To describe the epidemiology, clinical features and visual prognosis in uveitis associated with demyelinating disease (DD) of the CNS.
MethodsA clinical, retrospective, and descriptive study was performed. Data regarding age at presentation, gender, time from onset was recorded, as well as type of uveitis, complications, treatment and initial and final visual acuity (BCVA) on all patients with DD-associated uveitis diagnosed in our Unit between January 2009 and June 2011.
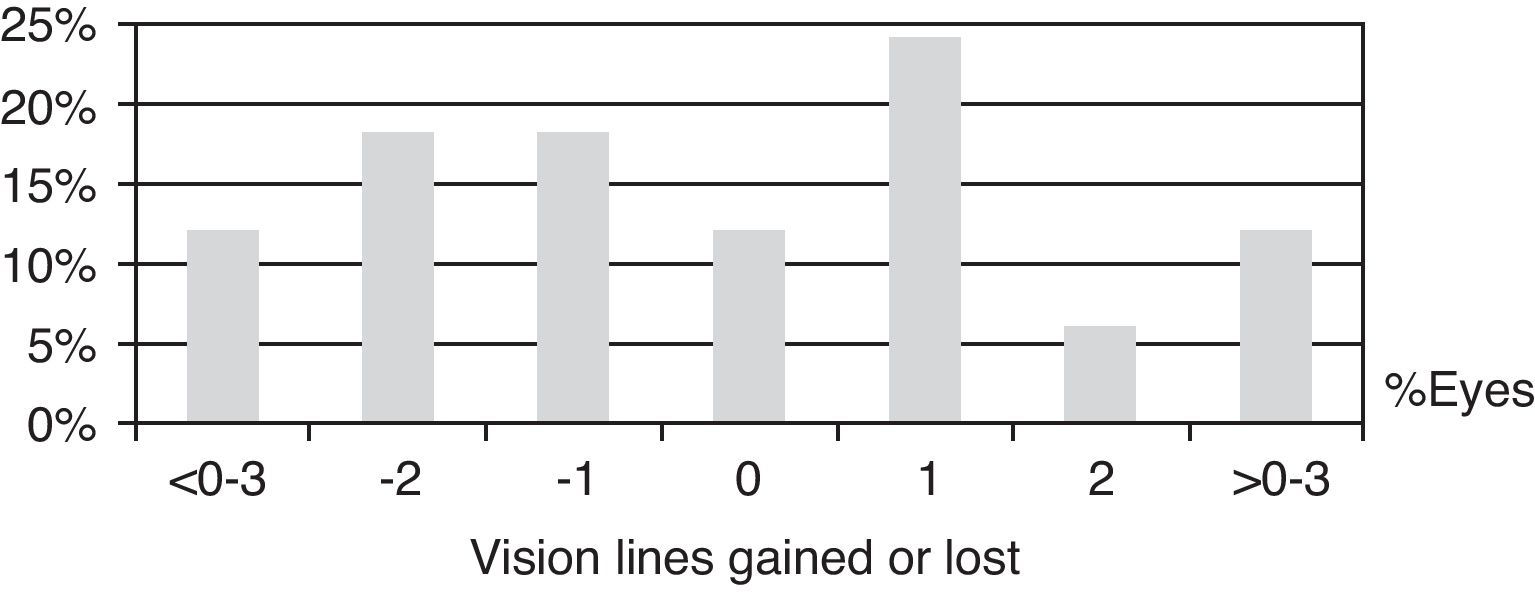
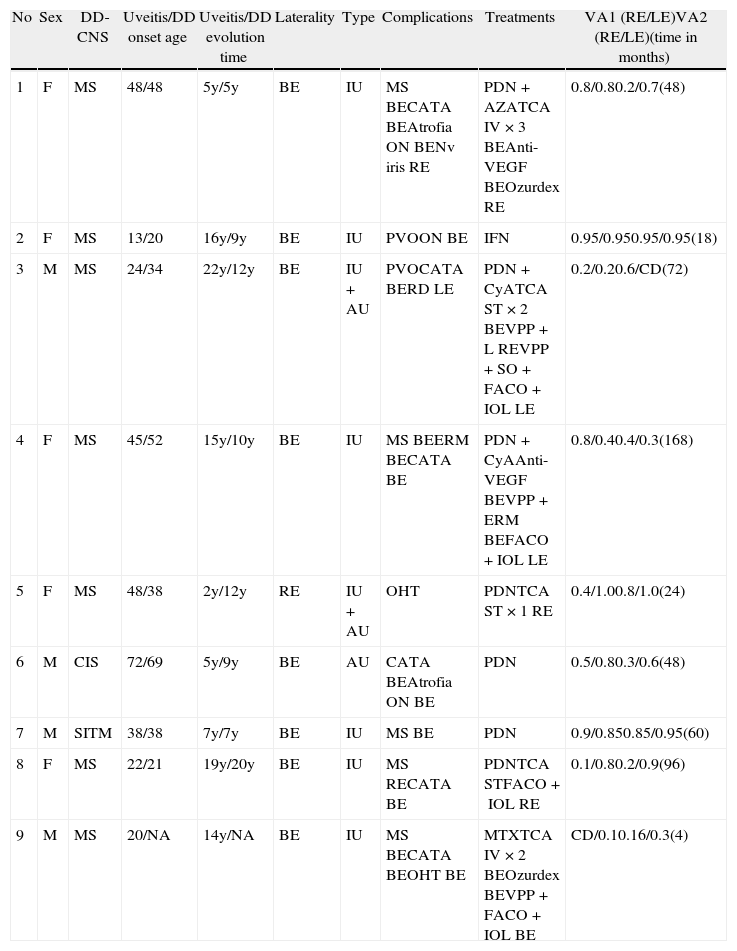
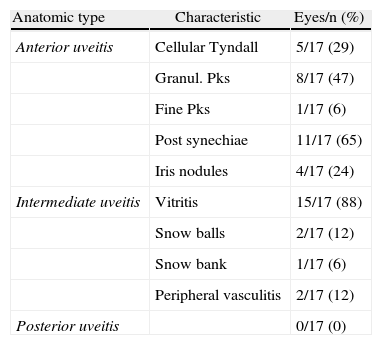
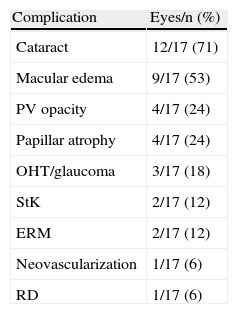
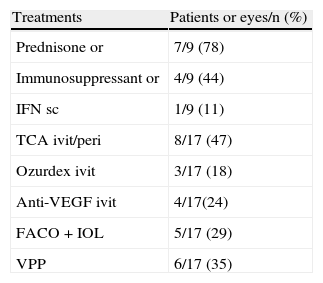
ResultsFive women and 4 men were finally included (1.3% of 697 with uveitis). There was associated multiple sclerosis in 78% of cases. Mean age at presentation was 36.6 years for uveitis and 40 years for DD. The uveitis preceded the DD in 3 cases (33%). Typically, uveitis was bilateral (89%), chronic (89%), intermediate (89%), and associated with previous inflammation (29%), with synechiae (65%), and granulomatous (44%). The most frequent complications were cataract (71%) and macular edema (53%). Besides local treatment, uveitis was managed with systemic steroids (78%), immunosuppressants (44%), and surgery (41% of eyes). After a mean follow up of 5 years, 47% of the eyes had a worse BCVA, among which, 12% lost ≥3 Snellen lines. The only patient treated with interferon (IFN) remained stable without treatment for the last 7 years.
ConclusionsDD-associated uveitis typically affected young adult women with intermediate-anterior uveitis of chronic, bilateral and synechiae type. Complications are common and there is a risk of visual loss, despite treatment. IFN therapy may be an effective alternative to be investigated.
Describir la epidemiología, características clínicas y pronóstico visual de las uveítis asociadas a enfermedad desmielinizante (ED) del SNC.
MétodosEstudio retrospectivo, descriptivo de serie clínica. Se recogieron la edad de presentación y el sexo, el tiempo de evolución, el tipo de uveítis, las complicaciones, el tratamiento instaurado y la agudeza visual (AVmc), basal y final, de todos los pacientes con uveítis asociada a ED diagnosticada en nuestro Servicio entre enero de 2009 y junio de 2011.
ResultadosSe incluyó a cinco mujeres y cuatro hombres (1,3% de 697 uveítis atendidas). Asociaron esclerosis múltiple un 78%. La edad media de presentación de la uveítis fue de 36,6 años y de la ED, 40 años. La uveítis antecedió a la ED en 3 casos (33%). La uveítis fue, típicamente, bilateral (89%), crónica (89%) e intermedia (89%) y asociada a inflamación anterior (29%), sinequiante (65%) y granulomatosa (44%). Las complicaciones más frecuentes fueron: catarata (71%) y edema macular (53%). Además del tratamiento local, la uveítis se manejó con esteroides sistémicos (78%), inmunosupresores (44%) y cirugía (41% de ojos). Tras un seguimiento medio de 5 anños, un 47% de los ojos empeoró su AVmc, perdiendo 3 líneas de Snellen en un 12%. La única paciente tratada con interferón (IFN), permaneció estable sin tratamiento durante los últimos 7 años.
ConclusionesLa uveítis asociada a ED afecta típicamente a mujeres adultas jóvenes con uveítis intermedias-anteriores, crónicas, bilaterales y sinequiantes. Las complicaciones son frecuentes y existe riesgo de pérdida visual, a pesar del tratamiento. La terapia con IFN podría ser una alternativa eficaz a investigar.