Catecholamine-secreting tumors are rare neoplasms with an annual incidence of 1–2 cases/100,000 inhabitants per year. Only 10% are malignant, with no histological or biochemical differences compared to benign presentations, except for local invasion of surrounding tissues and organs or distant metastasis.1–4
Patients with pheochromocytoma experience persistent disease in 3%–13% and recurrence in 6%–23%, both local and metastatic; the 5-year cumulative risk of recurrence is 5%, and the lifetime risk is 20%–25%. The greatest risk is associated with hereditary syndromes, primary tumor >5 cm, and extra-adrenal location (paragangliomas).3,5
Some authors have suggested that the mechanism responsible for peritoneal recurrence is the rupture of the capsule during tumor resection or leakage of tumor cells during the handling of friable, hemorrhagic tumors.2,3,5,6 It is a very rare form of recurrence, defined by some aspheochromocytomatosisin reference to the new, multiple, often small pheochromocytomas that grow in, around the surgical resection site of a previous adrenalectomy.5
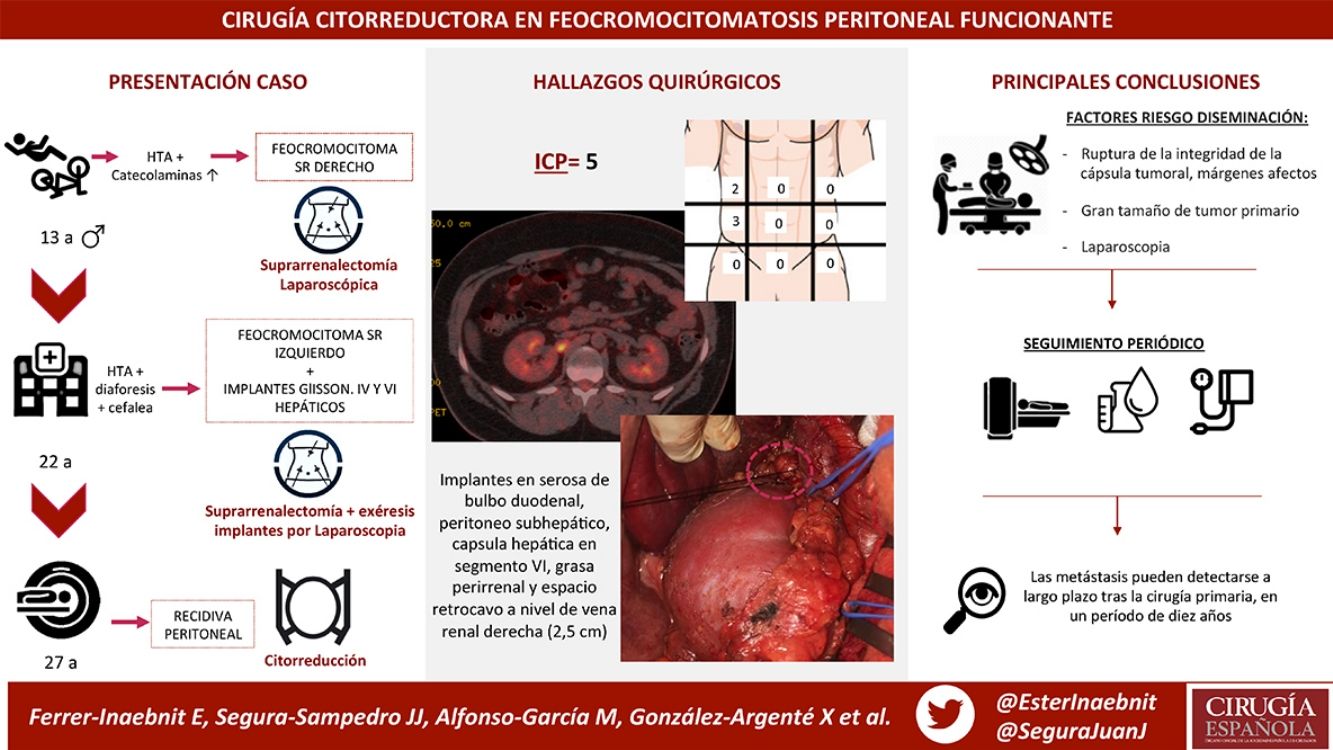
We present the case of a male patient who was diagnosed with right adrenal pheochromocytoma at the age of 13. Laparoscopic right adrenalectomy revealed a 6-cm gland and a partially encapsulated 4 × 3 cm tumor with non-assessable margins.
After periodic check-ups, he presented hypertension, diaphoresis and headache 9 years later (at the age of 22), at which time he was diagnosed with left pheochromocytoma and peritoneal capsular implants in Glisson’s capsule and liver segments IV and VI. Left adrenalectomy was performed, and the implants were removed laparoscopically. The adrenal gland measured 6.5 × 3 × 2 cm. Two nodules were observed, measuring 1.8 and 0.8 cm with tumor capsule integrity, although surgical margin involvement was also found. Two peritoneal implants were also discovered: one measuring 1 cm at the beginning of the round ligament, and one subcapsular hepatic implant measuring 1.5 cm in segment IV.
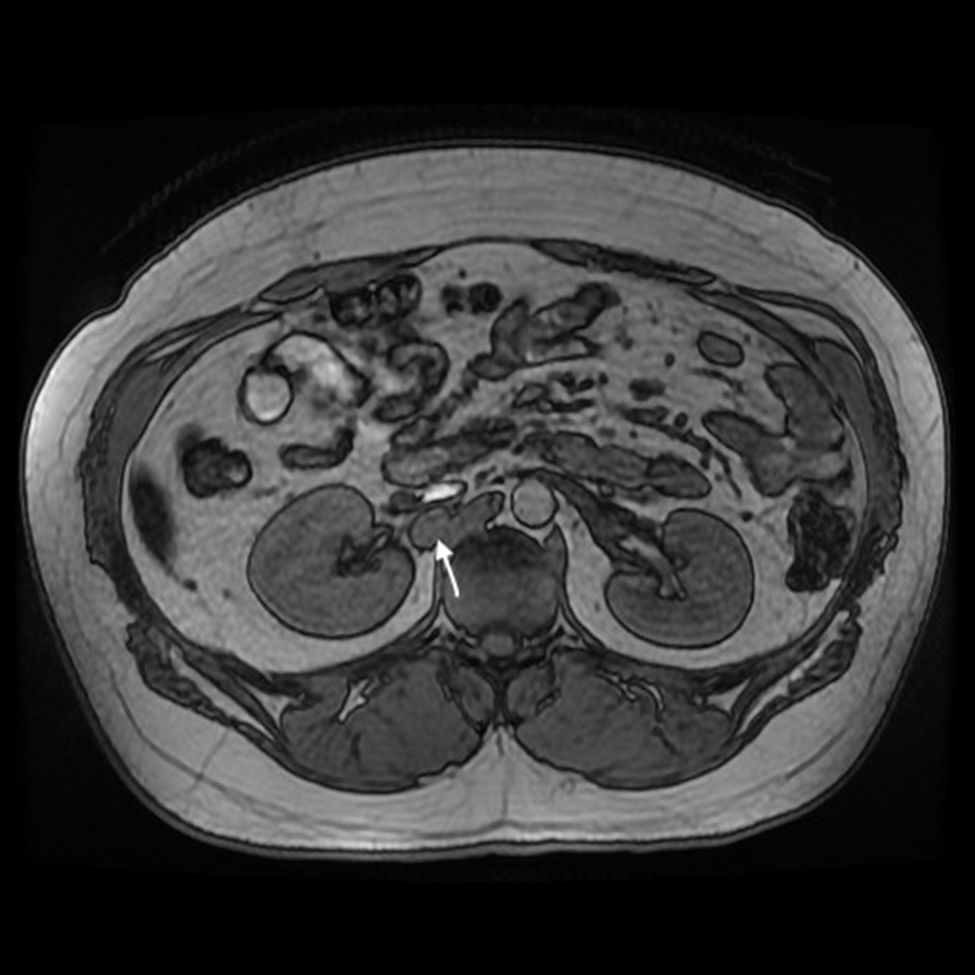
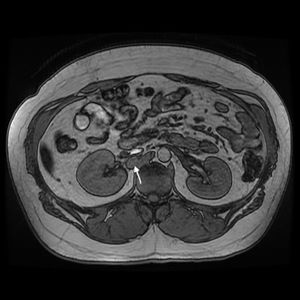
Currently, at the age of 27, the patient is obese and has adrenal insufficiency, which is being treated with replacement therapy. In periodic follow-up studies, increased metanephrine and chromogranin levels were detected in blood. The study was extended to include radiological tests (CT and magnetic resonance imaging) (Fig. 1), which diagnosed a new peritoneal and retroperitoneal recurrence that did not uptake 131I MIBG, with a negative octreotide scan.
After discussion in a multidisciplinary peritoneal tumor committee, premedication was carried out with nicardipine, and cytoreductive surgery was considered.
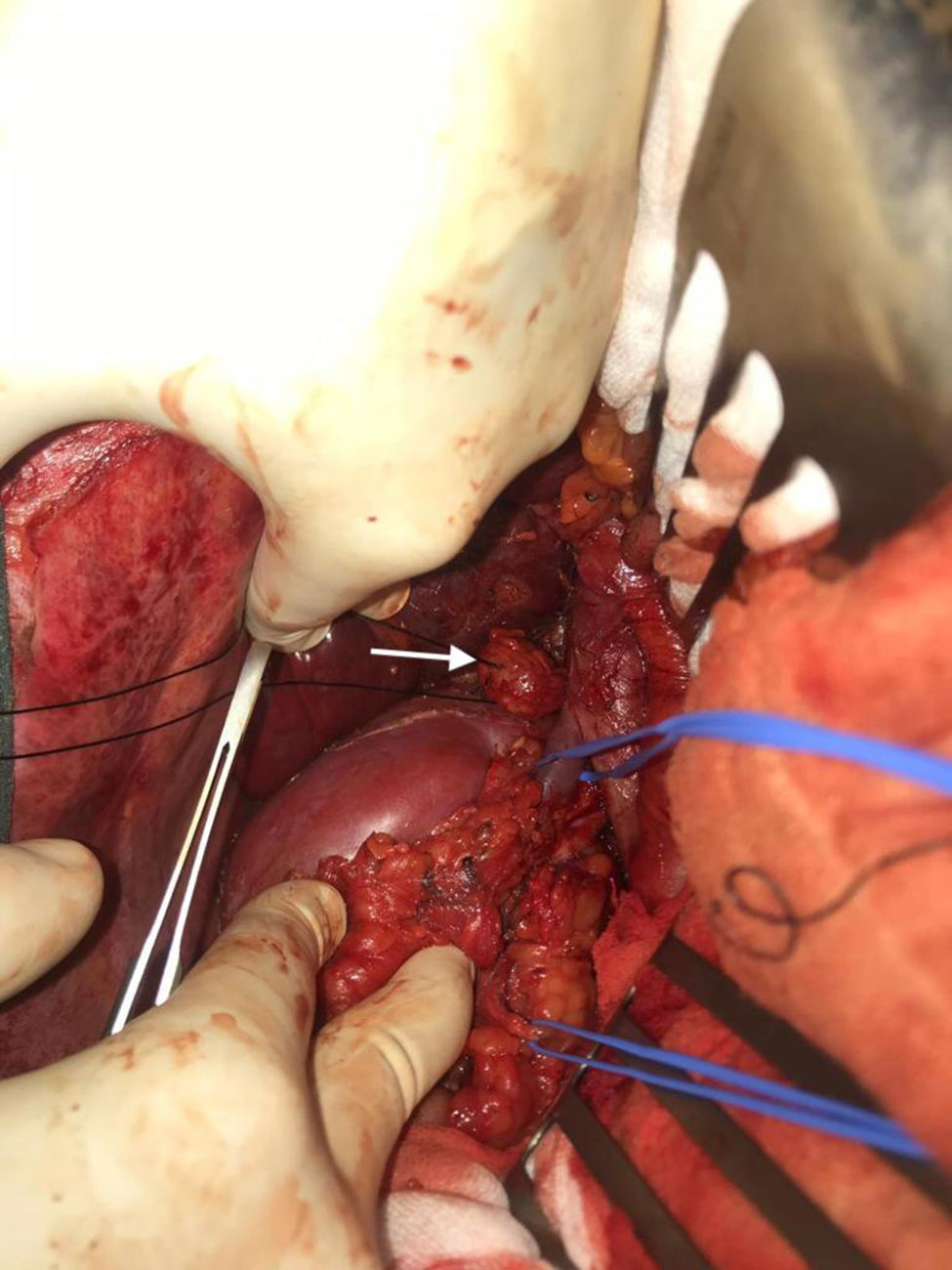
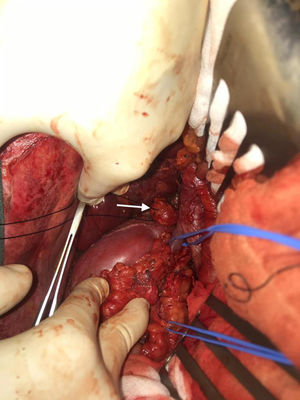
We performed midline laparotomy and found several millimetric implants (<6 mm) in the serosa of the duodenal bulb, subhepatic peritoneum, hepatic surface of segment VI, and Gerota’s fascia, as well as another larger implant (>2.5 cm) in the retrocaval space at the right renal vein (whose intraoperative mobilization caused a rise in blood pressure, monitored by Vigileo® [Edwards Lifescience, Irvine, CA, USA] and controlled by goal-directed therapy7) (Fig. 2). All of the implants were removed. The largest required mobilization of the duodenum with exposure of the vena cava, subsequent opening of Gerota’s capsule, mobilization of the right kidney, and dissection of the posterior side of the cava. An ICP of 5 was calculated, located in the right hypochondrium and flank.
The postoperative period was adequate, with no complications and good patient progress. The patient was discharged on the 5th postoperative day.
In the sample sent for pathology analysis, the surgical specimens were confirmed as neuroendocrine tumors compatible with pheochromocytoma (positive chromogranin and synaptophysin, Ki-67 was 5%).
One year after surgery, the patient continues to be disease-free.
Due to the lack of defined characteristics of malignancy for pheochromocytoma, it is difficult to determine the malignant potential of these tumors.1,4 The only proven malignant characteristics are the presence of distant metastases, previously diagnosed multiple endocrine syndromes or genetic disorders, in many cases of familial syndromes.2,4,5
Metastases can be detected in the long term after primary surgery, sometimes up to a 10-year period (mean: 60 months).5 The onset of characteristic symptoms of pheochromocytoma after surgical treatment of an adrenal tumor suggests the existence of distant metastases with hormonal activity, which requires a thorough endocrine evaluation as well as the exclusion of genetic predisposition by a mutational analysis for susceptibility genes and radiological tests (CT or 123I-MIBG scintigraphy).4
In our case, the recurrent symptoms began 9 years after the first operation, requiring a second procedure and periodic follow-up tests, which detected new peritoneal implants 5 years later.
Similar cases have been described in the literature, with a series of common factors:
- -
Disease-free interval for years (between 1 and 10 yrs) before recurrence2–4
- -
Recurrence in the peritoneum or retroperitoneum3
- -
Compromised tumor capsule integrity or manipulation of friable tumors in the initial surgery2,3,5,6
- -
Large size of primary tumor (median of 6 cm in diameter)2,3,5,6
In pheochromocytomas with a greater risk of rupture and friability (especially in large tumors), the suitability of the laparoscopic approach must be carefully considered because of the high risk of recurrence in cases of capsular rupture.2,3,6 In the current case, the first recurrence with subcapsular hepatic implants should have advised against a second laparoscopic approach. Tumor cell seeding secondary to loss of capsular integrity and affected margins is a determining factor in peritoneal pheochromocytomatosis.6
Preoperative injection of 123I-MIBG has been described for radioisotope-guided surgery in order to locate small tumor implants that have not been identified by radiological studies.2 Cytoreductive surgery provides complete excision of the disease, which is the only definitive therapy at the moment.8,9
Peritoneal tumor seeding during the surgical treatment of pheochromocytoma can cause functional pheochromocytomatosis even years after the original surgery, so follow-up should be continued for years due to the risk of chromaffin cell dissemination.2–6 The laparoscopic approach, loss of capsular integrity, and margin involvement contribute to this condition.3,5,6
When faced with a new compatible clinical condition, radiological follow-up studies, including CT scan and 123I-MIBG scintigraphy, are necessary for early detection and to prevent long-term damage caused by high levels of circulating catecholamines.1,2,4 Peritoneal cytoreductive surgery offers a radical surgical option for these patients.9
Conflict of interestsThe authors have no conflict of interests to declare and have received no funding for this publication.
Please cite this article as: Ferrer-Inaebnit E, Segura-Sampedro JJ, Alfonso-García M, González-Argente X, Morales-Soriano R. Cirugía citorreductora en feocromocitomatosis peritoneal funcionante. Cir Esp. 2021;99:73–76.