Muscle tension dysphonia (MTD) is a voice disorder in the absence of current organic laryngeal pathology, without obvious psychogenic or neurological aetiology. The laryngeal features of MTD include a posterior glottal gap and supraglottic hyperfunctional activities; however, it remains unclear if these features are specific to MTD. This report aims to compare the laryngeal features in telemarketer patients with MTD versus non-dysphonic control subjects.
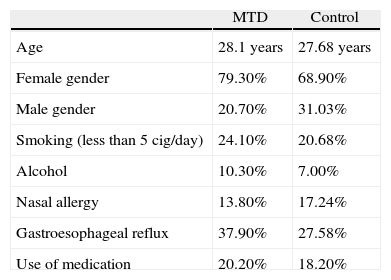
MethodsWe reported on an observational, analytic, and transversal study. Fiberoptic nasal endoscopy was performed on 57 patients (28 telemarketers with MTD and 29 control subjects). These random-sequence videotapes were independently rated by an expert laryngologist according to the modified Morrison and Rammage classification. In addition, a questionnaire about vocal symptoms and other details was completed.
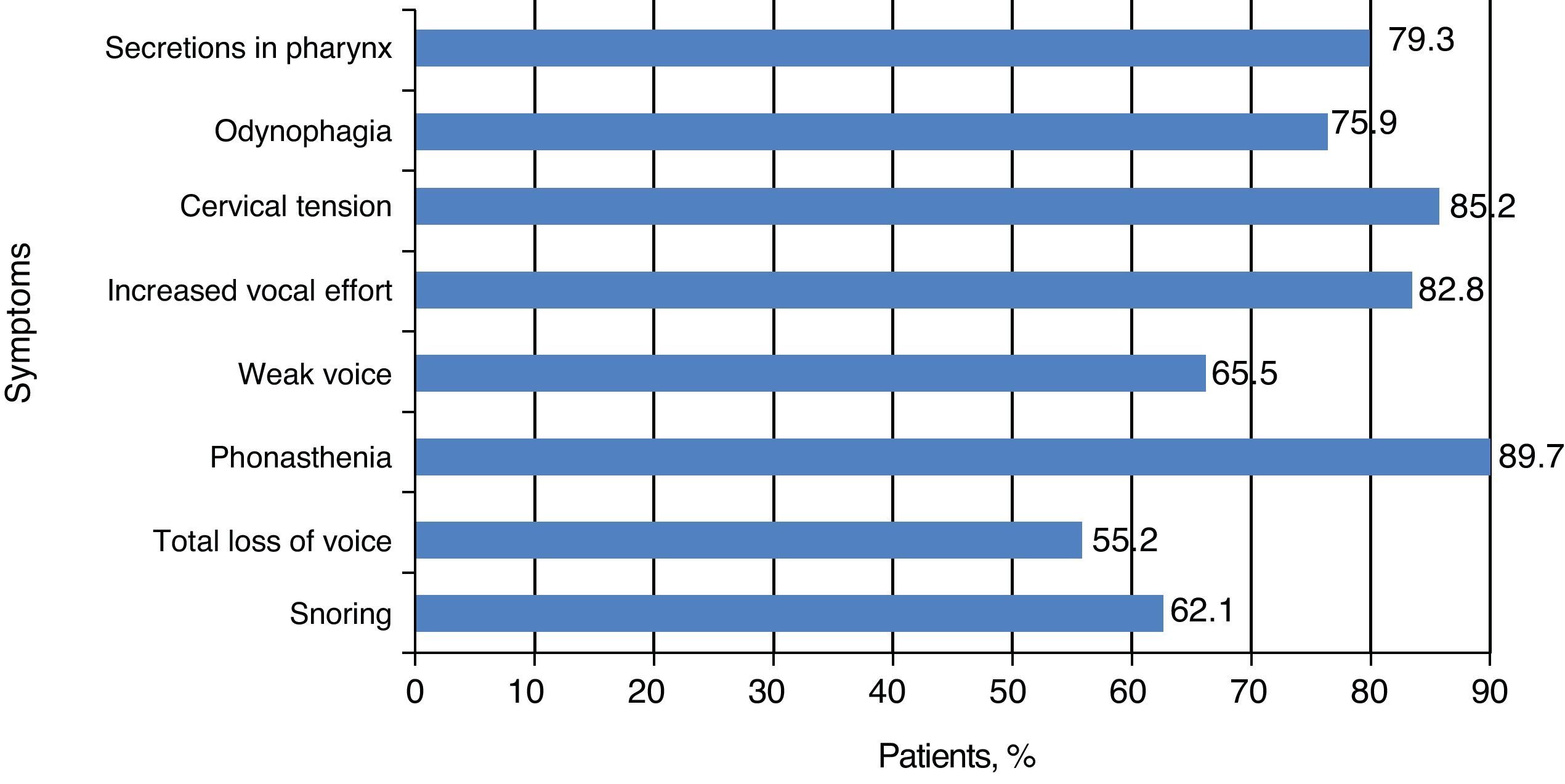
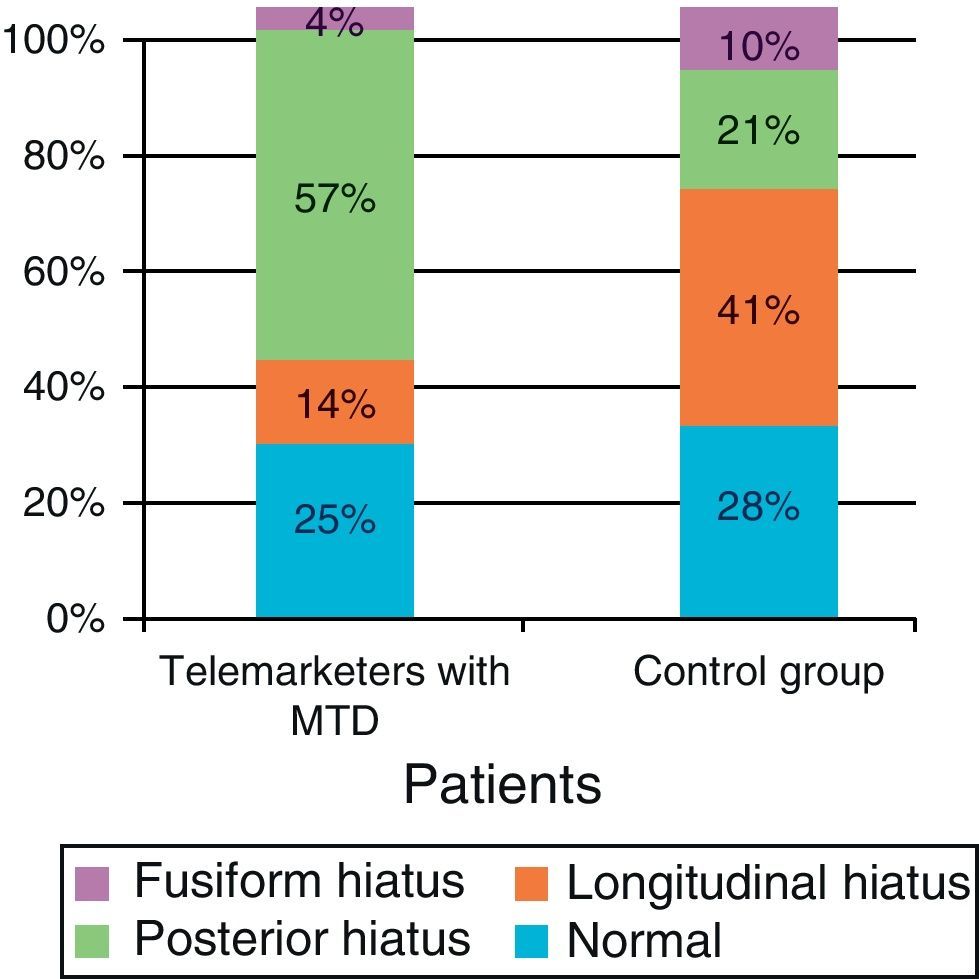
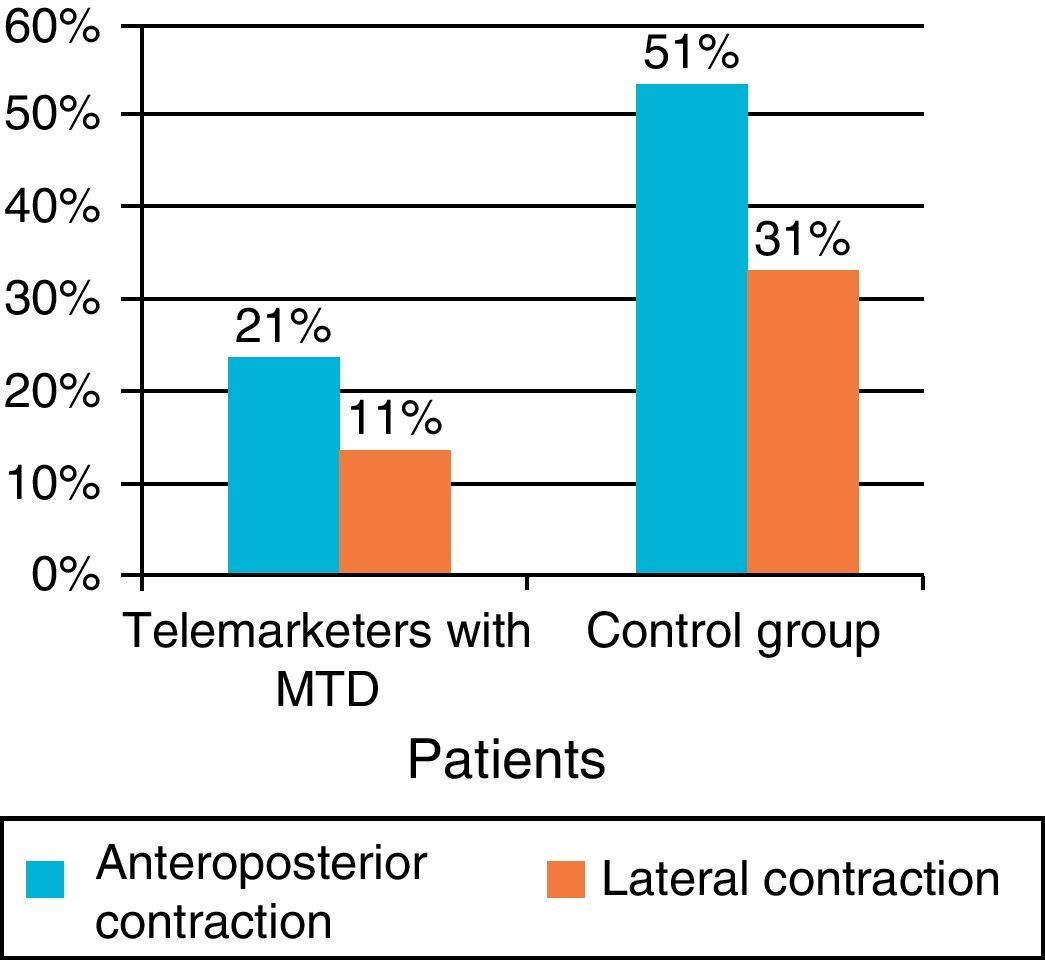
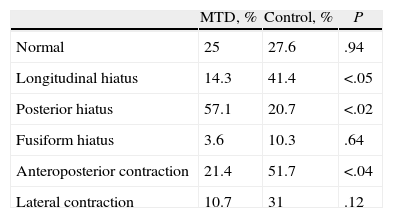
ResultsThe posterior glottal gap was the most common feature in telemarketers with MTD, while incomplete glottal gap was observed more frequently in non-dysphonic patients. More than 70% of the videotapes were rated as pathologic. There was no statistical difference in the prevalence of normal features or bowing glottal gap between patients and control subjects. Anterior–posterior supraglottic contraction was more frequent in the control group. The major symptoms found were: voice gets tired quickly, increased vocal effort and neck tension.
ConclusionsThe heterogeneity in the laryngeal features in telemarketers with MTD seen under fibroscopy and their presence among the non-dysphonic population suggest that they cannot determine by themselves the diagnosis of MTD.
La disfonía por tensión muscular (DTM) es una alteración de la voz en ausencia de patología laríngea orgánica, y sin alteraciones neurológicas o psicológicas evidentes. El hiatus posterior y la actividad supraglótica hipertónica son considerados como las manifestaciones fibrolaringoscópicas típicas de DTM, sin embargo, todavía permanece poco claro si estos patrones son específicos de esta patología. El objetivo principal de este estudio fue comparar los hallazgos fibrolaringoscópicos entre pacientes teleoperadores con DTM versus individuos sin síntomas vocales. Como objetivo secundario se persiguió describir las características personales, laborales y clínicas del grupo de teleoperadores.
MétodosEstudio observacional, analítico y transversal. Se reclutaron 57 pacientes (28 de DTM y 29 del grupo control) a los cuales se les realizó una fibrolaringoscopia, catalogados a ciegas por un laringólogo experto en función de la clasificación de Morrison y Rammage modificada. Además se llevó a cabo un cuestionario a ambos grupos acerca de antecedentes personales y laborales.
ResultadosEl hiatus posterior fue más prevalente en teleoperadores con DTM, mientras que en el grupo control lo fue el hiatus longitudinal. Más del 70% de las fibroscopias del grupo control fueron informadas como patológicas. La contracción supraglótica antero-posterior fue más frecuente en pacientes sanos. Los síntomas más relatados fueron fonastenia, tensión en musculatura del cuello y esfuerzo vocal aumentado.
ConclusiónLa heterogeneidad en los patrones fibroscópicos laríngeos en teleoperadores con DTM, así como su presencia en personas sanas, sugiere que los mismos en forma aislada no pueden establecer el diagnóstico de DTM.