To analyze the indications, dosage and efficacy of botulinum toxin A injection performed in patients in a Strabismus Department.
MethodsIn this prospective study, botulinum toxin A was injected into 28 patients diagnosed with strabismus. Data were obtained from the records of patients that were evaluated during 2013 in the Strabismus Unit of Rey Juan Carlos Hospital (Móstoles, Madrid, Spain) in order to assess the indications and dosage of botulinum toxin A use in strabismus, as well as its clinical effect and differences in pediatric and adult patients. The outcomes in the last visit, at least 14 months after the injections, were analyzed.
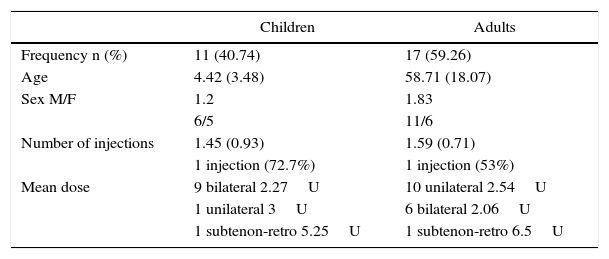
ResultsAn analysis was performed on the data from 11 children, 6 females (54.5%), and 17 adults, 11 males (64%). The mean age was 4.42±3.48 years and 58.71±18.07 years in the children and adult groups, respectively.
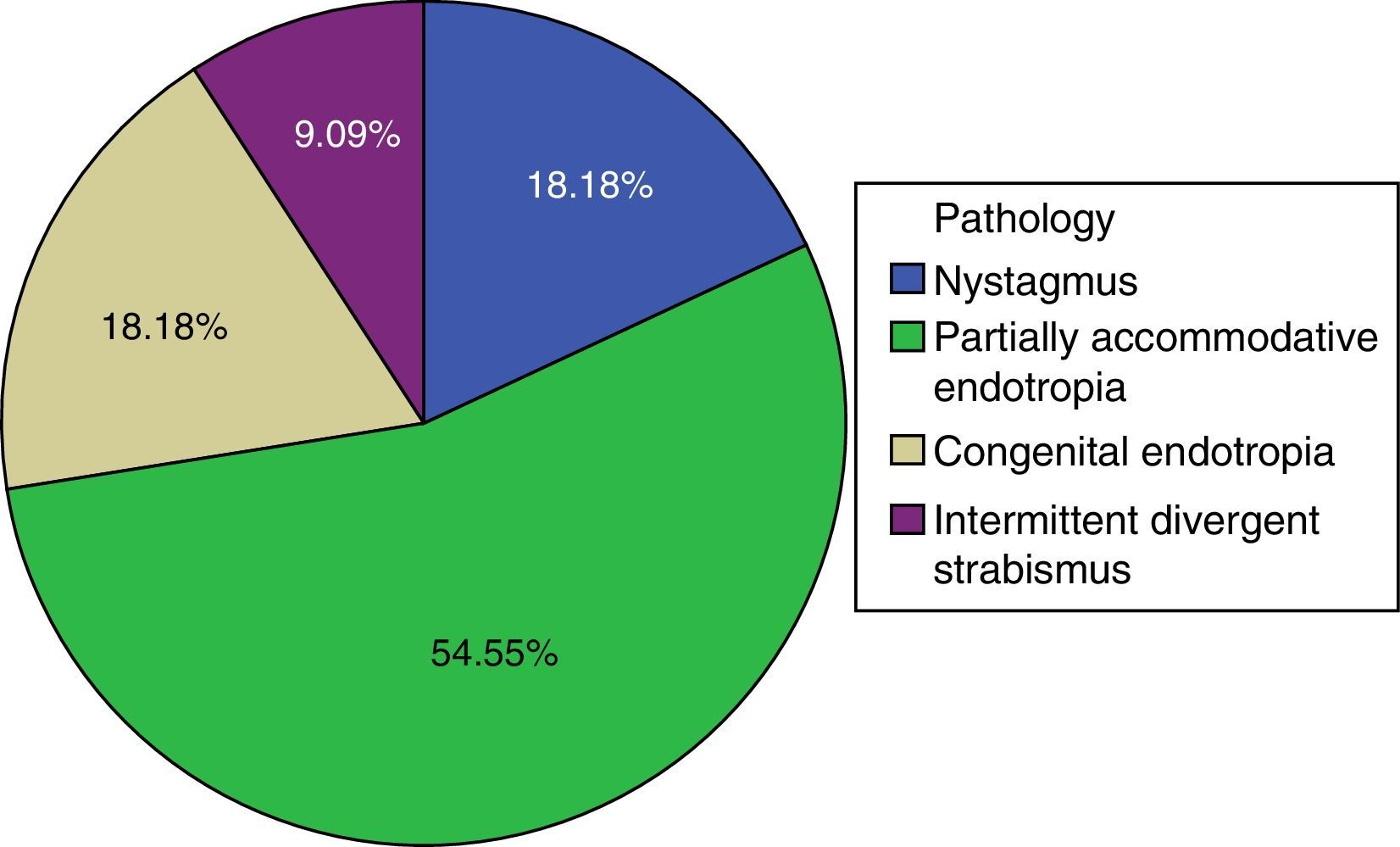
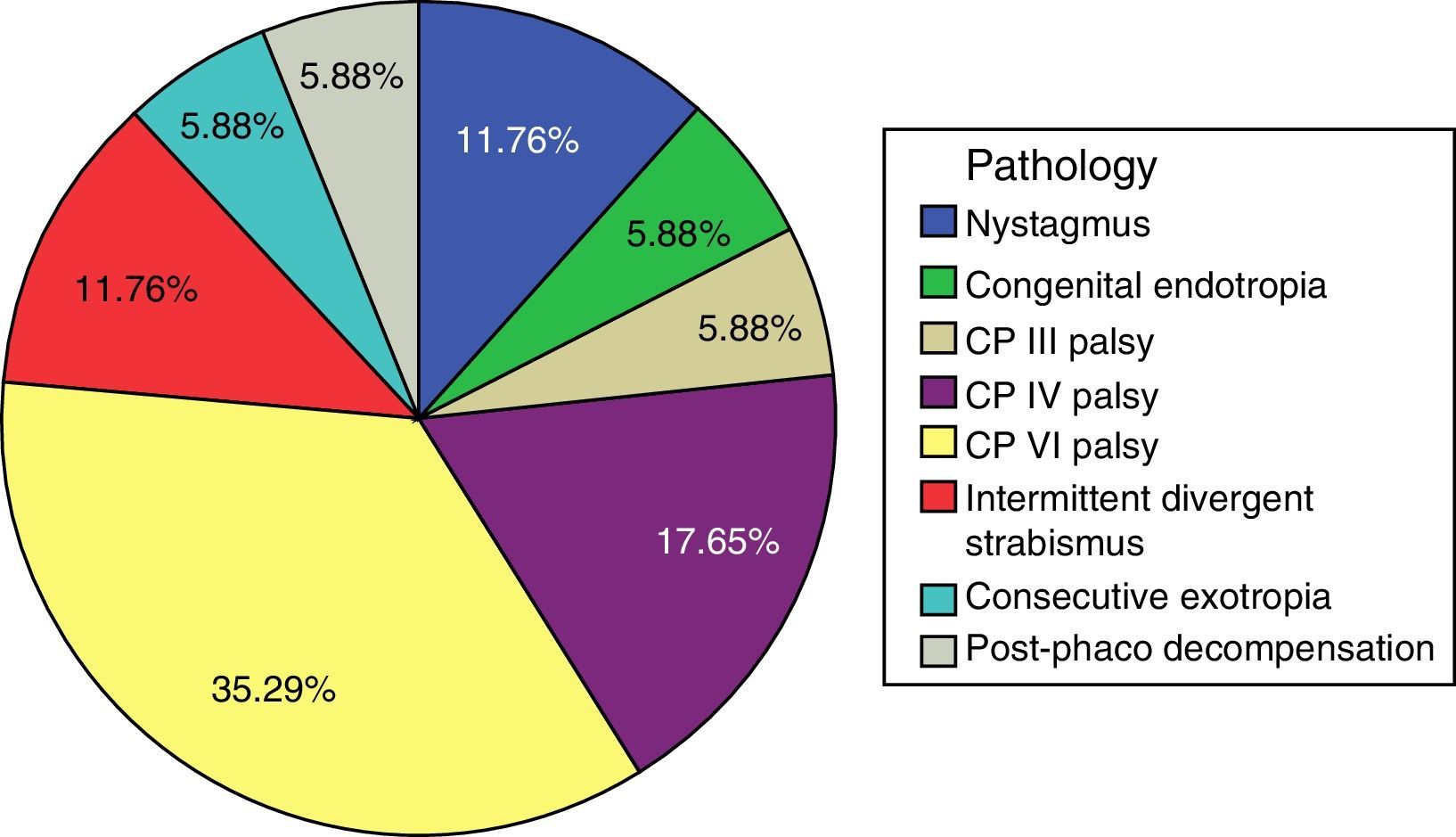
The majority of cases in both groups were esotropia (81.8% in children and 47.1% in adults). However, the pathologies in the adult group were quite heterogeneous, including four patients with exotropia (26.5%), four with hypertropia (26.5%), and one with isolated nystagmus (5.9%).
The mean number of the botulinum toxin injections in children was 1.45±0.93, although 72.7% received a single injection. In the adult group, the mean number of injections was 3.27±1.41.
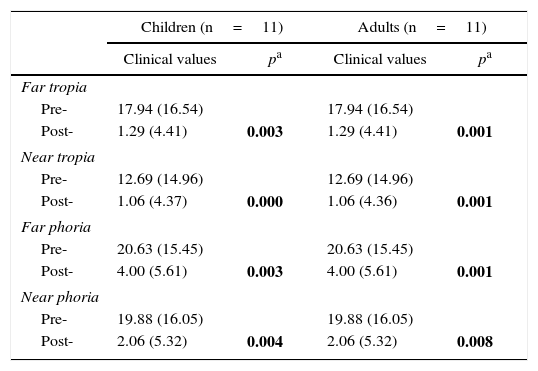
There was a statistically significant difference between pre- and post-injection in the tropia and phoria measurements in children and adults group (p<.05). In both groups there was a statistically significant improvement in post-injection torticollis when compared with the pre-injection measurement (p<.05).
An improvement in the stereoacuity could be detected in four children.
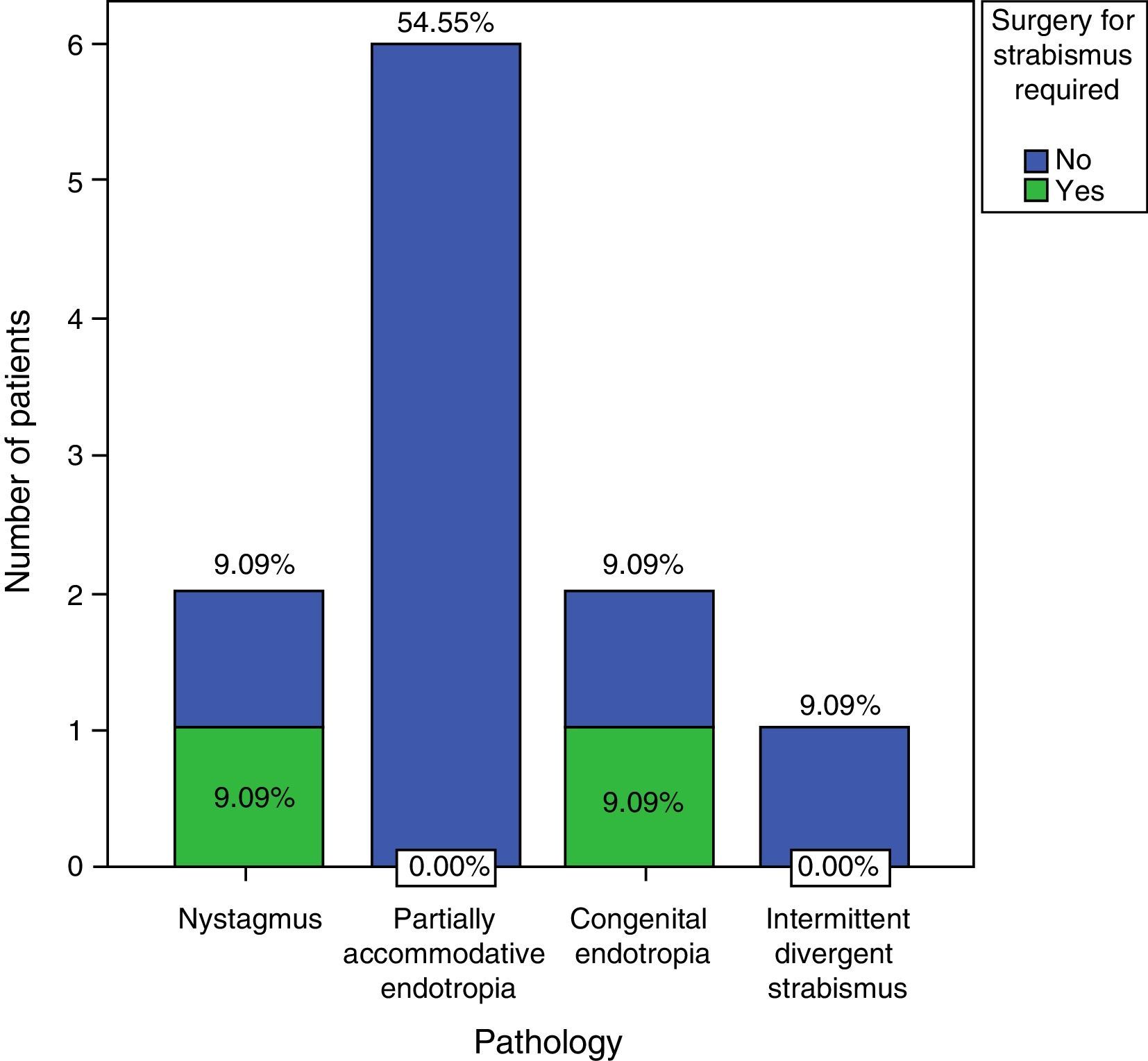
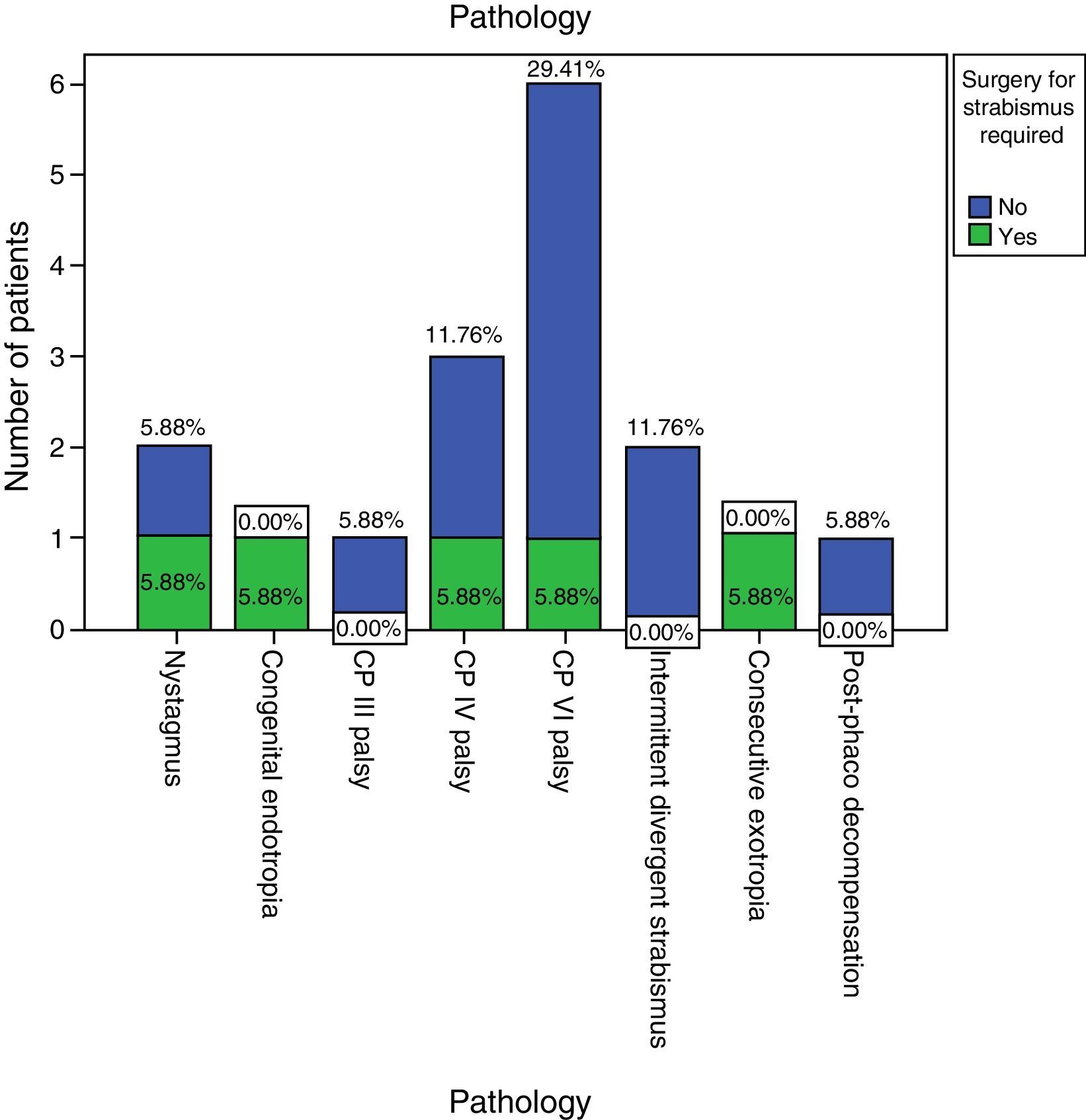
Two children (18.2%) and five adults (29.4%) required subsequent surgical intervention.
Eight adult patients (49.1%) complained of diplopia in the primary position, which was resolved in six cases with toxin injection, whereas two needed surgery for diplopia correction.
ConclusionsBotulinum toxin is a very useful tool in the management of strabismus, obtaining better sensory and motor results in children, but it is also effective as a symptomatic treatment in some types of strabismus in adults.
Analizar las indicaciones, dosis y eficacia de las inyecciones de toxina botulínica A en el departamento de Estrabología.
MétodoEn este estudio prospectivo, 28 pacientes diagnosticados de estrabismo fueron tratados con toxina botulínica. Se recopilaron los pacientes tratados en 2013 en el Hospital Rey Juan Carlos (Móstoles) para estudiar las indicaciones, la dosis empleada, y se analizaron los resultados de la última revisión, tanto en niños como en adultos, con un seguimiento mínimo de 14 meses.
ResultadosSe recogieron datos de 11 niños, 6 mujeres (54,5%), y 17 adultos, 11 varones (64%). La edad media fue 4,42±3,48 años y 58,71±18,07 años en niños y adultos respectivamente.
En ambos grupos la mayoría de los casos eran endotropias (81,8% en niños y 47,1% en adultos), aunque el grupo de adultos presentaba enfermedades más heterogéneas incluyendo 4 pacientes con exotropía (26,5%), 4 con hipertropía (26,5%) y uno con nistagmo aislado (5,9%).
La media de inyecciones en niños fue de 1,45±0,93, aunque el 72,7% recibieron una única inyección; en el grupo de adultos la media de inyecciones fue de 3,27±1,41.
Se encontró una diferencia estadísticamente significativa en la comparación de tropia y foria prepostinyección en niños y adultos (p<0,05). En ambos grupos hubo una mejoría significativa en el tortícolis postinyección comparado con el previo (p<0,05).
En 4 niños pudimos detectar una mejoría en la estereoagudeza.
Dos niños (18,2%) y 5 adultos (29,4%) precisaron intervención quirúrgica posterior. Ocho adultos (49,1%) presentaban diplopia en posición primaria de la mirada, que se resolvió en 6 casos con inyecciones de toxina, pero 2 necesitaron cirugía para la corrección de la diplopia.
Las diferencias entre tropia y foria pre- y postintervención fueron estadísticamente significativas (p<0,05), así como las diferencias entre el tortícolis pre- y postinyección. En 4 casos se pudo detectar mejoría en la estereoagudeza.
ConclusionesLa toxina botulínica es un fármaco muy útil en el estrabismo, con mejores resultados sensoriales y motores en los niños, pero eficaz como tratamiento sintomático en algunos casos de estrabismo en adultos.