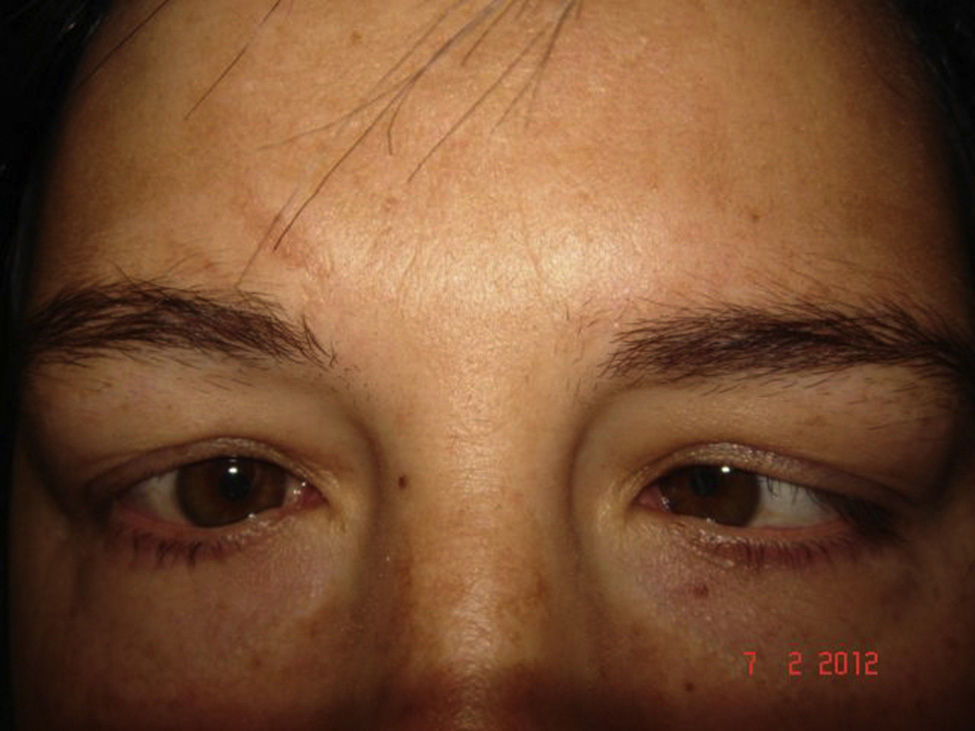
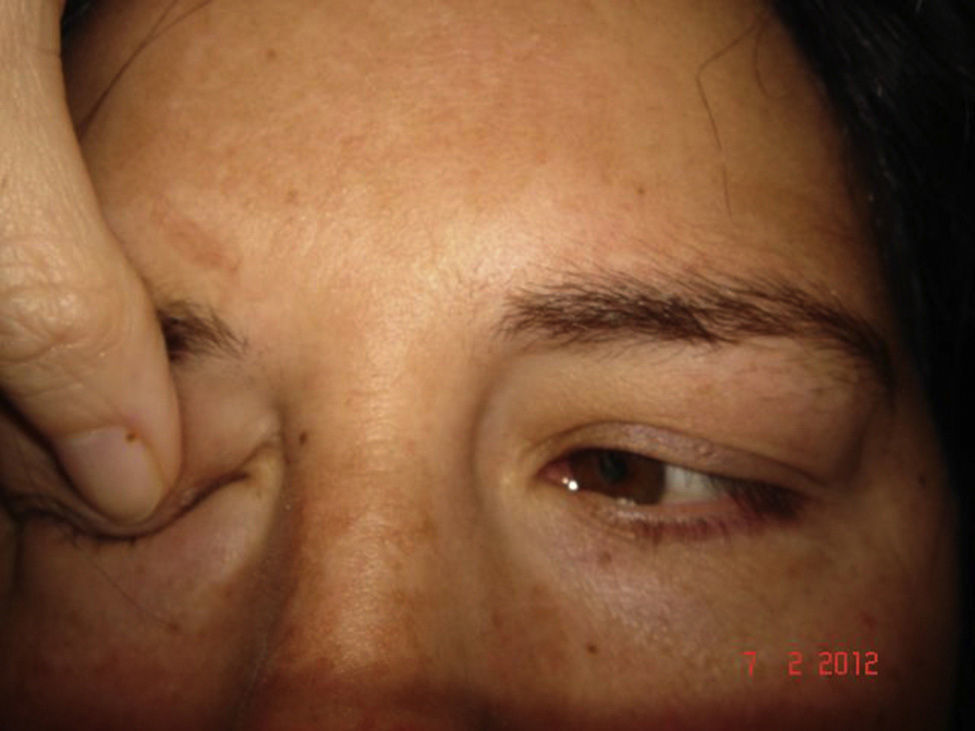
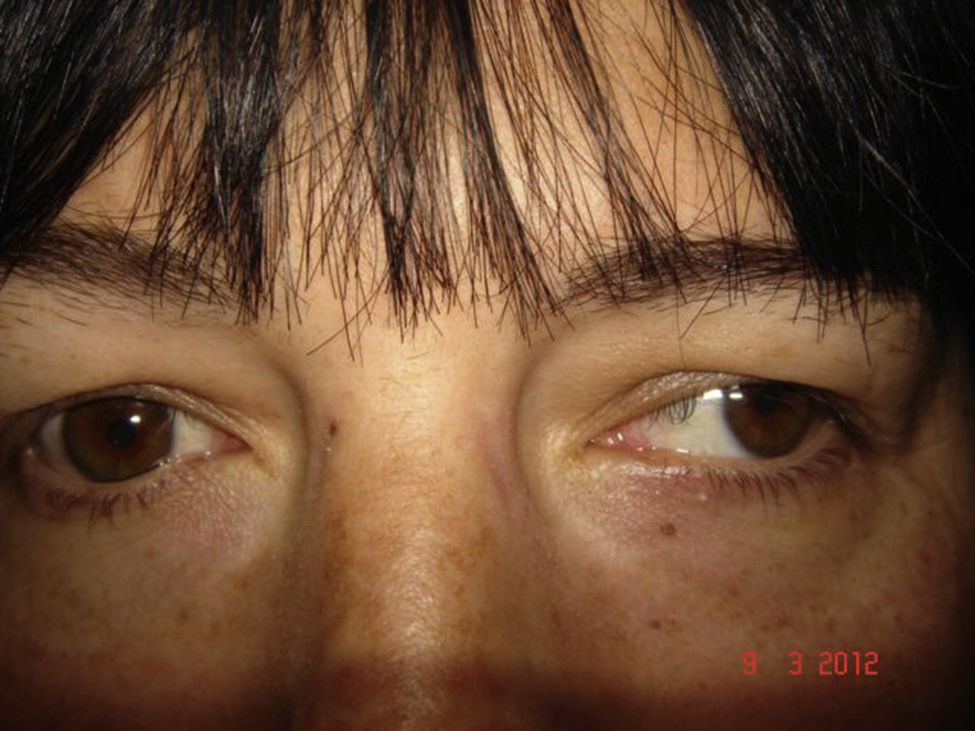
A 38-year-old female with diplopia and esotropia, with limitation of ocular abduction in both eyes, with full abduction after doll's head rotation also being observed. She was diagnosed with spasm of the near reflex. Treatment with injections of botulinum toxin in both medial rectus has temporally resolved the convergence spasm.
DiscussionNear reflex spasm is characterized as miosis, pseudomyopia, and convergent strabismus that lead to diplopia, blurred vision, headache, and variable, progressive, and intermittent esotropia. As the spasm worsens there will be limited ocular versions and ductions simulating a sixth nerve palsy. Botulinum toxin may be effective in some cases.
Mujer de 38 años con diplopía y endotropía. Limitación total de la abducción en AO al explorar las versiones, que se normalizan al explorar el reflejo de los ojos de muñeca. Es diagnosticada de espasmo del reflejo de cerca (ERC) y tratada con inyecciones repetidas de Botox en rectos medios, resolviéndose temporalmente el espasmo.
DiscusiónEl ERC se caracteriza por miosis, seudomiopía y convergencia que producen diplopía, visión borrosa, cefalea y endotropía variable, progresiva e intermitente. Se puede confundir con una paresia bilateral del vi nervio. El tratamiento con inyecciones repetidas de bótox puede ser efectivo en algunos casos.