To measure the magnitude and duration of the hypotensive effect of two prostaglandin analogues in glaucoma patients using the water drinking test (WDT).
MethodsPatients received latanoprost or travoprost every 24 h and then every 48 h. Untreated WDT were performed at 7 am and with treatment 12, 36 and 44 h after the last dose; intraocular pressure (IOP) peak, fluctuation and the difference between peak and isolated IOP measurements at consultation times were calculated.
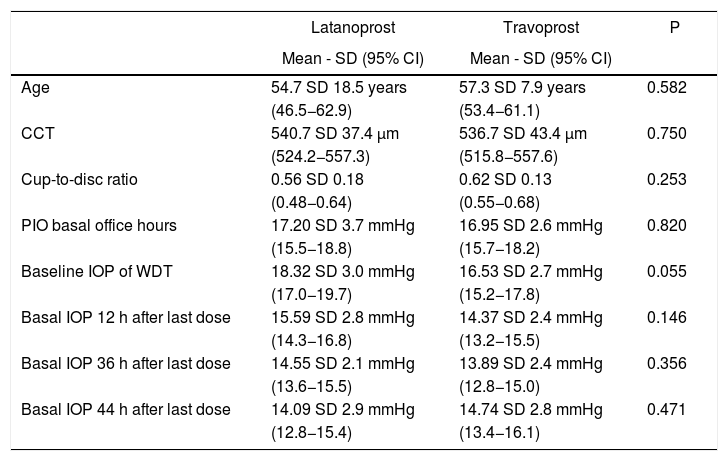
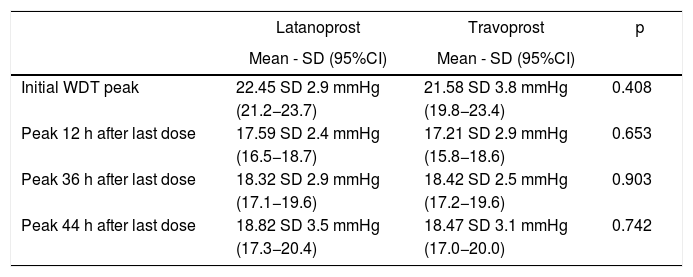
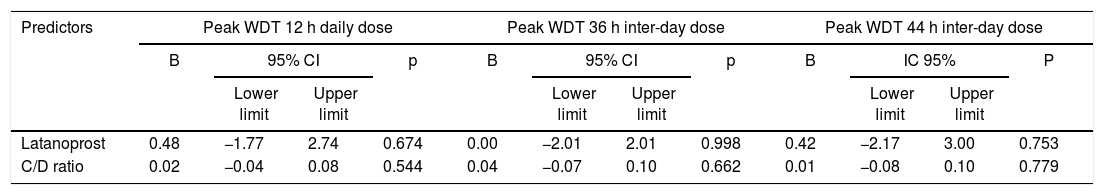
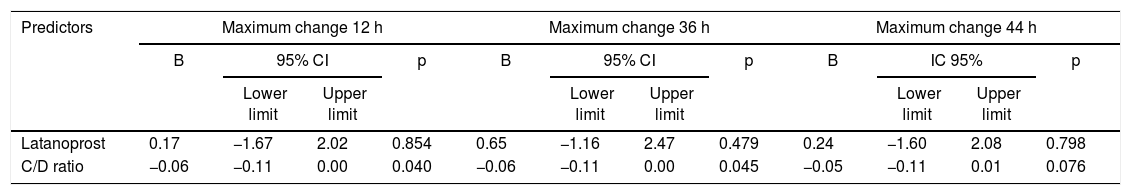
ResultsForty-one eyes of 21 patients with primary open-angle glaucoma were included; 22 eyes received latanoprost, and 19 received travoprost. Mean untreated isolated IOP was 17.20 standard deviation (S.D.) 3.73 and 16.95 S.D. 2.61 mmHg and peak pressure 22.45 S.D. 2.91 and 21.58 S.D. 3.79 mmHg, for the latanoprost and travoprost groups, respectively. With treatment, peak pressure was reduced by 22.64% and 20.29% at 12 h, 18.44% and 14.64% at 36 h and 16.17% and 14.46% at 44 h, respectively. The fluctuation without treatment was 4.36 and 5.11 mmHg, and with treatment at 12 h was reduced to 2.77 and 2.89 mmHg, increasing again at 36 and 44 h.
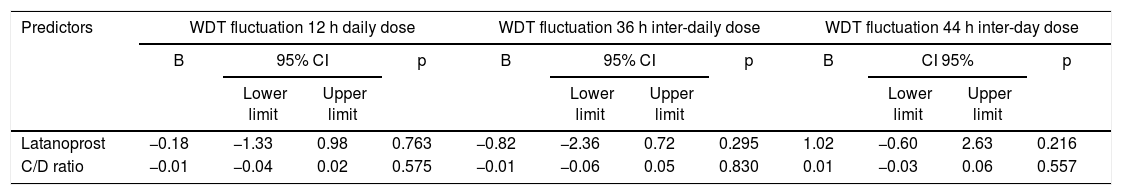
ConclusionsA hypotensive effect was evident up to 44 h after the last dose of latanoprost and travoprost, similar for the two drugs and decreasing over time. IOP fluctuation was only reduced at 12 h.
Medir con la prueba de sobrecarga hídrica (PSH) la magnitud y duración del efecto hipotensor de dos análogos de prostaglandinas en pacientes con glaucoma.
MétodosLos pacientes recibieron latanoprost o travoprost cada 24 horas y luego cada 48 horas. Se practicaron PSH sin tratamiento a las 7 am y con tratamiento 12, 36 y 44 horas después de la última dosis; se calcularon el pico de presión intraocular (PIO), la fluctuación y la diferencia entre el pico y las medidas aisladas de PIO en horas de consulta.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 41 ojos de 21 pacientes con glaucoma primario de ángulo abierto, 22 ojos recibieron latanoprost y 19, travoprost. La PIO aislada promedio sin tratamiento fue 17,20 desviación estándar (D.S.) 3,73 y 16,95 D.S. 2,61 mmHg y el pico de presión 22,45 D.S. 2,91 y 21,58 D.S. 3,79 mmHg, para los grupos de latanoprost y travoprost, respectivamente. Con tratamiento, la presión pico se redujo en 22,64% y 20,29% a las 12 horas, 18,44% y 14,64% a las 36 horas y 16,17% y 14,46% a las 44 horas, respectivamente. La fluctuación sin tratamiento fue 4,36 y 5,11 mmHg, y con tratamiento a las 12 horas se redujo a 2,77 y 2,89 mmHg, aumentando nuevamente a 36 y 44 horas.
ConclusionesSe evidenció un efecto hipotensor hasta 44 horas después de la última dosis de latanoprost y travoprost, similar para los dos medicamentos y decreciente en el tiempo. La fluctuación de la PIO sólo se redujo a las 12 horas.