados en los minutos 10, 15 y 20. Se midió la funcionalidad motora de los 4 músculos extraoculares y el control motor del párpado superior e inferior.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 137 pacientes. El 54% eran de género femenino y el 77% ASA II. A los 10 min de evaluación el 92% de los pacientes alcanzan anestésico apropiado paracirugía. Treinta y seis pacientes (26,3%) requirieron el uso de refuerzo mediante una nueva punción peribulbar. Veintidós pacientes (16%) refirieron presentar un dolor leve durante el procedimiento anestésico. En 4 casos (3%) se presentó quemosis.
ConclusionesCon el uso de la técnica de punción única caruncular la gran mayoría de los pacientes alcanzan un bloqueo ocular apropiado para diversos procedimientos quirúrgicos oftalmológicos. Este bloqueo se incrementa con el tiempo y la incidencia de complicaciones es baja.
Several ophthalmic surgical procedures may be done using regional anesthesia techniques.1 Peribulbar anesthesia is the technique of choice for most patients undergoing cataract surgery.2 In 1986, Davis and Mandel devised the classic dual peribulbar injection technique as an alternative to the retrobulbar technique.5 The peribulbar approach is associated with lower morbidity as compared to the retrobulbar approach.3 A systematic literature review comparing peribulbar vs. retrobulvar anesthesia reported the following complications, respectively: retrobulbar bleeding (0% vs. 0.3%), conjunctival chemosis (17.4% vs. 7.1%), eyelid hematoma (2.7% vs. 7.3%) and persistent blepharoptosis (1.1% vs. 1.3%). No systemic complications were reported with any of the two anesthetic techniques.4 However, Hustead et al., among other authors, have described other types of “peribulbar anesthetic” techniques using a single injection. One of these approaches is the caruncular anesthesia intended to further reduce the frequency of complications of the dual peribulvar injection, but expecting the same anesthetic efficacy.6,7 The purpose of this trial was to measure the efficacy and safety of the caruncular single beribulbar injection for various surgical procedures performed at an Ophthalmic clinic in Popayan city, Colombia.
MethodologyThe patients were recruited upon submission of their personal consent and the approval of the ethics committee of the Fundación Oftalmologica Vejarano. Using a cohort design, the patients who were candidates for peribulbar anesthesia underwent diverse ophthalmic procedures. The patients were consecutively selected as candidates for regional anesthesia by an expert anesthesiologist, in accordance with the requirements of the surgical procedure.
All patients were evaluated at the admissions department of the Fundación Oftalmológica Vejarano in Popayan, and then they were monitored and administered sedation with midazolam 1mg IV and fentanyl 50mcg IV. The anesthetic technique used was the caruncular single injection described at length and previously evaluated by the authors.1,2 The details of the technique may be obtained from Rizzo et al.7 The volume and concentration of the local anesthetic agent used were standard for all patients: 0.5% bupivacaine 2.5ml, 2% lidocaine 2.5ml with hyaluronidase 7IU/ml.
Following the administration of the anesthetic agent, the patients were evaluated at 10, 15, and 20min before being transferred to the OR. At each point in time, the motor function of the four extraocular muscles and the upper and lower eyelid motor control were measured. Each item was scored based on function: total akinesia: 2, partial akinesia: 1, normal movement: 0. This measurement scale has been used previously by Ghali and Hafez.8
The trial's primary outcome was the percentage of patients with a score ≥8 at each point in time evaluated. Furthermore, general information was collected about the study population and any side effects or adverse events resulting from the procedure. Preliminary studies have documented 78% effective block at 5min of the evaluation.7 Based on a variability of 10% the sample size was estimated at 66 patients with a 95% confidence interval.
The categorical variables are presented in a frequency table in percentages. The continuous variables are summarized as central tendency and scattered statistics (mean±standard deviation or median [interquartile range]) in accordance with the distribution characteristics. The outcomes are described as frequencies and proportions. For the proportion of patients with block >8 at 10, 15 and 20min, a 95% confidence interval was estimated (95% CI). All the analyses were done using STATA 12.0.9
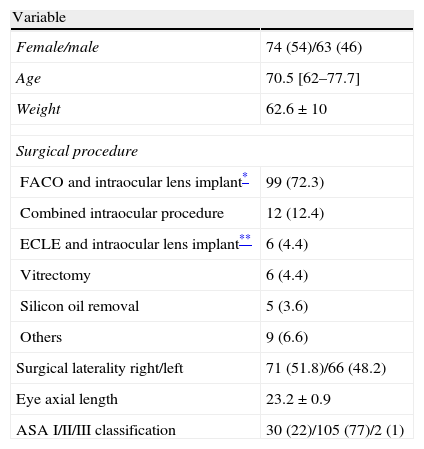
Results137 patients participated in the trial, most of them females (54%) and ASA II (77%). Table 1 shows the demographic characteristics of the patients and the surgical procedures performed.
Patient characteristics and surgical procedures n=137.
| Variable | |
| Female/male | 74 (54)/63 (46) |
| Age | 70.5 [62–77.7] |
| Weight | 62.6±10 |
| Surgical procedure | |
| FACO and intraocular lens implant* | 99 (72.3) |
| Combined intraocular procedure | 12 (12.4) |
| ECLE and intraocular lens implant** | 6 (4.4) |
| Vitrectomy | 6 (4.4) |
| Silicon oil removal | 5 (3.6) |
| Others | 9 (6.6) |
| Surgical laterality right/left | 71 (51.8)/66 (48.2) |
| Eye axial length | 23.2±0.9 |
| ASA I/II/III classification | 30 (22)/105 (77)/2 (1) |
36 (26.3%) of the total number of patients required a booster dose with an additional peribulbar injection. The average booster volume of the peribulbar injection was 4ml±1.1.
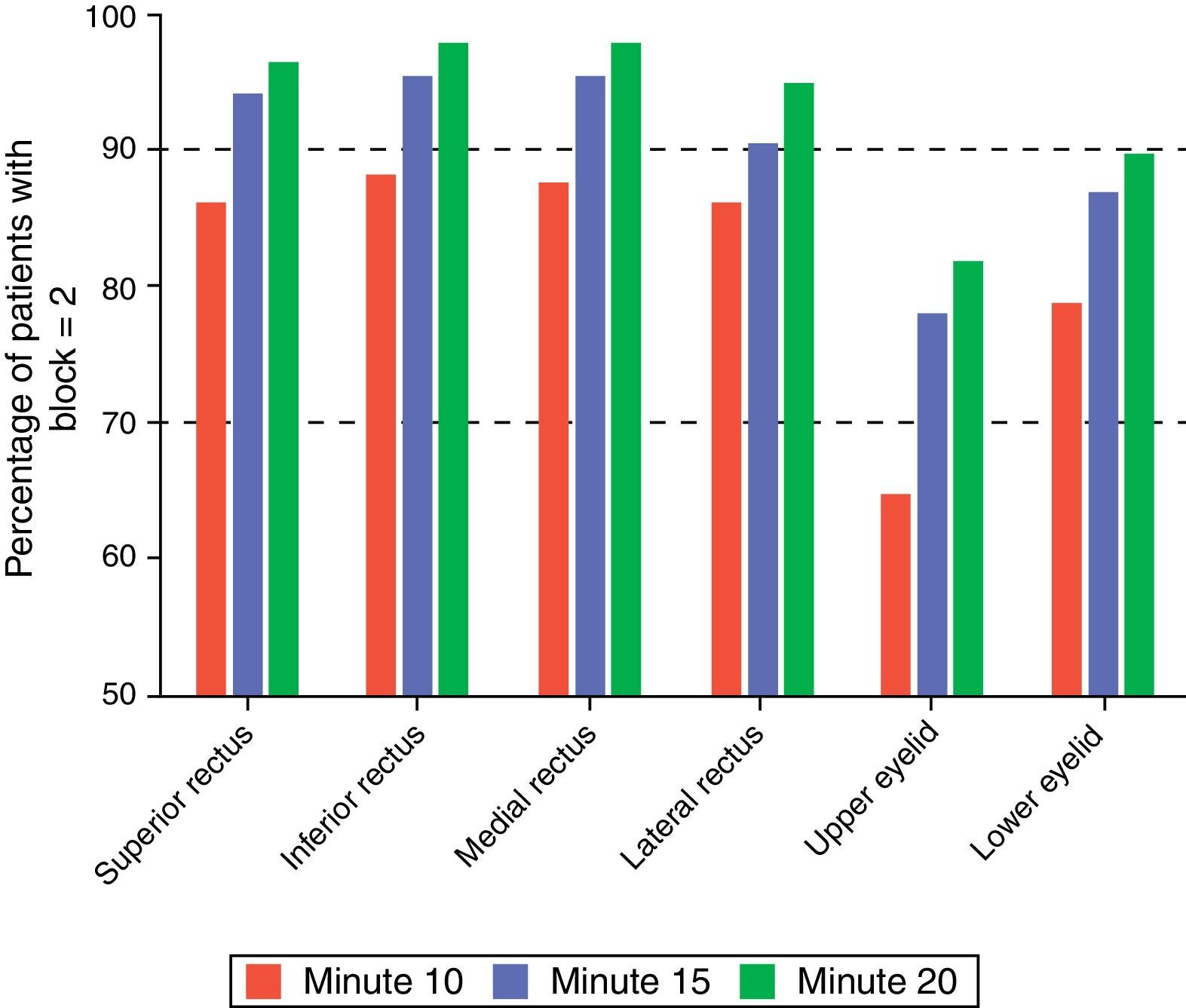
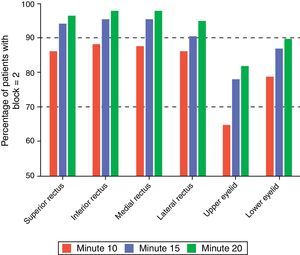
The percentage of patients achieving complete block increased as time went by, following the administration of the anesthetic agent. This finding was relevant for the six muscles evaluated. The functionality of the upper and lower eyelids resulted in lower block levels (Fig. 1). Twenty minutes into the evaluation, 97% of the patients attained a level 8 in the motor evaluation scale that is considered effective for surgery (Table 2).
Total maximum levels achieved with the block three points in time evaluated (n=137).
| Total level of block achieved | 10min | 15min | 20min |
| Greater than or equal to 6 (50%) | 133 (97.1) | 135 (98.5) | 135 (98.5) |
| Greater than or equal to 8 (effective for surgery) | 126 (91.9)* | 131 (95.6)** | 133 (97)*** |
| Greater than or equal to 10 | 113 (82.4) | 126 (91.9) | 130 (94.8) |
| Block of 12 (complete) | 78 (56.9) | 99 (72.3) | 108 (78.8) |
Twenty-two patients (61%) reported mild pain during the anesthetic procedure. There were four cases of chemosis (3%) and one case of conjunctival edema (0.7%).
DiscussionThe results of this trial provide additional evidence of the effectiveness of the caruncular single peribulbar injection technique. Notwithstanding the fact that the muscles experiencing the least blockade are those controlling the eyelid function, this technique lends itself to various ophthalmic procedures with good conditions for both the surgeon and the patient. Measurements of the effectiveness of the block continued for 20min, since there was enough time for follow-up. 92% of the patients achieved an effective level for surgery 10min after the block. Using the same anesthetic technique in 857 patients, 7min later 100% of the patients had proper block for surgery.7 Using this technique, other authors have documented effective block after 10min.8
It is worth mentioning however that akinesis and analgesia of the eyeball were obtained with a small volume of anesthetic agent (5ml) – in those patients that did not require a booster injection. Other series have reported the use of small volumes of anesthetic agent (maximum 6.5ml) for the initial injection.7
It is worth highlighting that 26% of the patients in this trial required additional anesthetic agent, so that the total volume increased. This fact could be due to our little technical experience with this approach; however, its clinical effectiveness was unaffected and the incidence of complications was consistent with other publications. The injection site of the caruncular technique is relatively avascular – theoretically reducing the risk of developing hematomas.7 There were no cases of hematoma of the orbit in this trial. Because the needle insertion is limited to the anterior orbit, injuries to the ophthalmic artery, the optic nerve or the retina are rare.7 Several authors report an incidence of hematoma of 0.6%.10 There were four cases of chemosis (3%) and one case of conjunctival edema with no surgical limitations or discomfort. Other trials have shown incidences of chemosis with single injection, ranging from 0.5% to 16%.2,7,8
In conclusion, using the caruncular single injection technique most patients achieve proper ocular block for various ophthalmic surgical procedures. This block is enhanced as time progresses and the incidence of complications is low.
FundingNone.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
We would like to acknowledge the health care and administrative staff of the Fundación Oftalmológica Vejarano, Popayán, Colombia and the residents of the Anesthesiology program – University of El Cauca, Popayan, Colombia, for their collaboration in the course of this project. In particular, our appreciation to Mr. Andrés Manquillo, medical student, for his active participation in the development of databases.
Please cite this article as: Calvache JA, López H, Castro-Delgado OE. Experiencia local con el uso de punción única peribulbar caruncular para anestesia oftálmica. Rev Colomb Anestesiol. 2014;42:16–19.