To assess the extraocular muscle thickness and chemosis after treatment with tocilizumab in patients with active Graves’ ophthalmopathy by optical coherence tomography.
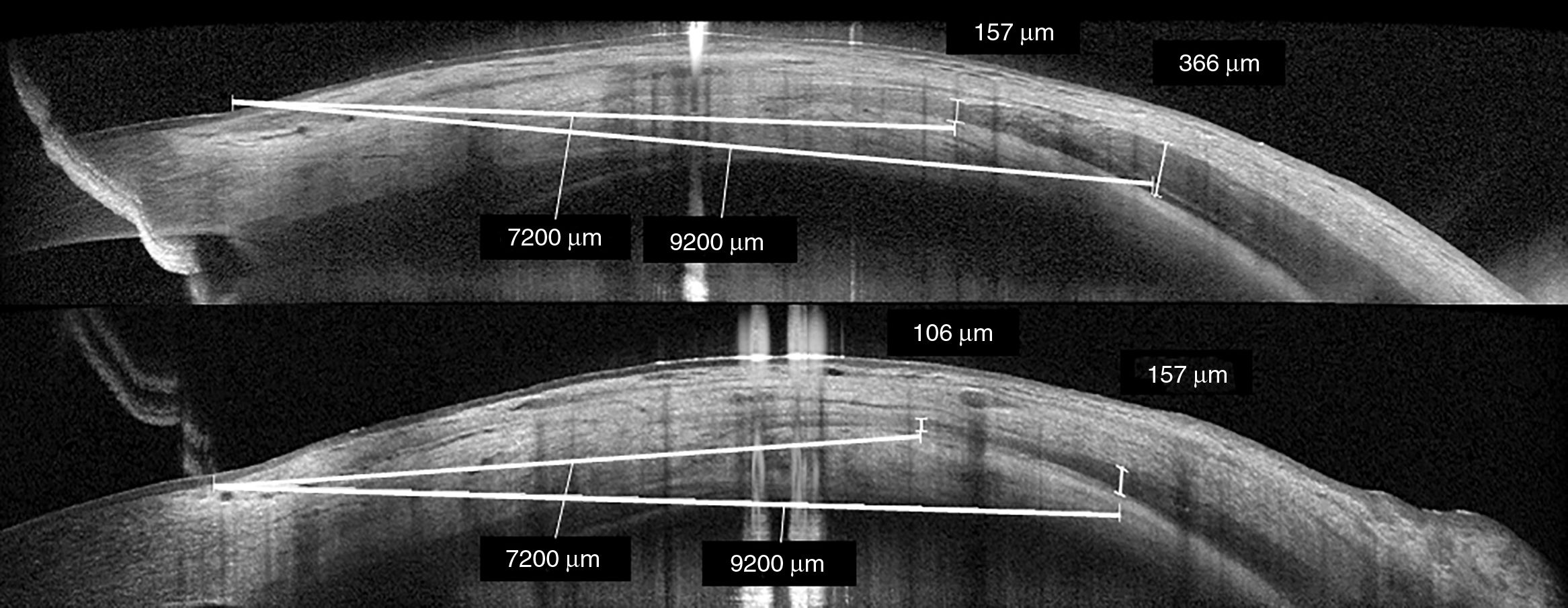
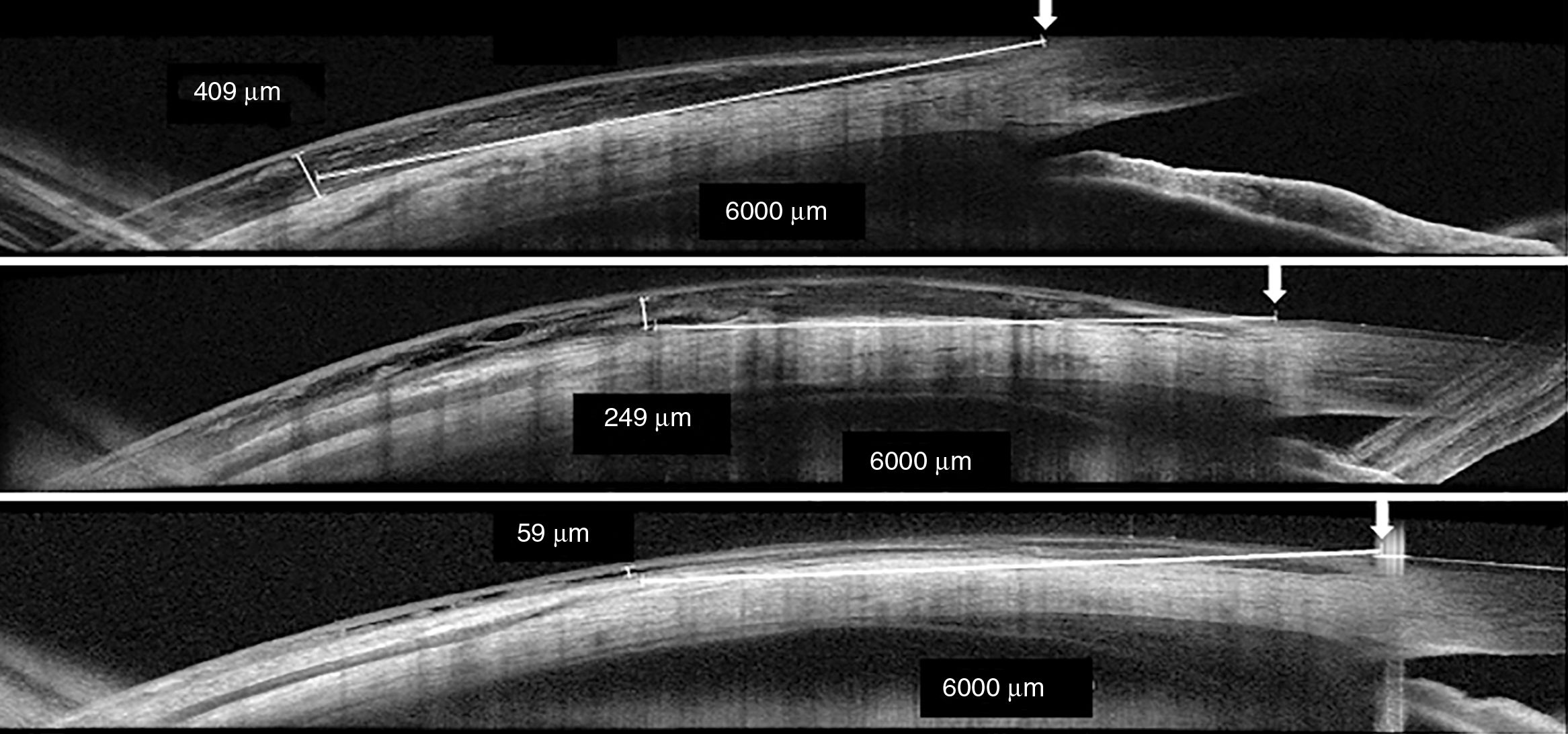
MethodsCase series of five patients with active Graves’ ophthalmopathy (clinical activity score ≥4/10) treated with 4 doses of tocilizumab. These patients had been previously treated with corticosteroids with no response. Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography was employed to determine lateral and medial rectus muscle thickness and chemosis before and after 4 doses of tocilizumab given monthly. Scanning was performed at 3 and 9 o’clock (nasal and temporal).
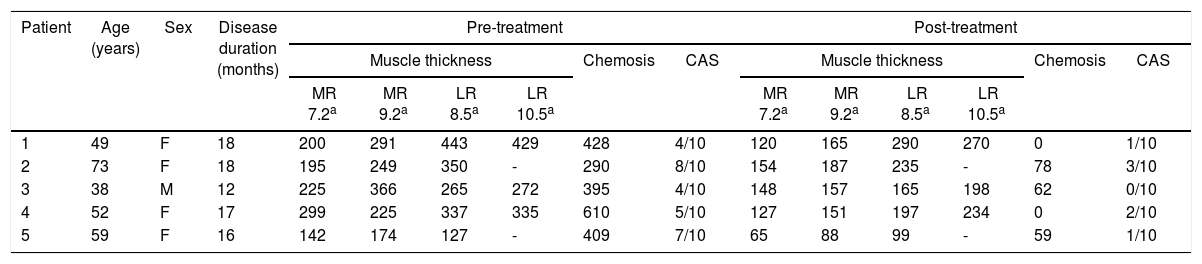
ResultsThe study included four women and one man with a median age of 52 years (range: 38–73). Median Graves’ ophthalmopathy activity duration was 17 months (12–18). Median medial rectus and determine lateral thicknesses pre-treatment were 249μm (174–366) and 337μm (142–443), respectively. Median chemosis was 409μm (290–610). After tocilizumab treatment, median muscle thicknesses reduced to 157μm (88–187) and 197μm (99–290), respectively (p=.043; Wilcoxon) and chemosis to 59μm (0–78). Median clinical activity score decreased from 5 (4–8) to 1 (0–3).
ConclusionsA reduction in extraocular muscle thickness and chemosis was observed after treatment with tocilizumab in Graves’ ophthalmopathy patients using an optical coherence tomography, so this technique could be a useful complementary technique to assess the therapeutic responses.
Evaluar el grosor de los músculos extraoculares y la quemosis tras el tratamiento con tocilizumab en pacientes con oftalmopatía de Graves activa mediante tomografía de coherencia óptica.
MétodosSerie de 5 casos con oftalmopatía de Graves activa (escala de actividad clínica ≥4/10) tratados mediante 4 dosis de tocilizumab. Estos pacientes habían sido tratados previamente con corticoides sin mejoría. Se empleó una tomografía de coherencia óptica de dominio espectral para determinar el grosor del recto lateral y del recto medial, y la quemosis antes y después de 4 dosis de tocilizumab administradas mensualmente. Se realizó el escaneado a las 3 y 9 h (nasal y temporal).
ResultadosSe estudiaron 4 mujeres y un hombre con una edad mediana de 52 años (rango: 38–73). La duración mediana de la actividad fue de 17 meses (rango: 12–18). El grosor muscular mediano del recto medial y del recto lateral pretratamiento fue 249μm (174–366) y 337μm (142–443) respectivamente, siendo la quemosis mediana 409μm (290–610). Tras el tratamiento con tocilizumab el grosor muscular disminuyó a 157μm (88–187) y 197μm (99–290) respectivamente (p=0,043; Wilcoxon), y la quemosis a 59μm (0–78). La escala de actividad clínica disminuyó de 5 (4–8) a 1 (0–3).
ConclusionesSe observó una reducción en el grosor muscular de los rectos horizontales y en la quemosis en pacientes con oftalmopatía de Graves tras el tratamiento con tocilizumab mediante tomografía de coherencia óptica, por lo que esta técnica podría ser útil para la valoración de la respuesta al tratamiento.