To evaluate intraoserver and inteobserver repeatability of the “exaggerated forced duction test” or “oblique traction test” (OTT) and the “excyclo and incyclo passive rotation test” or “Cyclorotation traction test” (CTT).
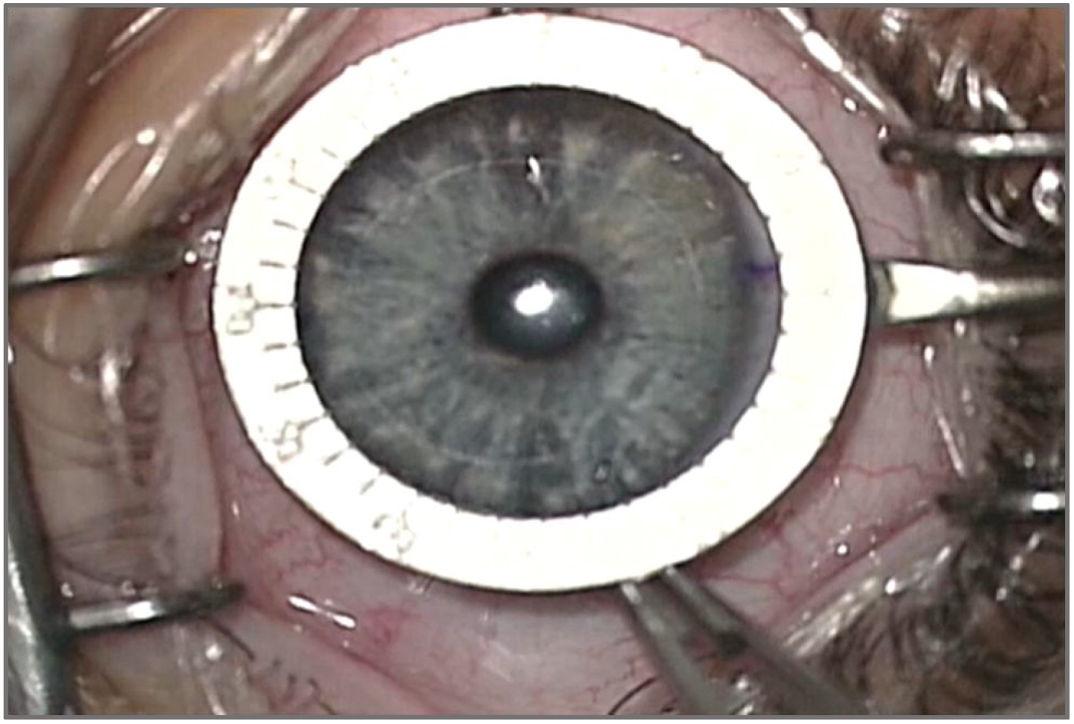
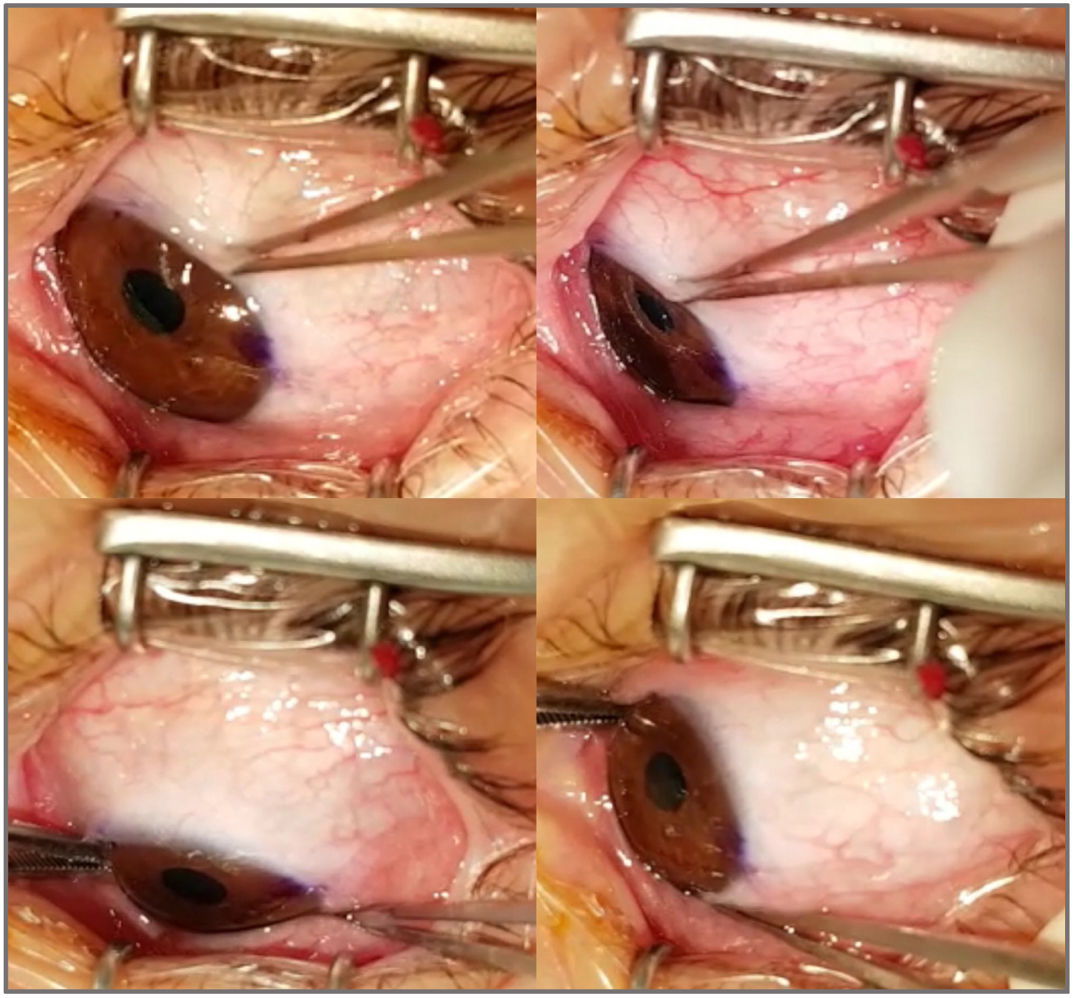
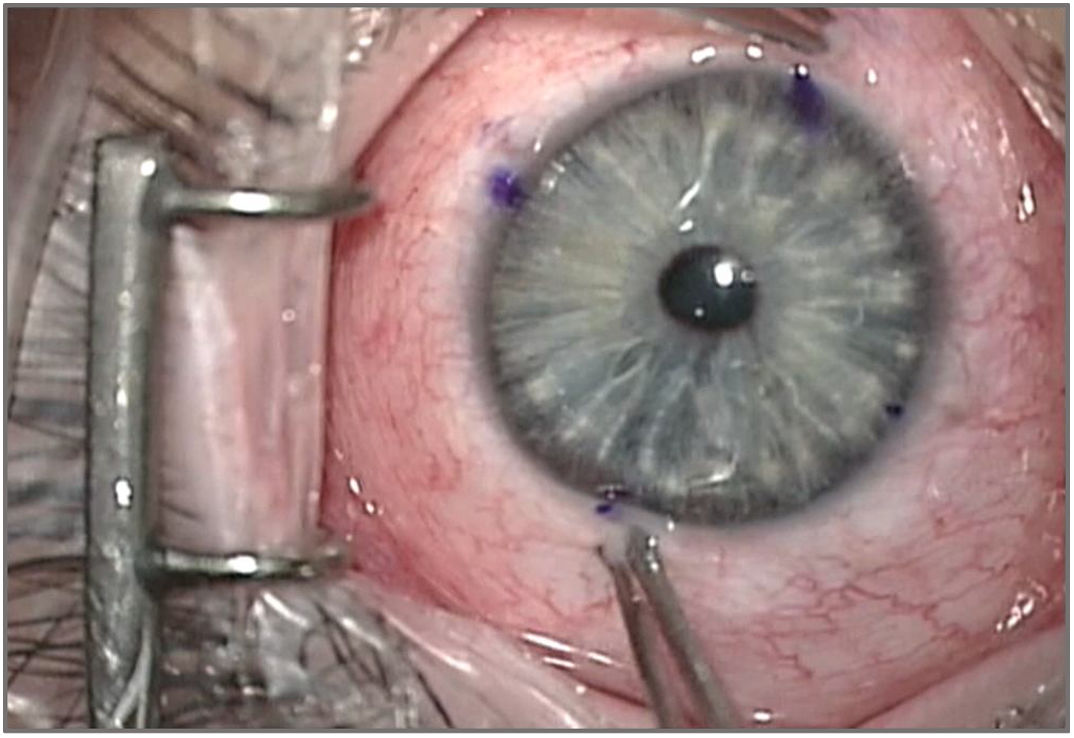
Methods44 eyes of 22 patients were evaluated under deep general anesthesia. Passive duction was tested on supraduction and infraduction by the “exaggerated duction test”. The limitation on movement was graduated from 0 to - 4. Passive cyclorotation test was evaluated with retropulsion of the globe until the first resistance is noted. We used the Mendez ring and blue dots marked on the limbus to measure the amount of cyclorotation. The results obtained of excyclo and incyclorotation were recorded. All measurements were made in duplicate for each of the two observers.
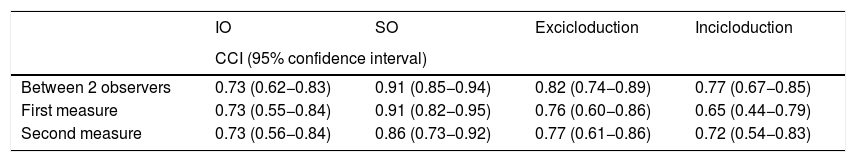
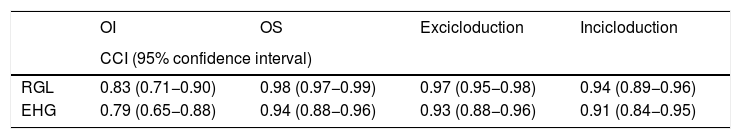
ResultsThe intraclass correlation of the OTT coefficient between the two observers was for the IO was 0,738 (95% confidence interval, 0,62–0,83) and 0,910 for the superior oblique (SO) (95% confidence interval, 0,85–0,94). The CTT intraclass correlation coefficient of the between the two observers was 0,827 (95% confidence interval, 0,74–0,89) for exclycloduction and 0,792 (95% confidence interval, 0,67–0,85) for inclycloduction. The percentage of patients within 5º of rotation interobserver was 84,1% for excyclorotation and 81,8% for inclyclorotation. Both tests had better correlation on the intraobserver than interobserver evaluation.
ConclusionsEvaluation of the OTT and CyRTT had moderate to good correlation between the two observers and good to excellent on the intraobserver evaluation.
Evaluar la repetibilidad intraobservador e interobservador de la "prueba de ducción forzada exagerada" o "prueba de tracción oblicua" (OTT) y la "prueba de exciclo e inciclorotación pasiva " o "prueba de tracción de ciclorotación" (CTT).
Materiales y métodosSe estudiaron 44 ojos de 22 pacientes. Fueron evaluados bajo anestesia general profunda. La ducción pasiva se probó en supraducción e infraducción mediante la "prueba de ducción exagerada". La limitación en el movimiento se graduó de 0 a - 4. La prueba de ciclorotación pasiva se evaluó con retropulsión del globo hasta que se observa la primera resistencia. Utilizamos el anillo de Mendez y los puntos azules marcados en el limbo para medir la cantidad de ciclorotación. Se registraron los resultados obtenidos de exciclo e inciclorotación. Todas las mediciones se realizaron por duplicado para cada uno de los dos observadores.
ResultadosEl coeficiente de correlación intraclase del OTT entre los dos observadores para el oblicuo inferior fue 0,738 (intervalo de confianza del 95%, 0,62-0,83) y 0,910 para el oblicuo superior (intervalo de confianza del 95%, 0,85-0,94). El coeficiente de correlación intraclase de CTT de los dos observadores fue de 0,827 (intervalo de confianza del 95%, 0,74-0,89) para excicloducción y 0,792 (intervalo de confianza del 95%, 0,67-0,85) para incicloducción. El porcentaje de pacientes dentro de 5º de rotación interobservador fue de 84,1% para exciclo y 81,8% para inciclorotación. Ambas pruebas tuvieron una mejor correlación intraobservador que en la evaluación interobservador.
ConclusionesLa evaluación de OTT y CTT tuvo una correlación de moderada a buena entre los dos observadores y buena a excelente en la evaluación intraobservador.