The objective is to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of a surgeon's learning curve for holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) in 125 consecutive cases.
Materials and methodsPreoperative baseline characteristics, functional outcomes, surgical times, and complications of the first 125 patients treated by HoLEP were recorded. The sample was divided into quintiles (25 cases/group), and statistical analysis was carried out using the ANOVA test, Kruskal-Wallis H test, Chi-squared test, and likelihood-ratio test.
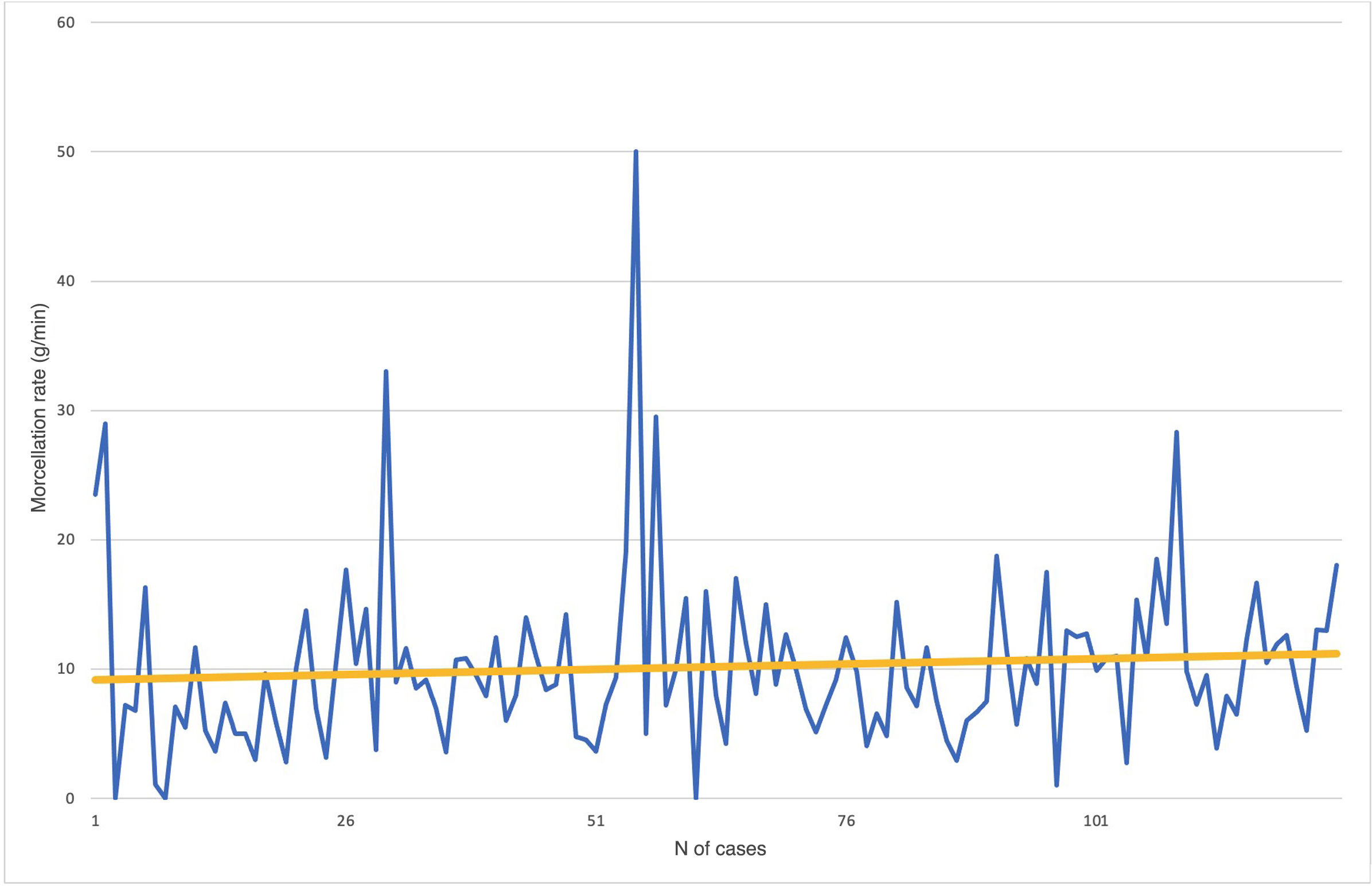
ResultsSurgical time decreased progressively: 92 min. (Q1), 65 min. (Q2), 54 min. (Q3), 45 min. (Q4) and 50 min. (Q5) (p < 0.001). Enucleation rate gradually increased: 1.08 g/min (Q1), 1.65 g/min (Q2), 1.82 g/min (Q3), 1.96 g/min (Q4) and 2.74 g/min (Q5) (p < 0.001). There were no differences in enucleated weight (Q1: 51 g, Q2: 57 g, Q3: 51 g, Q4: 53 g, Q5: 65 g) (p = 0.21), length of hospital stay (median 1.12 days), bladder catheterization (mean 1.51 days), intra- and postoperative complications or urethral stricture (5.6%) (p > 0.05). Time to continence recovery was similar in quintiles 1–4 (23, 27, 21, 20 days) and shorter in quintile 5 (3.5 days) (p < 0.001).
ConclusionThe initiation of a HoLEP program following the completion of training demonstrates a low morbidity rate and highly favorable functional outcomes. The efficiency of the technique demonstrates a linear and consistent increase from the outset of the learning curve, with significantly reduced surgical times achieved after 25 cases.
Evaluar la eficacia y seguridad de la curva de aprendizaje en enucleación prostática con láser de Holmio (HoLEP) de un cirujano en 125 casos consecutivos.
Materiales y métodosSe registraron características basales preoperatorias, resultados funcionales, tiempos quirúrgicos y complicaciones de los primeros 125 pacientes tratados mediante HoLEP, dividiendo la muestra en quintiles (25 casos/grupo), realizando el análisis estadístico con test de ANOVA, H de Kruskal–Wallis, test de Chi2 y razón de verosimilitud.
ResultadosEl tiempo quirúrgico disminuyó progresivamente: 92 min (Q1), 65 min (Q2), 54 min (Q3), 45 min (Q4) y 50 min (Q5) (p < 0,001). La velocidad de enucleación aumentó gradualmente: 1,08 g/min (Q1), 1,65 g/min (Q2), 1,82 g/min (Q3), 1,96 g/min (Q4) y 2,74 g/min (Q5) (p < 0,001). No hubo diferencias en volumen enucleado (Q1: 51 g, Q2: 57 g, Q3: 51 g, Q4: 53 g, Q5: 65 g) (p = 0,21), tiempo de hospitalización (mediana 1,12 días), sondaje vesical (media 1,51 días), complicaciones intra y postoperatorias ni estenosis de uretra (5,6%) (p > 0,05). El tiempo hasta continencia fue similar en los quintiles 1 a 4 (23, 27, 21, 20 días), siendo menor en el quintil 5 (3,5 días) (p < 0,001).
ConclusionesEl inicio de un programa de HoLEP tras realizar formación dirigida presenta baja morbilidad y excelentes resultados funcionales. La eficiencia de la técnica aumenta de forma lineal y constante desde el inicio de la curva de aprendizaje, consiguiendo tiempos quirúrgicos significativamente menores a partir de los 25 casos.