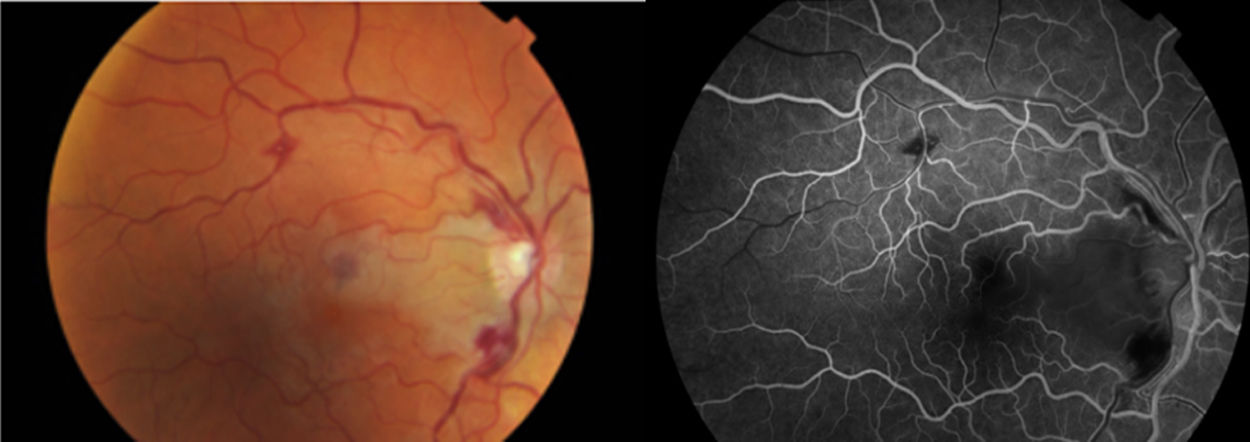
A 34 year-old woman presented with decrease in visual acuity in her right eye (RE). Her past medical history was unremarkable. Dilated fundus examination revealed a central venous occlusion and an obstruction of the cilioretinal artery. Given the patient age, a cardiology and haematology screen was obtained to rule out hypercoagulation disorders and thromboembolic disease. Antiplatelet, anticoagulant, and corticosteroid therapy were started. The laboratory result was positive for anticardiolipin and antiphospholipid antibody. A diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) was made.
DiscussionAntiphospholipid syndrome may cause thrombosis in any organ. The involvement of the retinal vessels may be the first manifestation of this entity. This diagnosis is important to prevent recurrent thrombotic events.
Mujer de 34 años sin antecedentes de interés que acudió por disminución de visión del ojo derecho. El examen reveló una obstrucción de vena central de la retina y de la arteria ciliorretiniana. Dada la edad de la paciente se consultó con cardiología y hematología para descartar un estado de hipercoagulabilidad y patología trombo-embólica. La analítica fue positiva para los anticuerpos anticardiolipina y antifosfolípidos. Se diagnosticó de un síndrome de anticuerpos antifosfolípidos. Se inició tratamiento antiagregante, anticoagulante y corticoideo.
DiscusiónEl síndrome antifosfolípidos puede causar trombosis en cualquier órgano. La afectación de los vasos retinianos puede ser la primera manifestación. Su diagnóstico es importante para evitar fenómenos trombóticos recurrentes.