To establish the success rate of salvage intra-arterial chemotherapy (IAC), defined as the percentage of eyes that achieved tumoral remission and avoided enucleation. The second objective was the clinical characterization, catheterization results, and associated local and systemic complications.
MethodsRetrospective, interventional case series of 29 patients (35 eyes) with persistent or recurrent retinoblastoma.
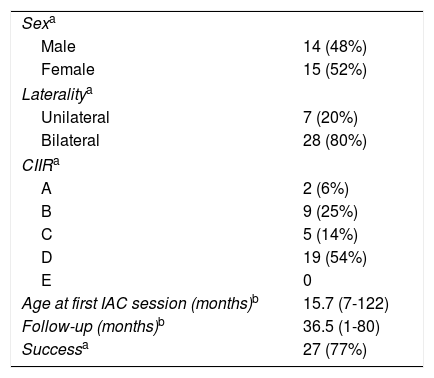
ResultsA total of 73 salvage IAC procedures with topotecan and melphalan were carried out. Success rate was 77% at a mean follow-up of 41.4 months. All patients with only one remaining eye avoided enucleation (10 cases). Catheterization was successful in 98.6% of cases. The types of catheterizations were as follows: 71.2% supraselective ophthalmic artery, 12.3% occlusion pump assisted supraselective ophthalmic artery, 16.4% selective external carotid with retrograde flow. 14% of patients suffered local adverse effects: 1 (2.8%) transitory ptosis, 1 (2.8%) transitory oculomotor nerve palsy, 2 (5.7%) aseptic cellulitis and 1 (2.8%) periorbitary pigmentation. 4.1% (3 cases) suffered neutropenia due to medullar chemosuppression. There were no cases of severe anemia or thrombocytopenia. There were no cerebral ischemic events or mortality associated to the procedure.
ConclusionIAC with melphalan and topotecan is a safe and effective treatment option for persistent or recurrent retinoblastoma, able to reduce enucleation rates.
Establecer la tasa de éxito de la quimioterapia intraarterial (QIA) en modalidad de rescate expresada en el porcentaje de ojos que lograron remisión tumoral y evitaron la enucleación. El segundo objetivo fue analizar la caracterización clínica, resultados del cateterismo, complicaciones locales y sistémicas asociadas.
MétodosEstudio retrospectivo de serie de casos intervencional de 29 pacientes (35 ojos) con retinoblastoma intraocular persistente o recidivado.
ResultadosSe realizaron un total de 73 procedimientos de QIA con topotecán y melfalán en modalidad de rescate. La tasa de éxito de la QIA fue del 77% en un seguimiento promedio de 41,4 meses. Todos los casos con ojo único evitaron la enucleación de su ojo residual (10 casos). El cateterismo fue exitoso en un 98,6%. Los tipos de cateterización logrados fueron los siguientes: supraselectiva por arteria oftálmica (71,2%), supraselectiva por arteria oftálmica asistida con balón de oclusión en carótida externa (12,3%), selectiva por rama de carótida externa con flujo retrógrado (16,4%). Se reportaron efectos adversos locales en el 14% de los pacientes: una (2,8%) ptosis palpebral transitoria, una (2,8%) parálisis del sexto par transitoria, 2 (5,7%) celulitis aséptica y una (2,8%) pigmentación de región periorbitaria. La frecuencia de neutropenia por quimiosupresión medular fue del 4,1% (3 casos). No hubo casos de anemia ni trombocitopenia severas. No hubo eventos isquémicos cerebrales ni mortalidad asociada al procedimiento.
ConclusiónLa QIA con melfalán y topotecán es una alternativa segura y efectiva para el tratamiento del retinoblastoma persistente o recidivado, permitiendo reducir las tasas de enucleación.