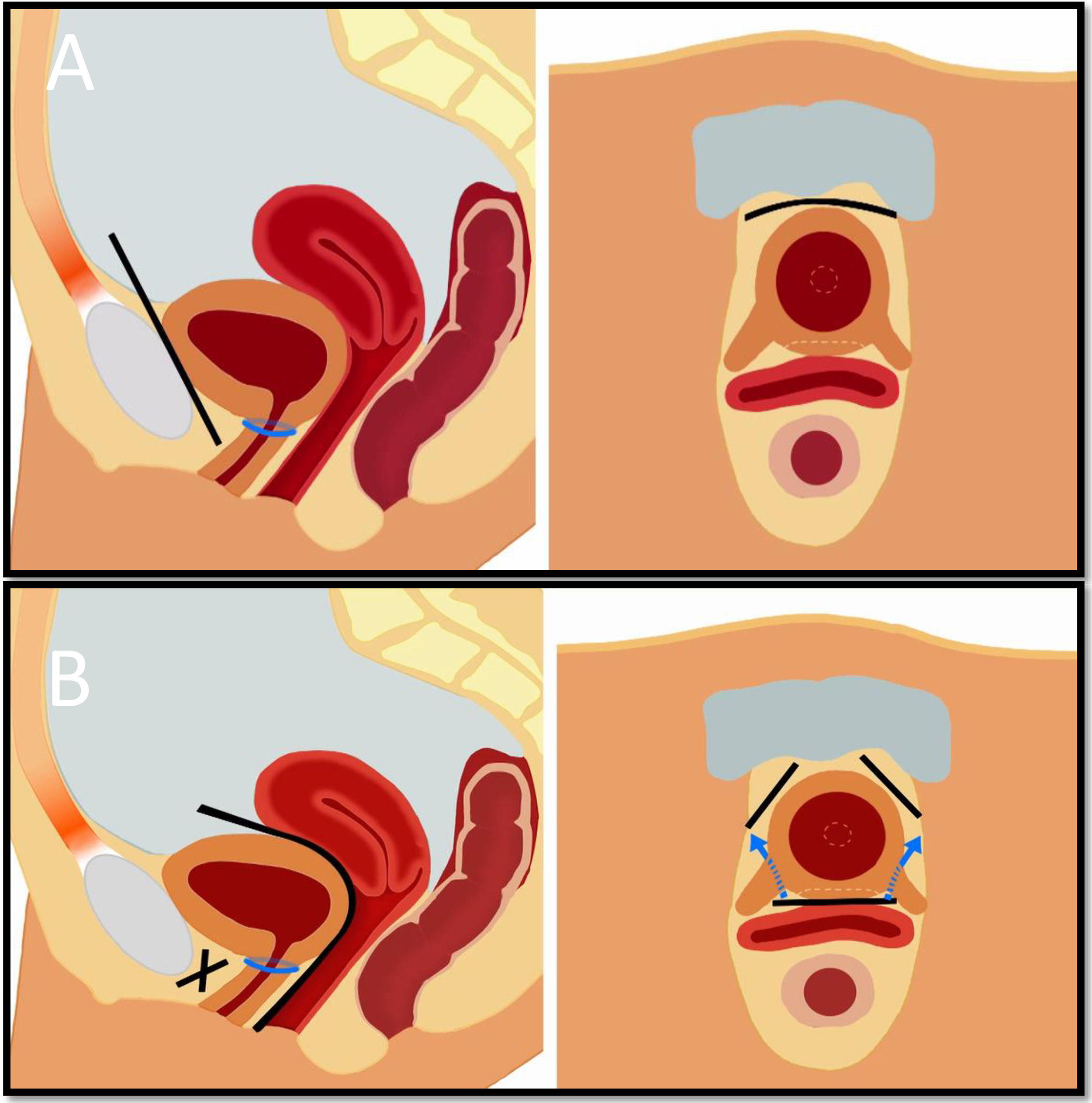
The artificial urinary sphincter (AUS) is not used extensively in the treatment of female urinary stress incontinence (USI) due to the poor reproducibility of the techniques used. We describe a new approach to laparascopic implantation, of which dissection of the vesicovaginal space is an essential step. This enables an approach under direct vision to the posterior surface of the bladder neck.
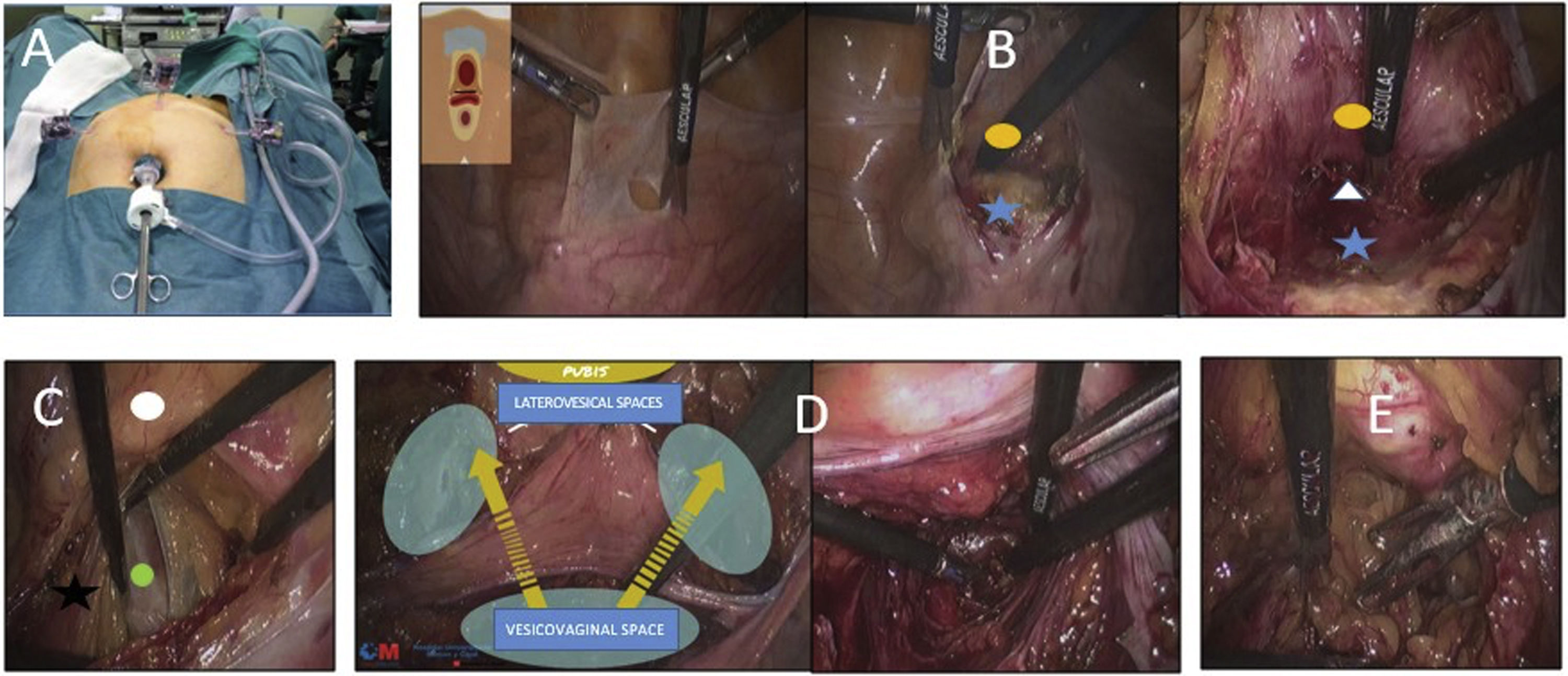
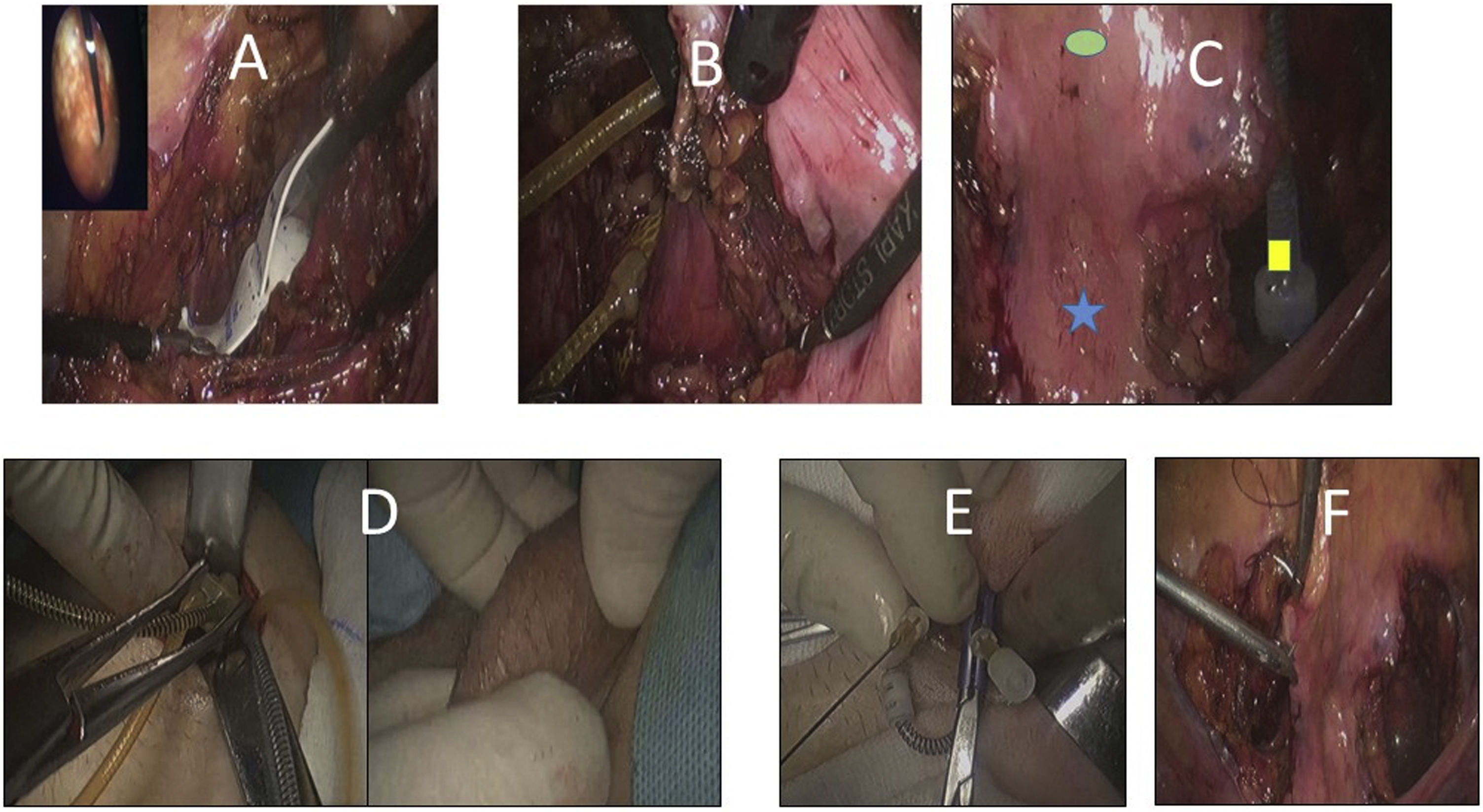
Material and methodsWe present two cases where this approach was used. A transperitoneal approach was made in the Trendelenburg position. The main steps were: creating the vesicovaginal space until identifying the bladder neck, creating two laterovesical spaces, communicating these with the vesicovaginal space, and dissecting the anterior surface of the bladder neck, attempting to preserve the pubovesical ligament. The cuff and reservoir were inserted through the 12mm infraumbilical trocar. The connections were externalized through a left suprapubic incision and a subcutaneous tunnel created up to the labia majora where the activation pump was placed. The procedure was completed with closure of the peritoneum. It is essential to use a vaginal valve to facilitate dissection.
ResultsSurgery time: 140 and 135min, with no intraoperative complications. After removing the urinary catheter, one patient had elevated postvoid residual urine volume, which was managed conservatively. Hospital stay: 72h. At 3 and 9 months the patients were fully continent.
ConclusionsWe present the preliminary results of laparoscopic implantation of an AUS through a vesicovaginal approach to the posterior surface of the bladder neck, which might reduce potential complications that have been observed after the routine techniques.
El esfínter urinario artificial (EUA) no está extendido en el tratamiento de la incontinencia urinaria de esfuerzo (IUE) femenina debido a la baja reproducibilidad de las técnicas empleadas. Describimos un nuevo abordaje de implante laparoscópico, cuyo paso fundamental consiste en disecar el espacio vesicovaginal. Esto permite una aproximación bajo visión directa a la cara posterior del cuello vesical.
Material y métodosPresentamos dos casos realizados con esta aproximación. Se realiza un abordaje transperitoneal en posición de Trendelenburg. Los principales pasos son: creación del espacio vesicovaginal hasta identificar el cuello, creación de dos espacios laterovesicales, comunicación de los mismos con el espacio vesicovaginal y disección de la cara anterior del cuello intentando preservar el ligamento pubovesical. El manguito y reservorio se introducen a través del trocar infraumbilical de 12mm. Por una incisión suprapúbica izquierda se externalizan las conexiones y se crea un túnel subcutáneo hasta el labio mayor, donde se coloca la bomba de activación. Finaliza el procedimiento con el cierre del peritoneo. Es fundamental la utilización de una valva vaginal para facilitar la disección.
ResultadosTiempo quirúrgico: 140 y 135min, sin complicaciones intraoperatorias. Tras la retirada de la sonda vesical una paciente presentó residuo posmiccional elevado que se manejó de forma conservadora. Estancia hospitalaria: 72h. A los 3 y 9 meses, las pacientes presentaron continencia total.
ConclusionesPresentamos resultados preliminares de implante laparoscópico de EUA mediante la aproximación vesicovaginal a la cara posterior del cuello, que podría disminuir las potenciales complicaciones observadas con las técnicas habituales.