Evaluation of the effectiveness of cognitive biopsy (CB) in patients with clinical suspicion of prostate cancer (PC), and at least one negative biopsy (TRB).
Material and methodRetrospective study of 144 patients with at least one previous TRB and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The MRI nodules were classified based on PI-RADS v2 grouping pZa, pZpl and pZpm as the peripheral zone (PZ), Tza, Tzp and CZ as the transitional zone (TZ), and the AS zones as the anterior zone (AZ). A biopsy was indicated for nodules ≥PI-RADS 3. Uni and multivariate analysis was undertaken (logistic regression) to identify variables relating to a PI-RADS 3 tumour on biopsy.
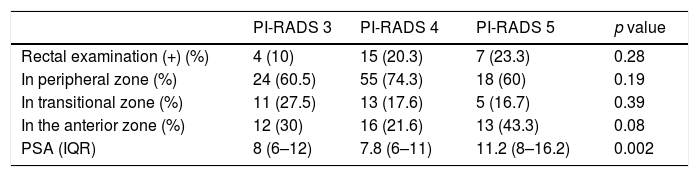
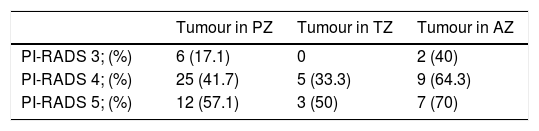
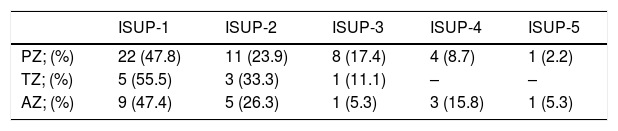
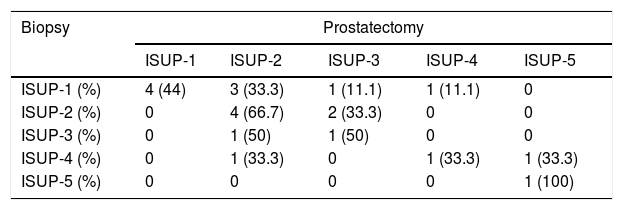
ResultsThe median age was 67 (IQR: 62–72) years, the median PSA was 8.2 (IQR: 6.2–12)ng/ml. A nodule was identified on MRI in the PZ in 97 (67.4%) cases, in the TZ in 29 (20.1%), and in the AZ in 41 (28.5%). PC was diagnosed on biopsy in 64 (44%) patients. The cancer rate in the PI-RADS 3 lesions was 17.5% (7/40), in the PI-RADS 4 47.3% (35/73), and in the PI-RADS 5 lesions it was 73.3% (22/29) (p=0.0001). Multivariable analysis with variables that could influence the biopsy result in patients with PI-RADS 3: none (age, PSA, number of previous biopsies, rectal examination, PSAD, prostate volume or number of extracted cylinders) behaved as an independent tumour predictor.
ConclusionsThe diagnostic performance of CB in patients with at least one previous negative biopsy was 44%, increasing according to the PI-RADS grade, and low in PI-RADS 3. No clinical variable predictive of cancer was found in patients with PI-RADS 3.
Evaluación de la efectividad de la biopsia cognitiva (BC) en los pacientes con sospecha clínica de cáncer de próstata (caP) y al menos una biopsia negativa (BTR).
Material y métodoAnálisis retrospectivo de 144 pacientes con al menos una BTR y una resonancia magnética nuclear (RMN) previa. Los nódulos de la RMN se clasificaron según la clasificación PI-RADS v2 agrupando pZa, pZpl y pZpm como zona periférica (ZP), Tza, Tzp y CZ como zona transicional (ZT) y áreas AS como zona anterior (ZA). Se indicó biopsia en nódulos ≥PI-RADS 3. Se llevó a cabo análisis uni y multivariante (regresión logística) tratando de identificar variables relacionadas con tumor en biopsia de PI-RADS 3.
ResultadosLa mediana de edad fue de 67 (IQR: 62-72) años, la de PSA 8,2 (IQR: 6,2-12)ng/ml. Se identificó nódulo en la RMN en la ZP en 97 (67,4%) casos, en la ZT en 29 (20,1%) casos y en ZA en 41 (28,5%) casos. Se diagnosticó caP en la biopsia en 64 (44%) pacientes. En PI-RADS 3 se obtuvo un 17,5% (7/40) de cáncer, PI-RADS 4 un 47,3% (35/73) y en los PI-RADS 5 un 73,3% (22/29) (p=0,0001). Análisis multivariable con variables que pudieran influir en el resultado de la biopsia en pacientes con PI-RADS 3: ninguno (edad, PSA, número de biopsias previas, tacto rectal, PSAD, volumen prostático ni número de cilindros extraídos) se comportó como factor predictor independiente de tumor.
ConclusionesEl rendimiento diagnóstico de la BC en pacientes con al menos una biopsia previa negativa fue del 44% incrementándose según el grado de PI-RADS, siendo en PI-RADS 3 bajo. No se identificó ninguna variable clínica predictora de caP en pacientes con PI-RADS 3.