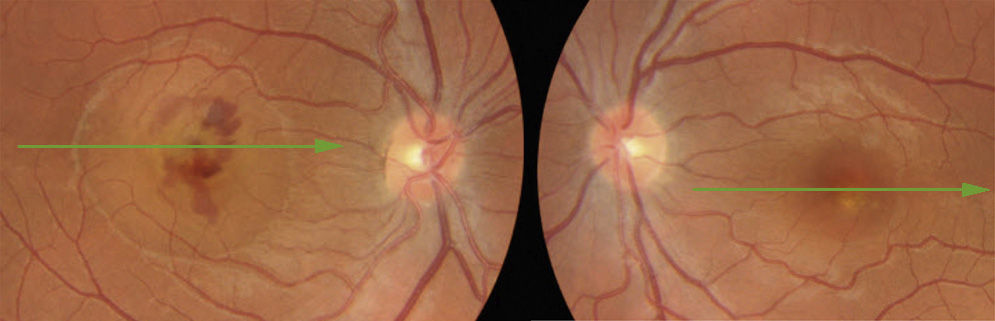
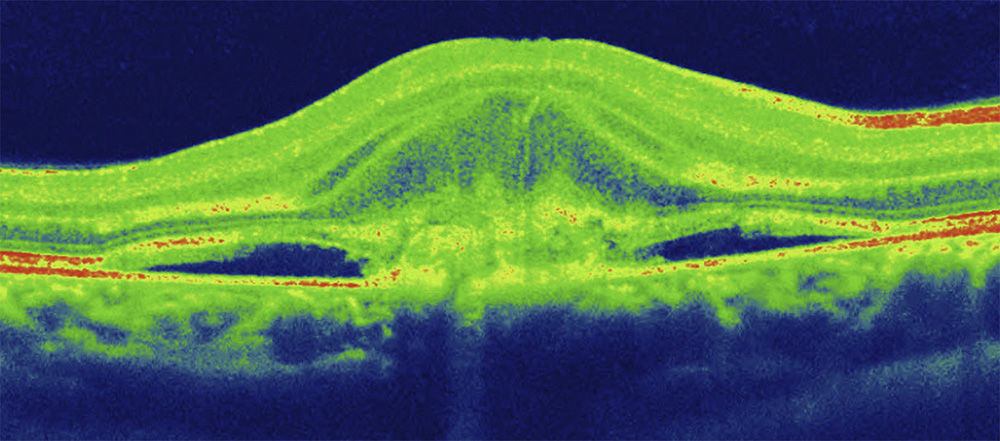
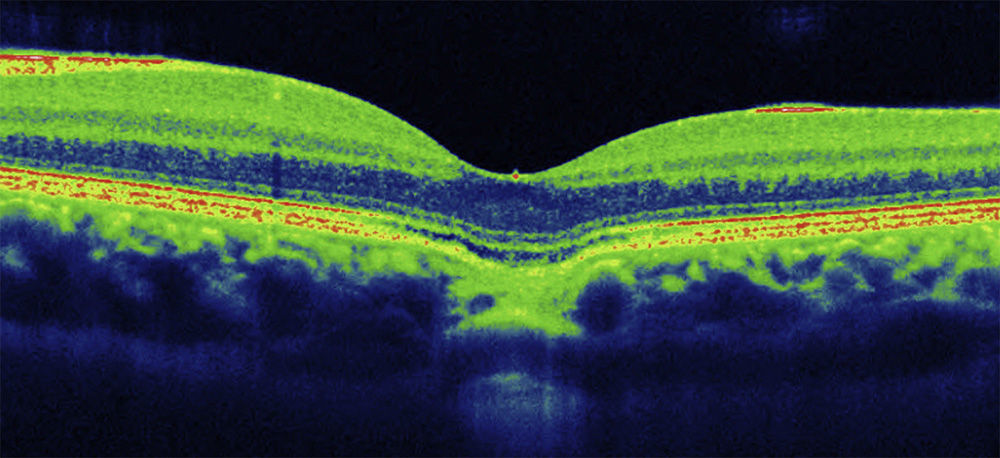
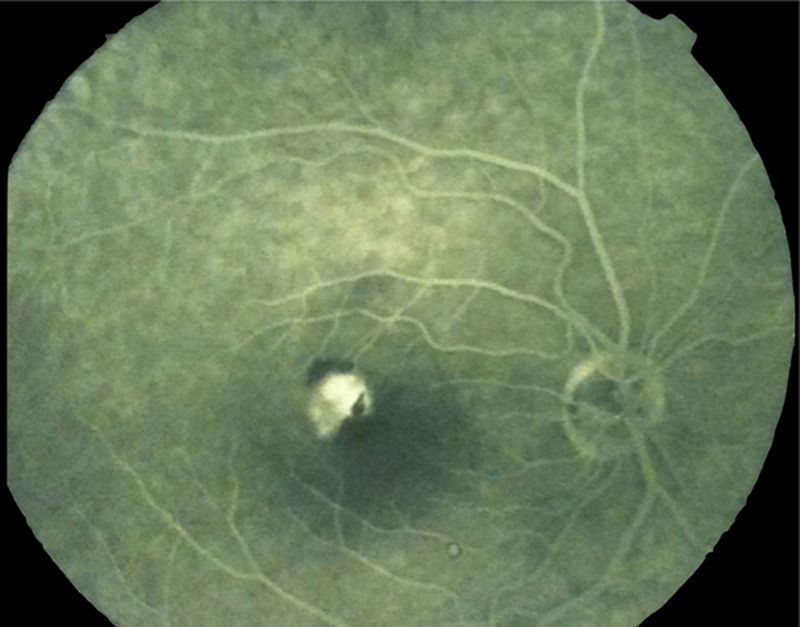
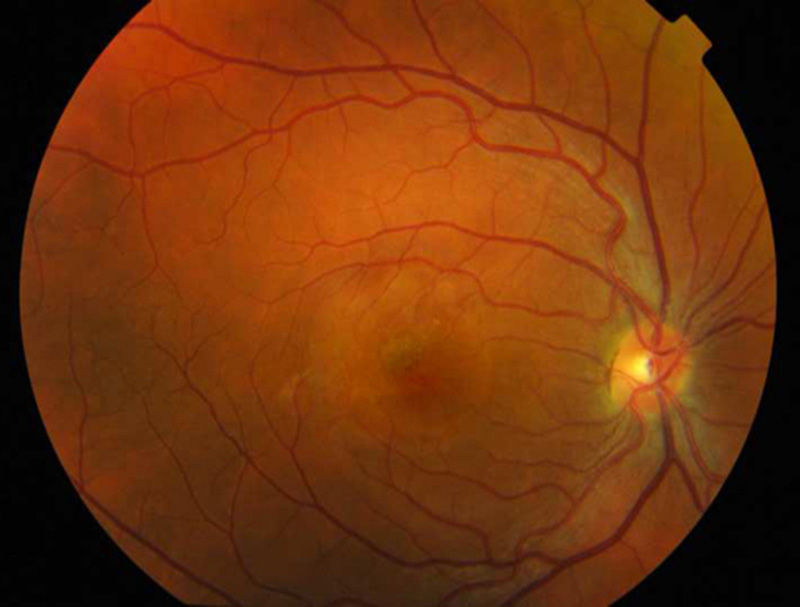
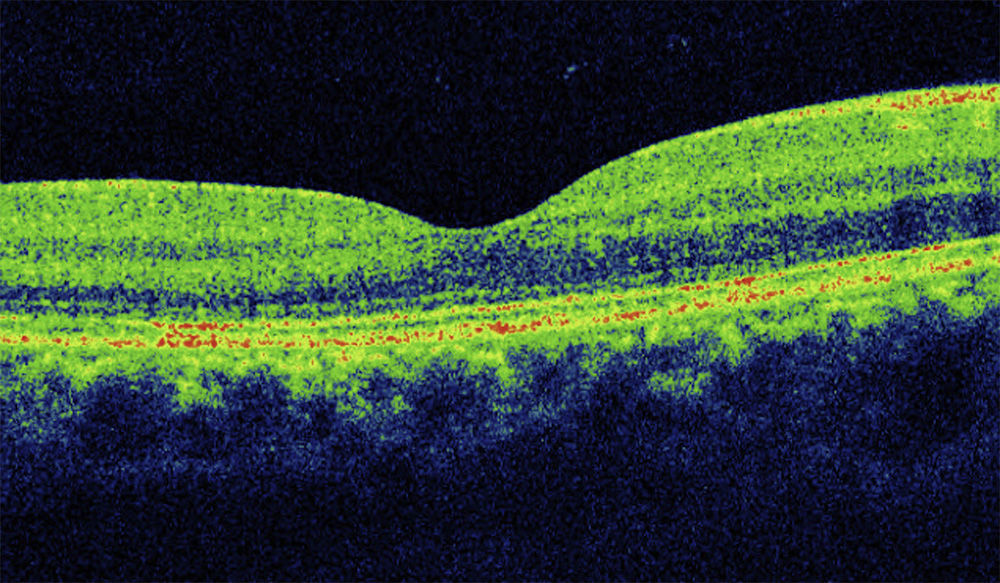
A 27-year-old woman presented with loss of vision in the right eye (20/200). Ophthalmoscopic examination showed intraretinal hemorrhage in the macular region with neurosensory detachment in the right eye, and viteliform deposit in the left eye. Fluorescein angiography and the electrooculogram confirmed the diagnosis of choroidal neovascularization associated with Best's disease. Four weeks after a single bevacizumab intravitreal injection, visual acuity was restored (20/25) and remained stable after a 12 month follow-up.
DiscussionIntravitreal bevacizumab appears to be an effective treatment for choroidal neovascularization associated to Best's disease.
Mujer de 27 años que presentaba disminución de visión en ojo derecho (20/200). El examen funduscópico reveló una hemorragia intraretiniana macular con desprendimiento neurosensorial en ojo derecho, y un depósito de material viteliforme en el ojo izquierdo. La angiografía fluoresceínica y el electrooculograma confirmaron el diagnóstico de neovascularización coroidea asociada a enfermedad de Best. Cuatro semanas después de una única inyección de bevacizumab intravítreo, la agudeza visual a la normalidad (20/25) y se mantuvo estable tras 12 meses de seguimiento.
DiscusiónEl bevacizumab intravítreo puede ser una opción terapéutica eficaz en la neovascularización coroidea secundaria a enfermedad de Best.