To determine the efficacy of topical 0.3% ciprofloxacin in reducing conjunctival biota in patients undergoing cataract surgery.
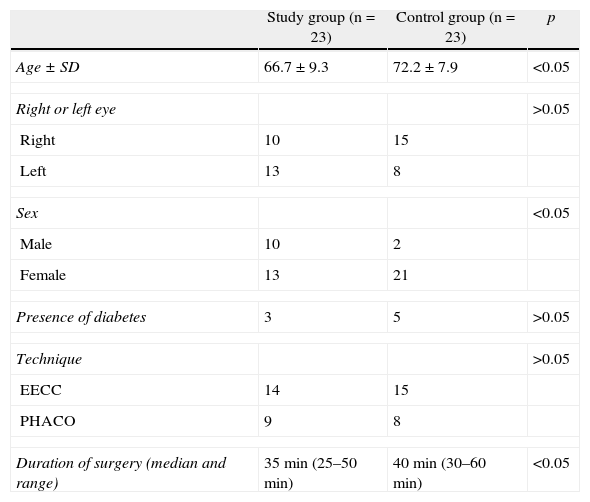
Patients and methodsExperimental, prospective, randomized, controlled and single-blind study. Forty-six eyes of 46 patients were randomized into 2 groups, the study group (n=23) received topical 0.3% ciprofloxacin one day before surgery for six times, and on the day of the surgery one drop every 15min starting 1h before surgery until 3 doses were completed. The control group (n=23) did not receive any antibiotics. For both groups for the surgical field 10% povidone-iodine was applied. Samples from the conjunctiva were taken at four different times and then cultured on solid media (chocolate agar, blood agar) and enrichment broth (thioglycolate). The aqueous humor samples were also cultured in thioglycolate. The presence of bacteria was identified quantitatively and qualitatively, and the frequency of contamination was measured by considering the presence of bacteria in liquid and solid culture media. The number of colony forming units (CFU) was counted in the solid culture medium.
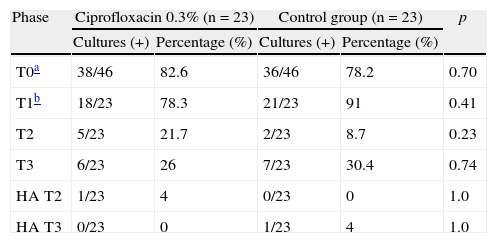
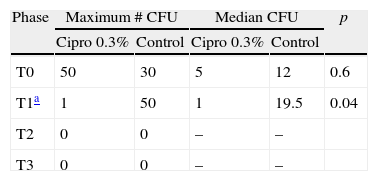
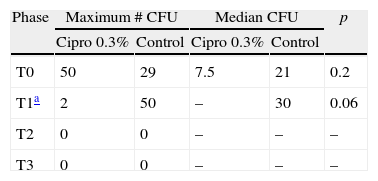
ResultsPositive cultures were obtained in 82.6% and 78.2% of the patients in the study and control groups, respectively, before the administration of 0.3% ciprofloxacin. The administration of 0.3% ciprofloxacin significantly reduced the CFU compared to the control group (p<.05). Immediately after the use of povidone-iodine, the proportion of patients with a positive culture decreased to 21.7% in the study group, and 8.7% in the control group. At the end of the surgery, this percentage was 26% and 30.4%, respectively. The most common isolated pathogen was negative-coagulase Staphylococcus (66.7%).
ConclusionThe administration of 0.3% ciprofloxacin reduces conjunctival bacterial load in the preoperative period. However, it was unable to eradicate the bacteria completely. The administration of povidone-iodine reduced conjunctival biota in 50–70% of patients undergoing cataract surgery.
Determinar la eficacia de la ciprofloxacina tópica al 0,3% en la reducción de la biota conjuntival en pacientes operados de cataratas.
Pacientes y métodosEstudio experimental, prospectivo, aleatorizado, controlado a simple ciego. Cuarenta y seis ojos de 46 pacientes fueron distribuidos al azar en dos grupos: el grupo de estudio (n=23) recibió ciprofloxacina al 0,3% un día antes de la cirugía a razón de una gota cada 6h y, luego, en el día de la cirugía, una gota cada 15min, empezando una hora antes de la cirugía hasta completar tres dosis; el grupo control (n=23) no recibió antibiótico; en ambos grupos para el campo quirúrgico se utilizó iodopovidona al 10%. Se tomaron muestras de la conjuntiva en cuatro momentos diferentes, cultivadas en medios sólidos (agar chocolate, agar sangre) y en caldo de enriquecimiento (tioglicolato). Además se obtuvieron muestras de humor acuoso que fueron cultivadas en tioglicolato. La presencia de bacterias fue identificada cuantitativa y cualitativamente y la frecuencia de contamización fue medida considerando el desarrollo de microorganismos en los medios de cultivo tanto líquido como sólido, y se contabilizaron los números de colonias (UFC) en el sólido.
ResultadosAntes de la administración de ciprofloxacina al 0,3% se obtuvieron cultivos positivos en el 82,6 y 78,3% de los pacientes en los grupos de estudio y control, respectivamente. La administración de ciprofloxacina al 0,3% redujo significativamente las UFC en comparación con el grupo control (p<0,05); inmediatamente después del uso de la iodopovidona el porcentaje de pacientes con cultivo positivo disminuyó a 21,7% en el grupo de estudio y a 8,7% en el grupo control; al final de la cirugía este porcentaje fue de 26 y 30,4%, respectivamente. El germen más frecuente fue el estafilococo coagulasa-negativo (66,7%).
ConclusiónLa administración de ciprofloxacina al 0,3% reduce la carga bacteriana conjuntival en el período preoperatorio, pero no la erradica de forma significativa. La administración de iodopovidona erradica la biota conjuntival en el 50–70% de los pacientes operados de cataratas.