A reflection based on the article “The blind spot of obstetric anesthesia: intraoperative fetal monitoring” is made, with examples of non invasive monitoring developed in other fields, and a discussion about the expectation of a new device that could prove to be useful for intra-surgical fetal monitoring.
MethodsReading the above-mentioned article, manual search of information about new non-invasive monitoring devices currently being developed that are applicable to diverse situations and patients, and may open up new avenues for intraoperative fetal monitoring in the future.
ResultsDescription of examples of non-invasive monitoring tools that have been developed in the last few years as a result of the need to obtain reliable and real-time information about target organ behavior during the perioperative period.
ConclusionA practical and reliable intraoperative fetal monitoring device is not yet available for obstetric patients in the OR. We suggest the implementation of a novel device similar to those available for the detection of arrhythmias, as a potential tool for non-invasive intraoperative fetal monitoring.
A partir del artículo «El punto ciego de la anestesia obstétrica: monitoría fetal intraquirúrgica» se realiza una reflexión con ejemplos de monitoría no invasiva desarrollada en otros campos y se plantea la expectativa de un nuevo dispositivo que pueda ser de utilidad para monitoría fetal intraquirúrgica.
MétodosLectura del artículo en mención, búsqueda manual de información respecto a nuevos dispositivos de monitoría no invasiva en desarrollo, aplicables a diversos escenarios y pacientes, que ofrezcan perspectivas a futuro en la monitoría fetal intraquirúrgica.
ResultadosSe describen ejemplos de herramientas de monitoría no invasiva que se han des-arrollado en los últimos años y que surgen de la necesidad de obtener información fidedigna y en tiempo real del comportamiento de órganos blanco durante el periodo perioperatorio.
ConclusiónAún no existe un dispositivo de monitoría fetal intraoperatoria que sea práctico y confiable en el quirófano para la paciente obstétrica. Se propone la implementación de un dispositivo novedoso como el que ya existe para la detección de arritmias como herramienta posible en el campo de la monitoría fetal intraquirúrgica no invasiva.
Gestation represents an incredible process of change and adaptation for women during the development of the fetus inside the womb.1 An increased metabolic demand leads to physiological alterations during normal gestation, in order to supply the proper amount of oxygen and nutrients to the fetus through the uterine–placental circulation.2
The major cardiovascular and hemodynamic changes arising from the first trimester become increasingly evident until the end of pregnancy: heart rate, systolic volume and contractility (and consequently cardiac output), in addition to a decreased systemic and pulmonary vascular resistance.3
These hemodynamic alterations are mainly in response to an increased uterine blood flow from 50 to 100ml/min prior to gestation up to 800ml/min at the end of pregnancy, due to the progressive uterine vasodilatation and the increased requirements of a growing fetus that may take up 12–15% of the cardiac output. Any situation affecting the supply/demand equilibrium maintained by the uterine–placental flow could be potentially threatening and cause injury.2
The fetus is a vital organ during the gestation period and plays a key role, as Dr. Alejandro Bautista puts it: “it is a dynamic force orchestrating its own destiny”.4
The article “The blind spot of obstetric anesthesia: intraoperative fetal monitoring” highlights the importance of developing and implementing trans-operative monitoring tools to follow the fetal status throughout the various interventions the mother may be subject to in the course of abdominal delivery. The characteristics of such monitor should be non-invasive, practical, and easy to adapt to the patient.5
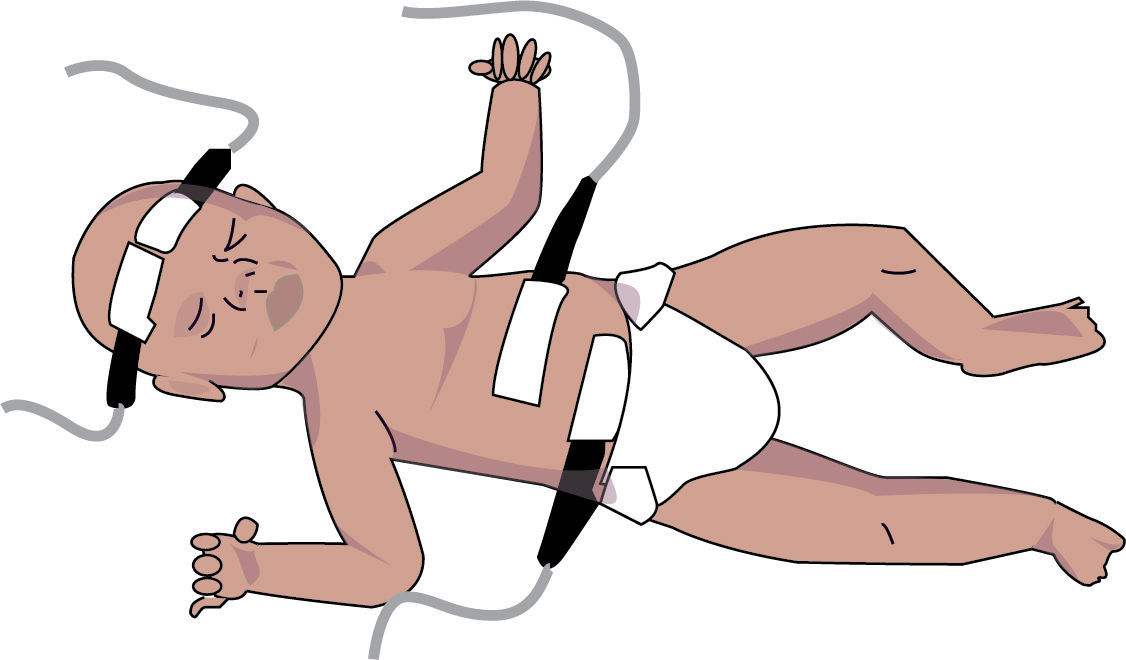
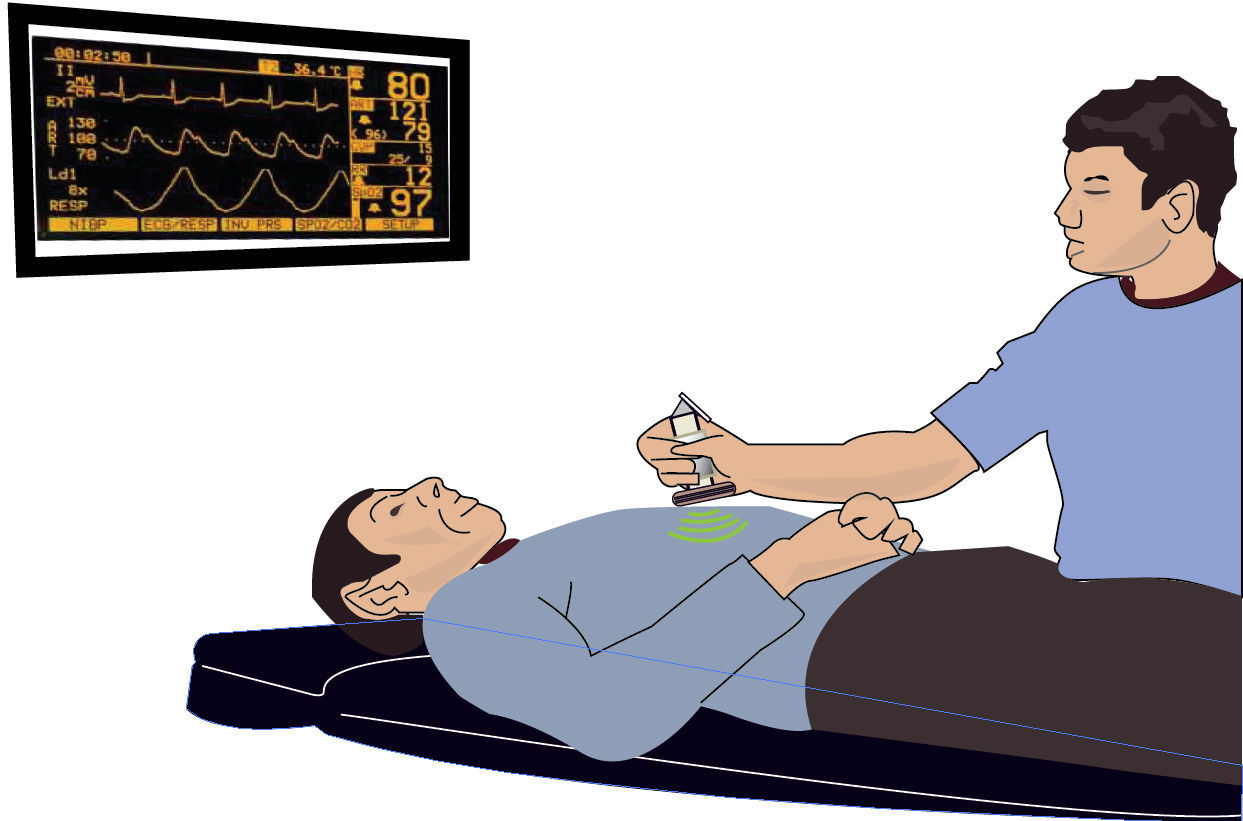
The interest in non-invasive devices for intraoperative monitoring has encouraged the development of tools in various areas to respond to the need for reliable and real-time information to identify any alterations and intervene accordingly. There are several examples of non-invasive devices being implemented for regional monitoring of oxygen saturation (RO2S) using spectrophotometry of the cranial (see Fig. 1).
These devices provide information about the oxygen delivery/output balance of the most sensitive organ to oxygen deprivation – the brain – via 4 channels located on the surface (frontally) to monitor the cerebral and systemic oxygen saturation continuously and in real time. This becomes a valid alternative during neurosurgical and cardiovascular procedures.6,7
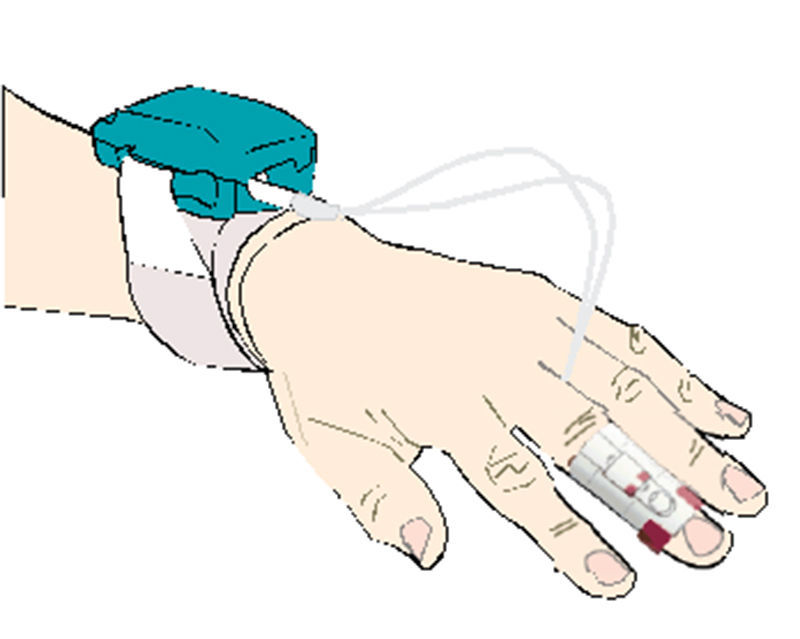
More recently, other non-invasive continuous monitoring devices have been developed for measuring finger blood pressure (see Fig. 2).
The physiological model reconstruction represents an alternative to non-invasive blood pressure measurement using oscillometry; there are however some limitations in patients with serious perfusion involvement. This digital method was tested and the results were published last month, with value readings similar to the intra-arterial invasive technique.8,9
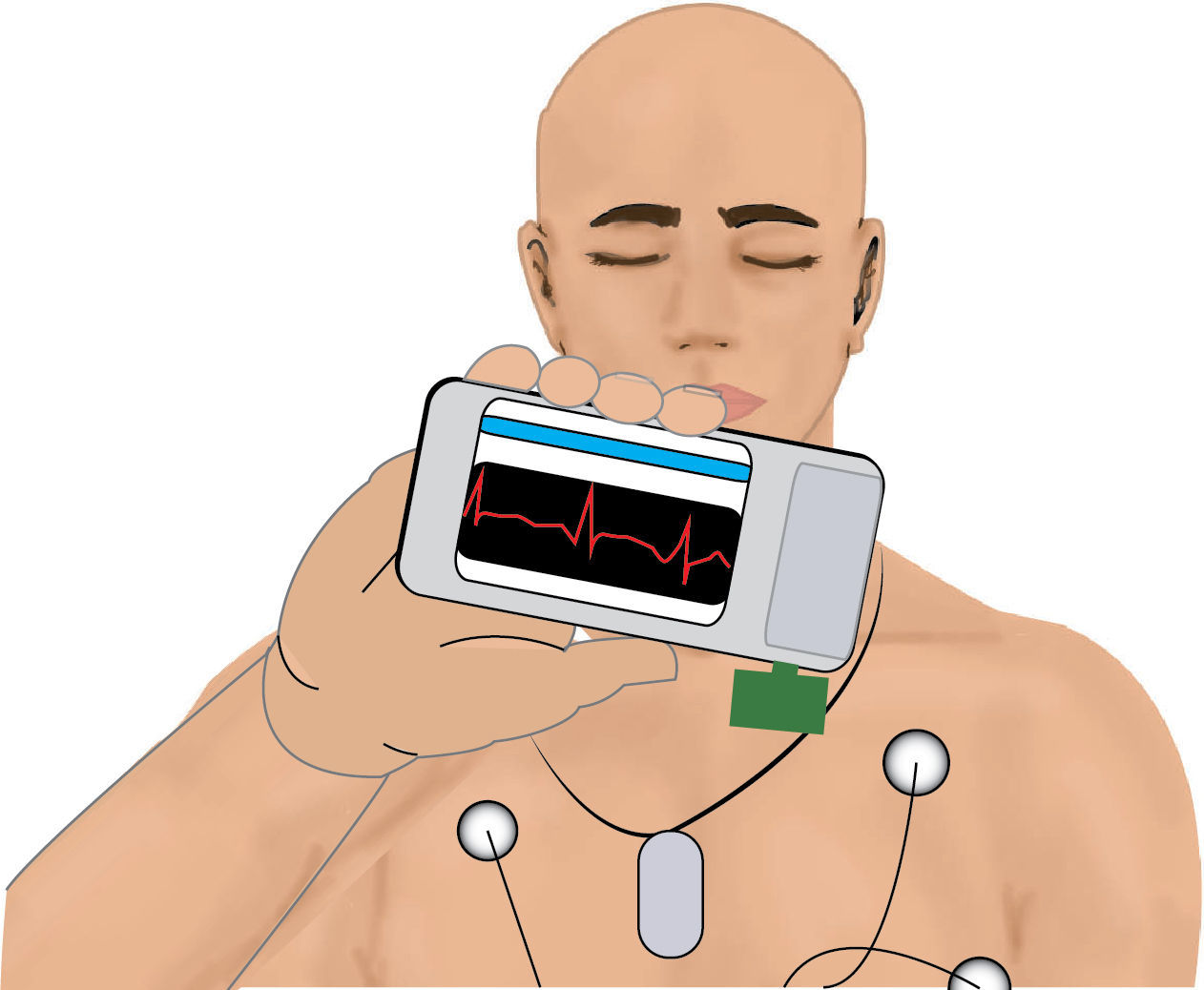
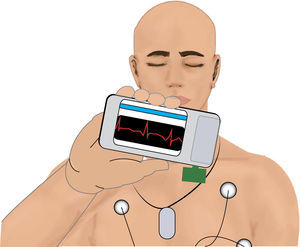
In our search for a non-invasive monitoring method or tool applicable to intraoperative fetal monitoring, we came across a publication dated October 2011 that describes the development and initial implementation in a test sample of a WBSN device (“wireless body sensor network”) publicized by a team from the Polytechnic University of Lausanne, Switzerland, led by Dr. David Atienza. The device is a practical portable unit that collects the information from the electrocardiography tracing in real time and identifies abnormalities. The information from the ECG tracing is sent via GPS, 3G or Bluetooth to a mobile communications device – i.e., any mobile phone available in the market. Although the device has not yet been produced and commercialized, it may become an excellent tool for distant cardiac monitoring (see Fig. 3).10
Although the WBSN was designed for a scenario other than intraoperative fetal monitoring, it certainly generates some expectation in terms of a potential application in an intraoperative situation such as fetal monitoring. Rocket science was considered to be science fiction, but “Star Trek” scenes depicting the use of non-invasive monitors to collect physiological data from the body have become a reality (see Fig. 4).
ConclusionIt would not be long before technology will make this type of devices available to the anesthesiologist as an additional, safer and practical tool for improved safety of the obstetric patient and her baby.
FundingThe authors’ own resources.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Our acknowledgement to Jorge Humberto Reyes for the illustrations.
Please cite this article as: Navarro Vargas JR, Romero Fuentes SM. Monitoria fetal intraquirúrgica: el feto como órgano blanco. Rev Colomb Anestesiol. 2014;42:117–119.