The case is presented of a 32 year-old male with no medical history of interest who suffered a traffic accident with mild traumatic brain injury. He had a left supraciliary incised and contused wound that extended to the left upper eyelid, with no loss of vision.
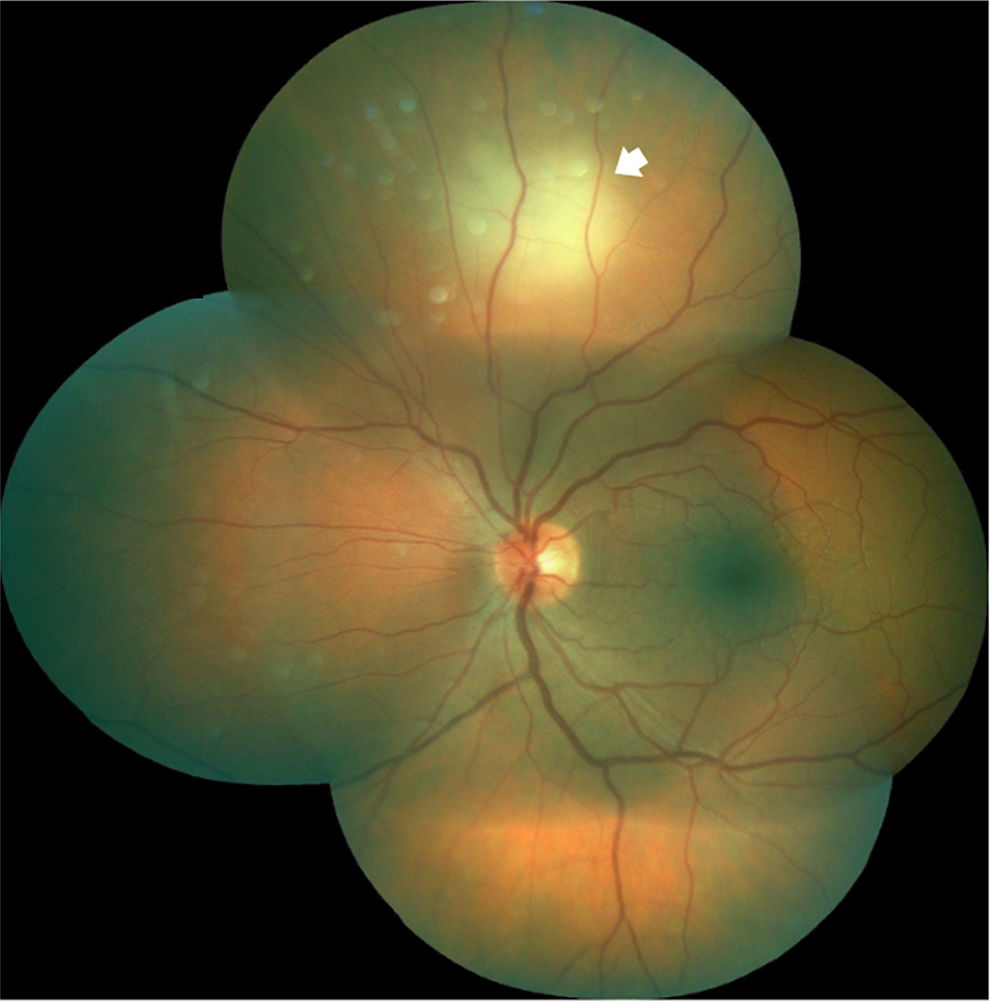
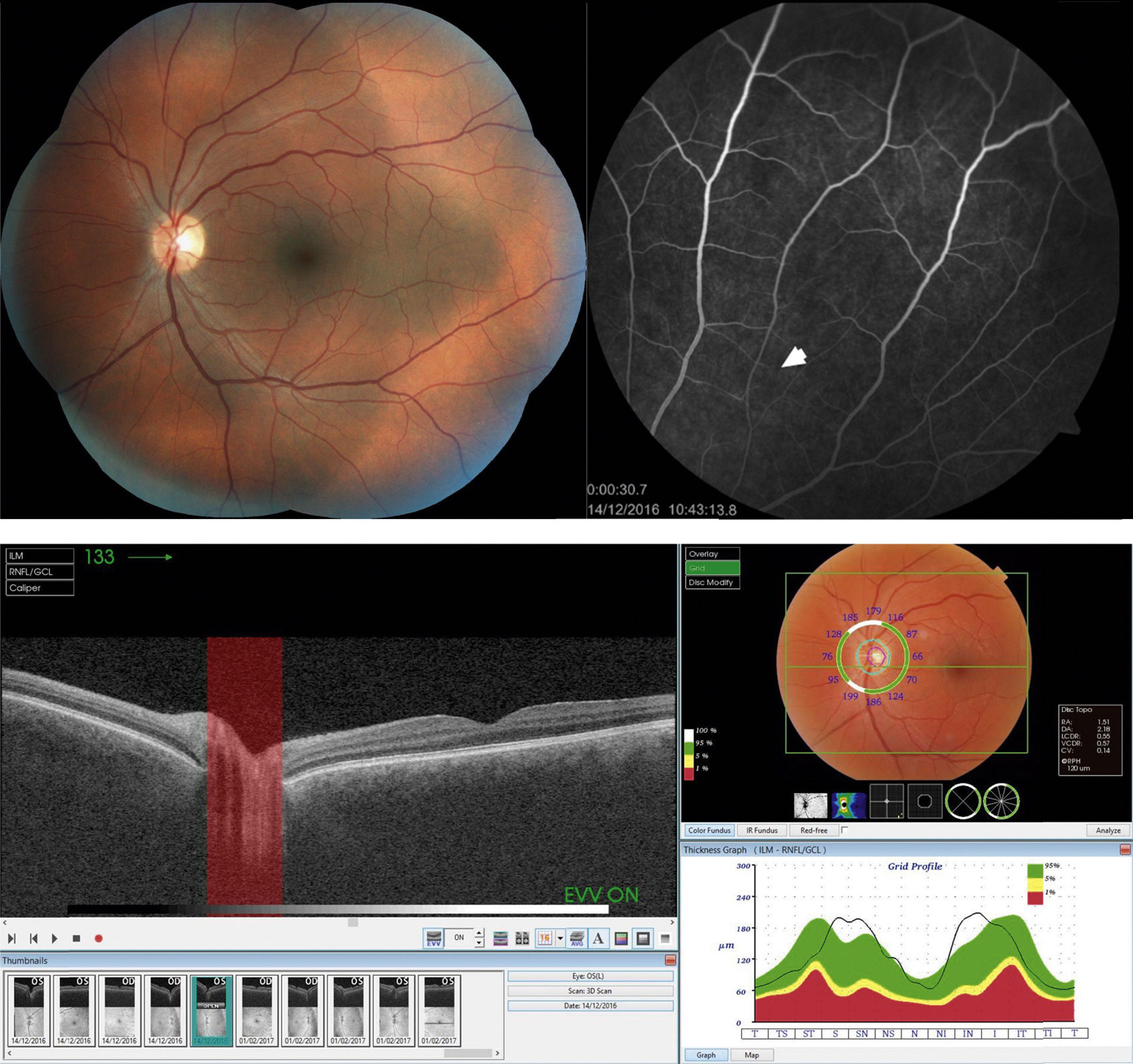
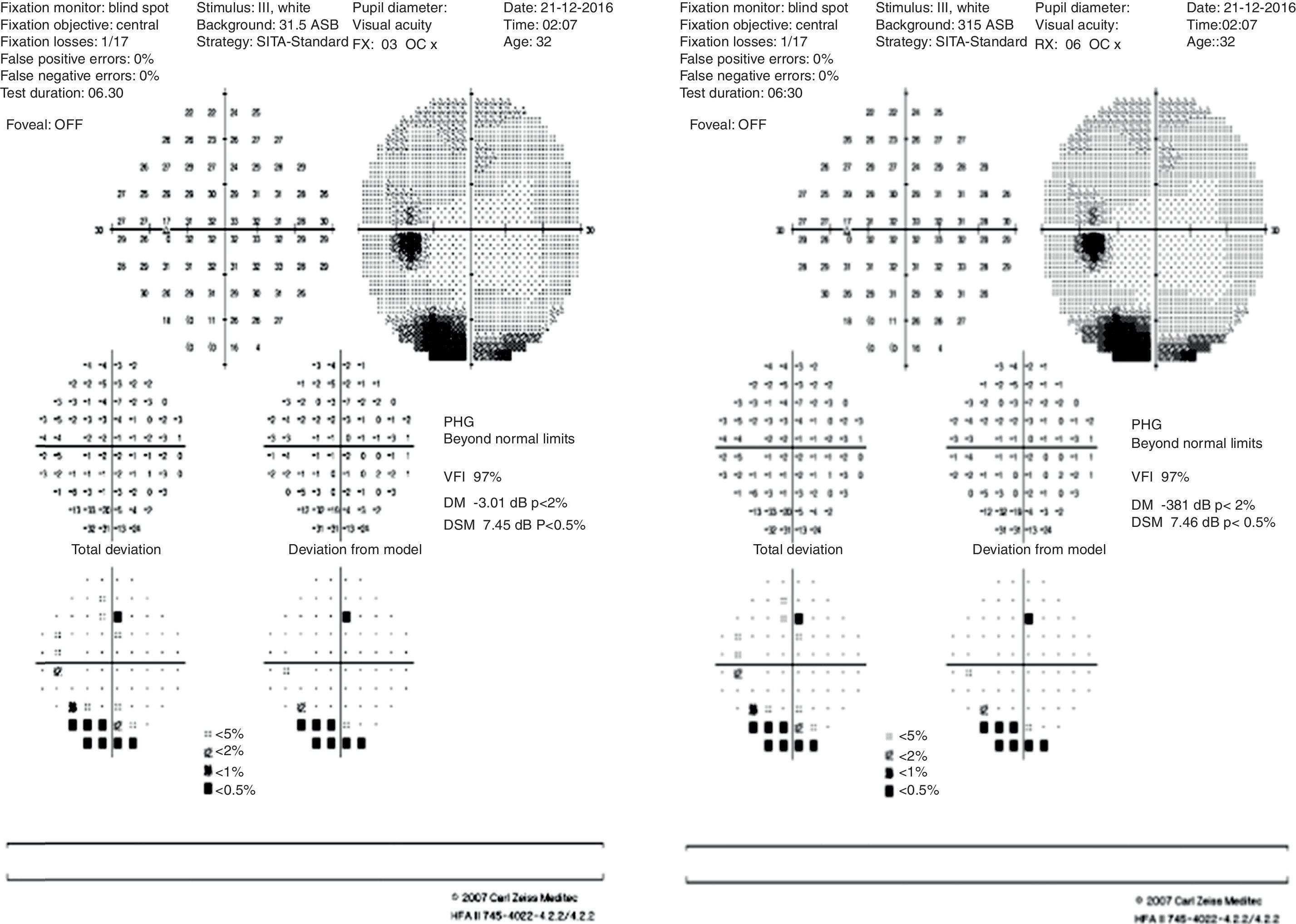
After palpebral anesthetic injection, there was a sudden visual acuity decrease in the left eye and hyposphagma located between I–III at 4mm from the limbus, with increased intraocular pressure. A whitish lesion with a central hemorrhagic focus was observed in the ocular fundus, corresponding to the area where the hyposphagma was located.
DiscussionAnesthetic injection during palpebral repair may be complicated by inadvertent penetration of the eyeball. Intravitreal mepivacaine and adrenaline could cause macular and retinal lesions.
Varón de 32 años sin antecedentes de interés que sufre accidente de tráfico con trauma craneoencefálico leve, con herida inciso-contusa supraciliar izquierda que se extiende al párpado superior izquierdo sin pérdida de visión.
Tras la inyección anestésica palpebral se produjo disminución de agudeza visual súbita del ojo izquierdo e hiposfagma localizado entre la I-III a 4mm del limbo, con aumento de la presión intraocular. En el fondo de ojo se observó una lesión blanquecina con un punto hemorrágico central que se correspondía con el área del hiposfagma.
DiscusiónLa infiltración anestésica durante la reparación palpebral puede complicarse con la penetración inadvertida del globo ocular. La mepivacaína y epinefrina intravítreas pueden causar lesiones maculares y retinianas por sí solas, así como por el aumento súbito de la presión intraocular.