Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease is a multisystem disorder characterized by a bilateral granulomatous panuveitis. Multiple therapeutic regimens have been used to control inflammation in acute uveitic stage to prevent irreversible visual loss. The purpose of this paper is to compare the effect, on functional and anatomic outcomes, of early treatment with standard corticotherapy vs. corticotherapy plus immunosuppressive (IMT) therapy in acute Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease (Group A vs. Group B).
MethodsA retrospective chart review of patients with Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease, with an evolution time of 2 weeks or less, who attended the Inflammatory Eye Disease Clinic, from 2001 to 2015. Data collected included demographic information, presenting features, treatment and improvement in visual acuity (VA).
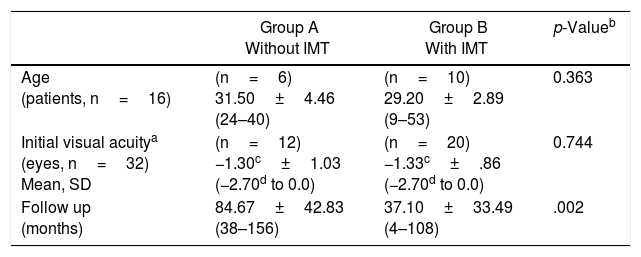
ResultsSixteen charts were reviewed; 15 females (93.75%). Mean age: 30.81±10.53 years, follow-up time (months): 54.94±43.43. Ten patients (66.6%) had IMT, azathioprine, methotrexate and cyclophosphamide.
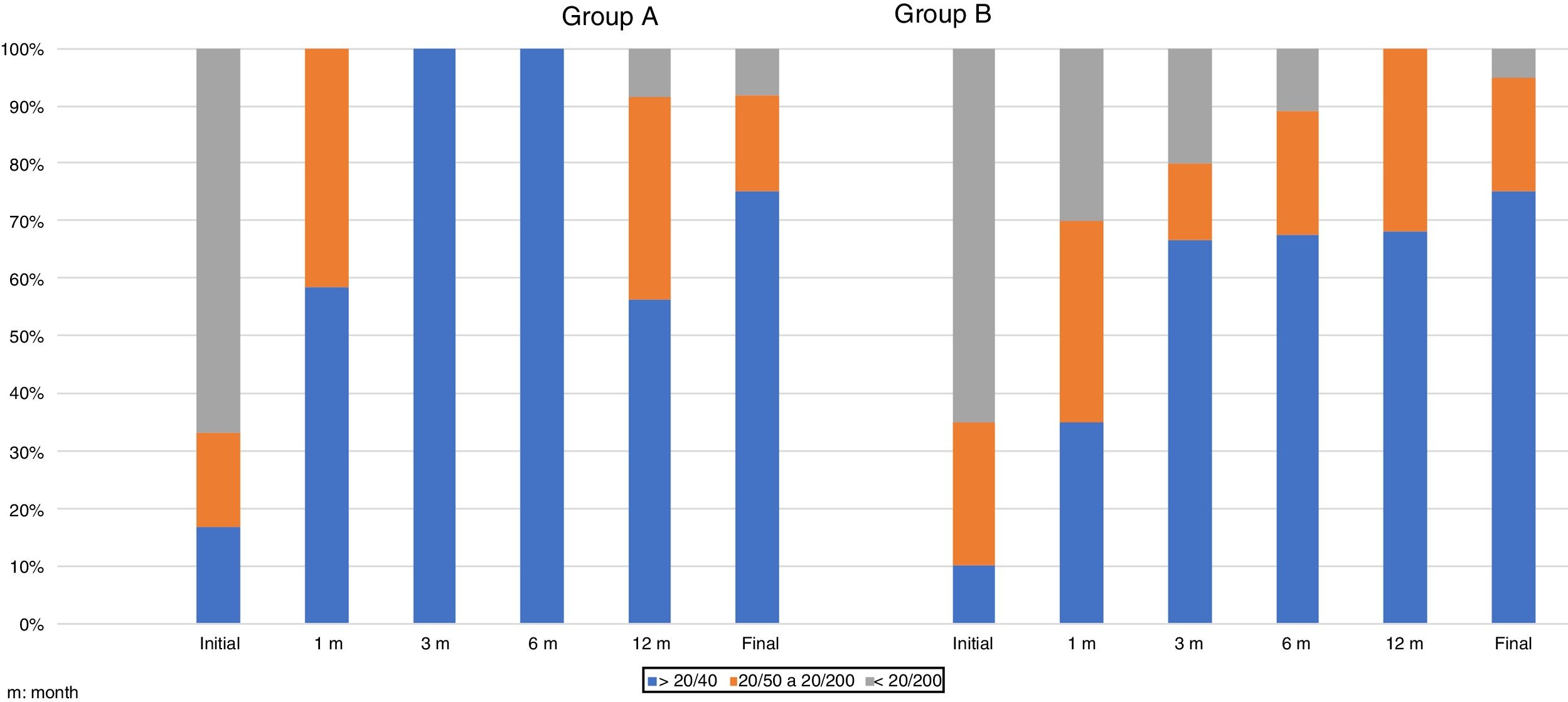
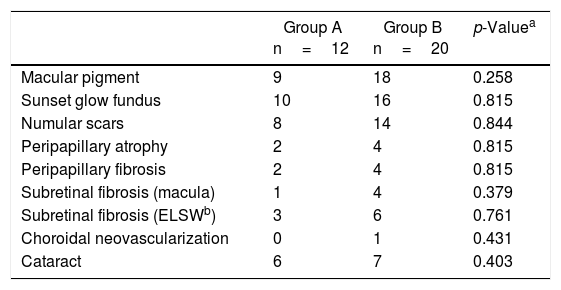
In group A, initial VA <20/200 in 66.7%; final VA was ≥20/40 in 9 eyes (75%). In group B, initial VA <20/200 in 65%; final VA ≥20/40 in 15 eyes (75%). In group A, VA improved faster at one and 3 months (ANOVA p<.057). Clinical characteristics in convalescent stage and complications were similar.
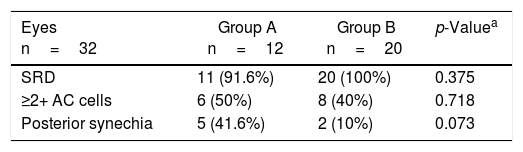
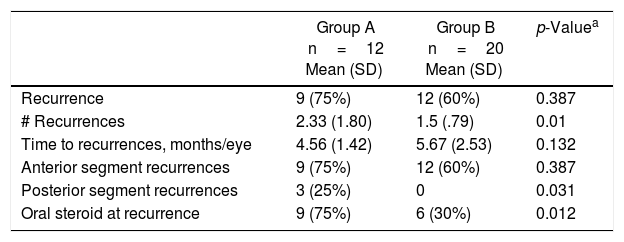
Anterior chamber recurrences occurred in both groups and posterior pole recurrences were observed in group A. Time to first recurrence was similar (P<.279).
Frequency of recurrence was 2.33±1.80 vs. 1.5±0.79 (P<.01). At recurrence 15 patients were still having oral steroids, nine in group A, 6 in Group B. In group A, prednisone was given during more time: mean 15.17±12.08 months, and time to reach to 10mg dose was longer: 8.60±11.7 (P<.008 and P<.046).
ConclusionsAdding IMT as first line therapy to corticosteroids, do not matter significantly in terms of final VA or development of visually significant complications. In the IMT plus corticosteroids group number of recurrences was significantly lower, and a steroid sparing effect was evident.
La enfermedad de Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada es un trastorno multisistémico que se caracteriza por ser una panuveítis bilateral granulomatosa. Diferentes esquemas de tratamiento se han usado para controlar la inflamación en la fase aguda con el fin de prevenir la pérdida visual irreversible. El propósito de este trabajo es comparar el efecto en el resultado funcional y anatómico del tratamiento en la fase aguda de la enfermedad con esteroides vs. esteroides con inmunosupresores (IMT) (grupo A vs. grupo B).
MétodosEstudio retrospectivo de una serie de casos con enfermedad de Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada, con una evolución menor o igual a 2 semanas, que acudieron a la Clínica de Enfermedades Inflamatorias Oculares, de 2001 a 2015. Se incluyeron datos demográficos, características clínicas, tratamiento y mejoría de agudeza visual (AV).
ResultadosSe incluyeron 16 casos; 15 mujeres (93,75%). Edad media: 30,81±10,53 años, y seguimiento (meses): 54,94±43,43. Diez pacientes con IMT (66,6%) (azatioprina, metotrexato y ciclofosfamida).
En el grupo A, la AV inicial fue<20/200 en el 66,7%; y la final≥20/40 en 9 casos (75%). En el grupo B, la AV inicial<20/200 en el 65%; y la AV final≥20/40 en 15 ojos (75%). En el grupo A, la AV mejoró más rápido en el primer y tercer mes (ANOVA p<0,057). Los datos clínicos de fase de convalecencia y complicaciones fueron similares.
Las recurrencias del segmento anterior se observaron en los dos grupos; en el grupo A, también se vieron recurrencias de polo posterior. El tiempo hasta la primera recurrencia fue similar (p<0,279).
La frecuencia de recurrencia fue de 2,33±1,80 vs. 1,5±0,79 (p<0,01). En ese momento 15 pacientes continuaban con esteroide vía oral, 9 del grupo A, y 6 del grupo B. En el grupo A, la prednisona se dio por un tiempo mayor: media 15,17±12,08 meses, y el tiempo en llegar a dosis de 10mg o menor fue mayor: 8,60±11,7 (p<0,008 y p<0,046).
ConclusionesEl agregar IMT a los corticoesteroides como primera línea de tratamiento no cambió el resultado final de AV, ni de complicaciones. En el grupo de IMT más corticoesteroides el número de recurrencias fue menor y se observó un efecto ahorrador de esteroides.