Corynebacterium urealyticum (CU) affects patients who are immunosuppressed, chronically ill or have undergone numerous operations. Obstructive uropathy (OU) is a complication of infection.
Study objectiveTo demonstrate the growing increase in cases of infection by CU and OU in the past 5 years.
Material and methodsA descriptive study was conducted of urological patients with CU-positive urine cultures (January 2009–December 2014). We calculated the annual distribution and clinical characteristics of infection by CU and OU. Minimum follow-up: 6 months. We obtained the statistical means and ranges of clinical parameters pre/post-therapy.
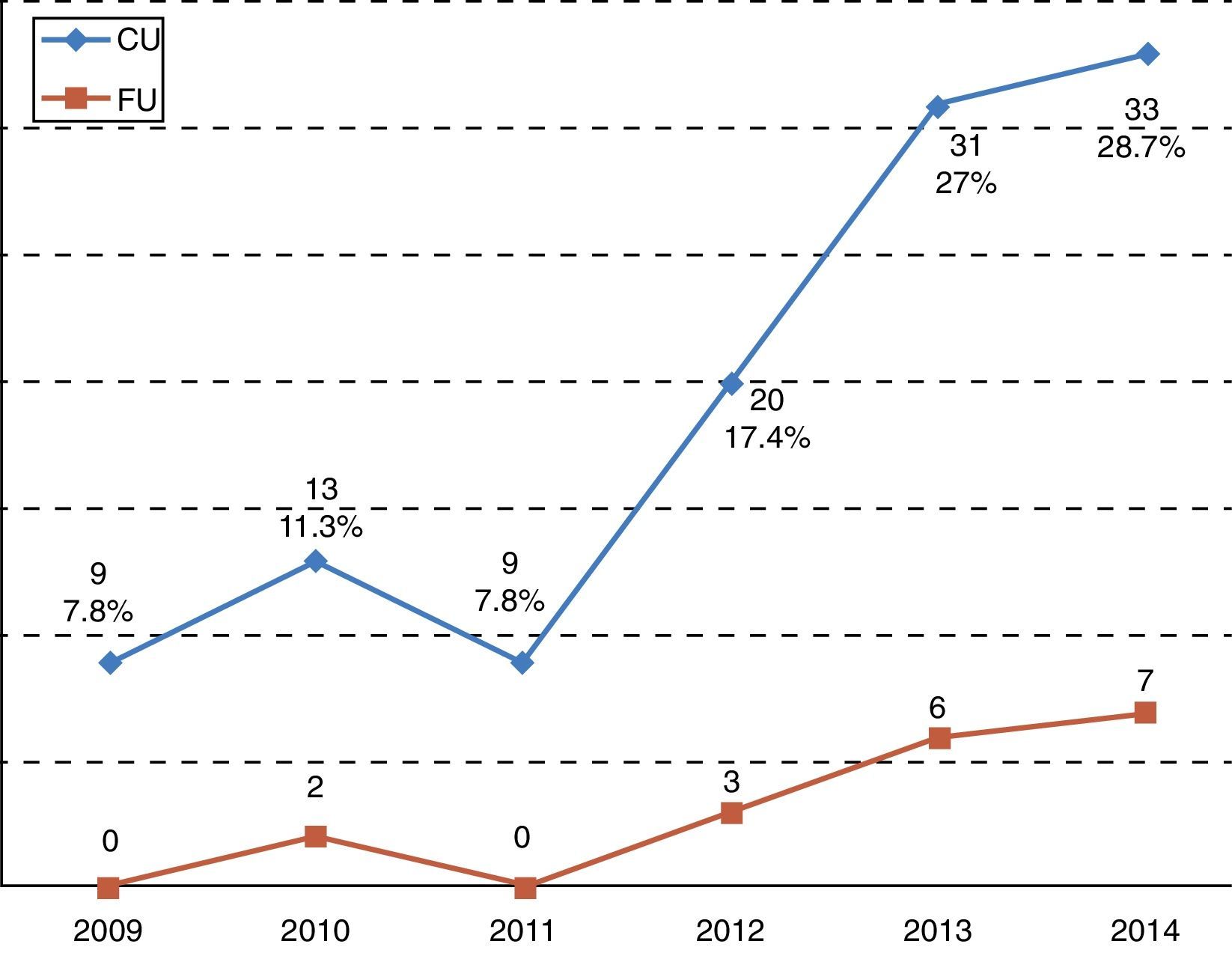
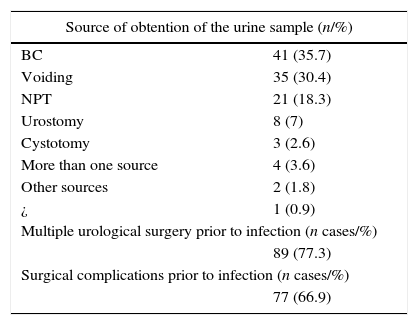
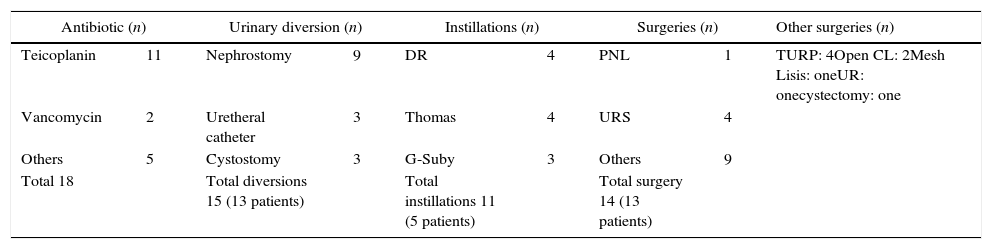
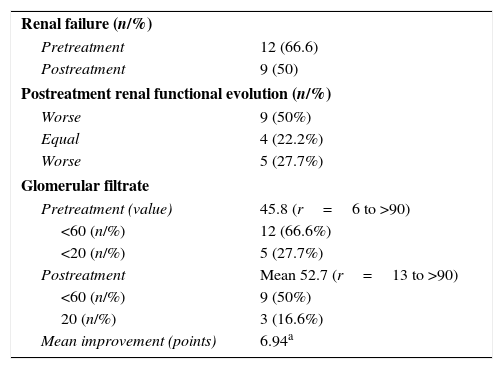
ResultsThe total number of patients with CU was 115 (men, 87; women, 28). The mean age was 67.9 years (range, 6–95 years), and the annual distribution of cases for 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013 and 2014 was 9 (7.8%), 13 (11.3%), 9 (7.8%), 20 (17.4%), 31 (27%) and 33 (28.7%), respectively. The increase in cases for 2009–2014 was 300%. Multiple urological surgeries were performed in 89 cases (77.3%), with surgical complications in 77 cases (66.9%). Eighteen (15.6%) patients had OU (men, 13; women, 5), 12 had pyelitis (66.7%), 3 had cystopathy (16.6%), 2 had prostatic capsule disease (11.2%) and 1 had mesh calcification (5.5%). The analysis of the 18 cases with OU showed pre/postantibiotic therapy urine pHs of 8 (r, 6–9) vs. 6 (r, 5–7). All postantibiotic cultures were negative. Acidifying solution was applied in 5 cases, and surgery was performed in 13 cases (72.2%). The results from before/after the multimodal therapy showed renal impairment in 12 (66.6%) vs. 9 cases (50%) and glomerular filtration rates (GFR) of 45.8 (r, 6 to >90) vs. 52.7 (r, 13 to >90). The improvement in GFR was 6.94 points (T Wilcoxon; p=.102). The radiology results (incrustations) showed improvement in 13 patients (72.2%) and no change in 5 (27.8%). There was no specific mortality for CU.
ConclusionsThe prevalence of infection by CU and OU is increasing. Antibiotic treatment is highly effective. Acidifying solutions are an acceptable option for reducing calcifications.
Corynebacterium urealyticum (CU) afecta a pacientes inmunodeprimidos, crónicos o multioperados. La uropatía incrustante (UI) representa una complicación de la infección.
Objetivo del estudioDemostrar el aumento creciente de casos de infección por CU y UI en los últimos 5 años.
Material y métodosEstudio descriptivo de pacientes urológicos con urocultivo positivo a CU (enero de 2009-diciembre de 2014). Cálculo de distribución anual y características clínicas de infección por CU y UI. Seguimiento mínimo: 6 meses. Obtención de medias y rangos estadísticos de parámetros clínicos pre/postratamiento.
ResultadosTotal de pacientes con CU: 115 (hombres 87: mujeres 28). Edad: 67,9 años (rango 6-95). Distribución anual (casos) 2009: 9 (7,8%), 2010: 13 (11,3%), 2011: 9 (7,8%), 2012: 20 (17,4%), 2013: 31 (27%), 2014: 33 (28,7%). Incremento 2009-2014: 300%. Cirugía urológica múltiple: 89 casos (77,3%). Complicaciones quirúrgicas: 77 casos (66,9%). Pacientes con UI: 18 casos (15,6%) (hombres 13: mujeres 5): pielitis 12 (66,7%), cistopatía 3 (16,6%), prostatic capsule disease 2 (11,2%), calcificación de la malla uno (5,5%). Análisis de 18 casos con UI: PH orina pre/postantibiótico: 8 (r=6-9) vs 6 (r=5-7). Cultivo negativo postantibiótico: 100%. Aplicación de solución acidificante: 5 casos. Cirugía: 13 casos (72,2%). Resultados pre/postratamiento multimodal: insuficiencia renal: 12 (66,6%) vs 9 (50%), filtrado glomerular (FG): 45,8 (r=6->90) vs 52,7 (r=13->90). Mejoría del FG: 6,94 puntos (T Wilcoxon p=0,102). Radiología (incrustaciones): mejoría 13 (72,2%), igual 5 (27,8%). No mortalidad específica por CU.
ConclusionesLa prevalencia de infección por CU y la UI está aumentando. El tratamiento antibiótico es muy eficaz. Las soluciones acidificantes son una opción aceptable para reducir calcificaciones.