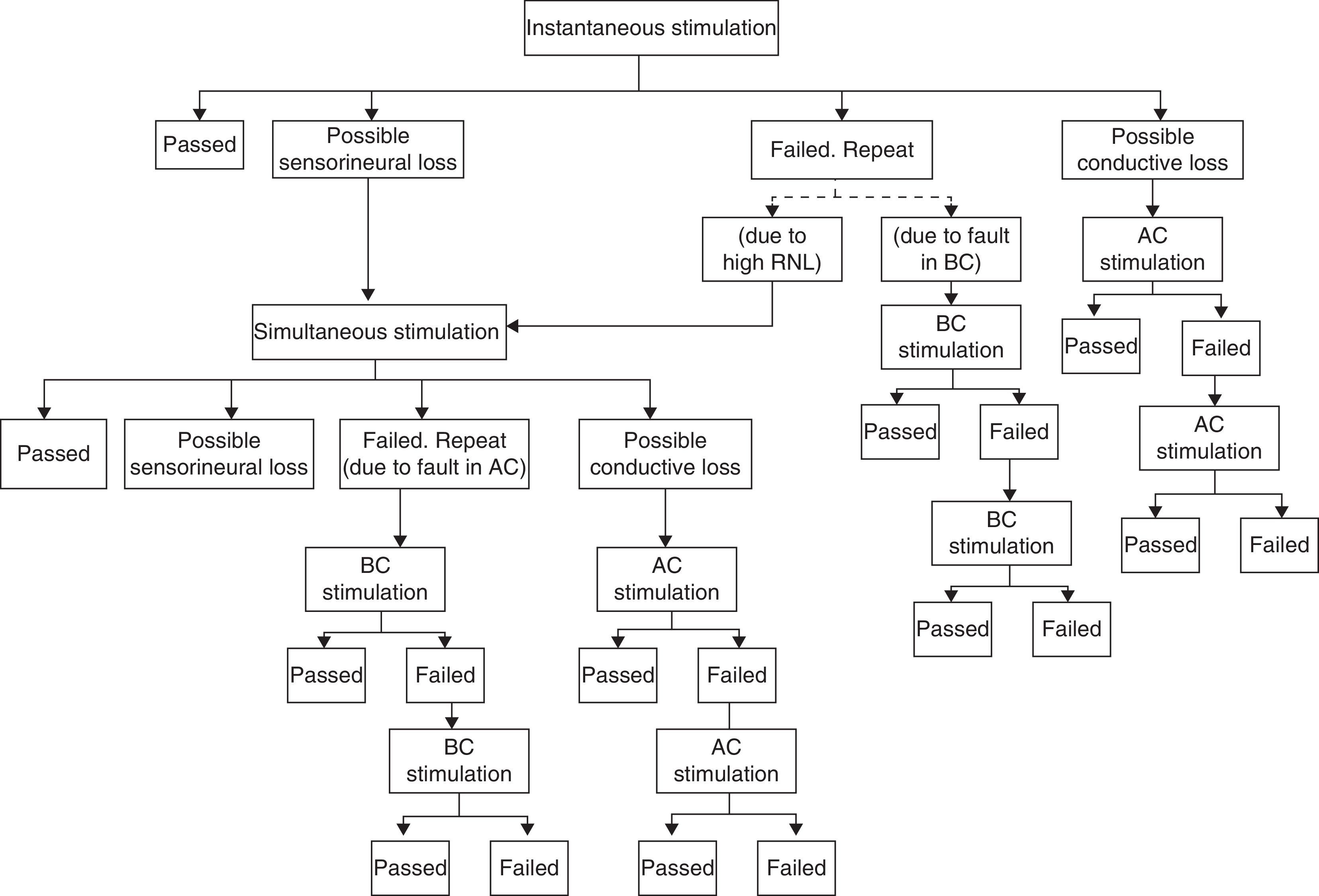
Minimising false positives rates is an important goal of universal newborn hearing screening programmes. An adequate way for reaching that goal could be differentiating between transient conductive hearing losses (false positives) and permanent sensorineural hearing impairments (true positives) by means of a methodology that studies electrophysiological responses obtained using both air- and bone-conduction stimuli.
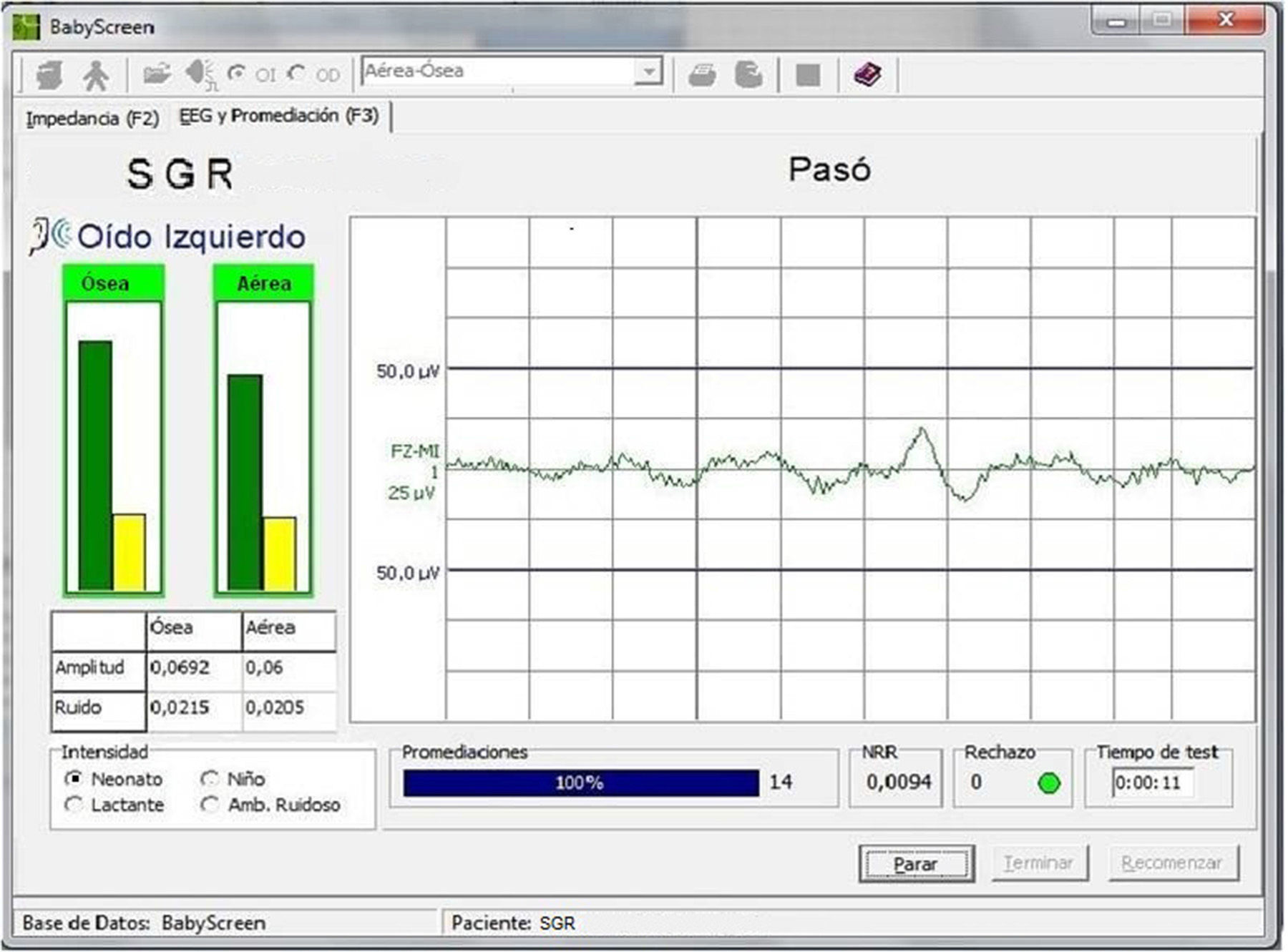
Our objective was to evaluate the efficiency of an automated hearing screening test based on auditory steady state responses obtained using simultaneous air- and bone-conduction stimuli.
MethodsA sample of 80 high risk babies less than 2 months of born were screened using the automatic screening test. A confirmatory clinical and electrophysiological evaluation was used as the gold standard.
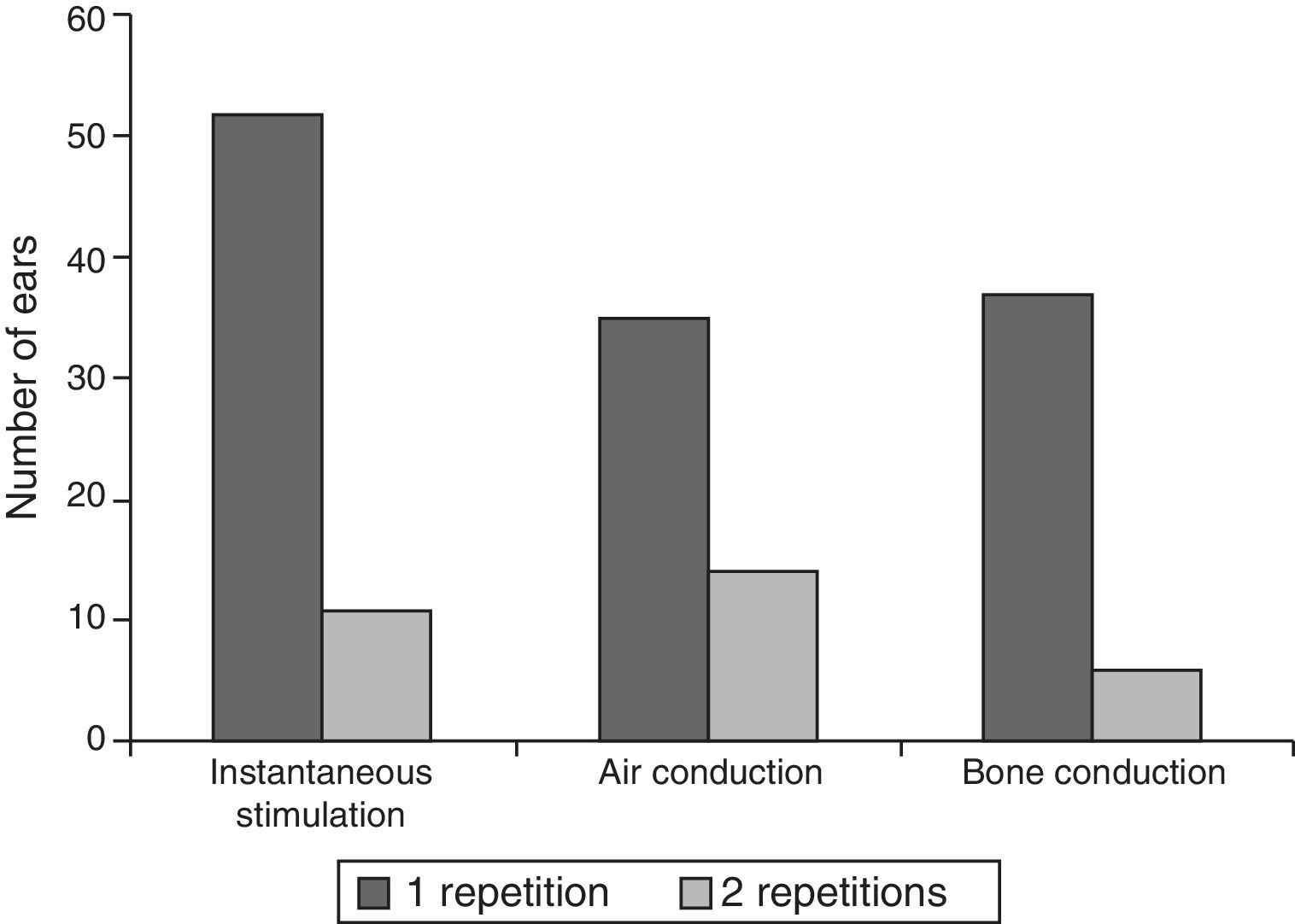
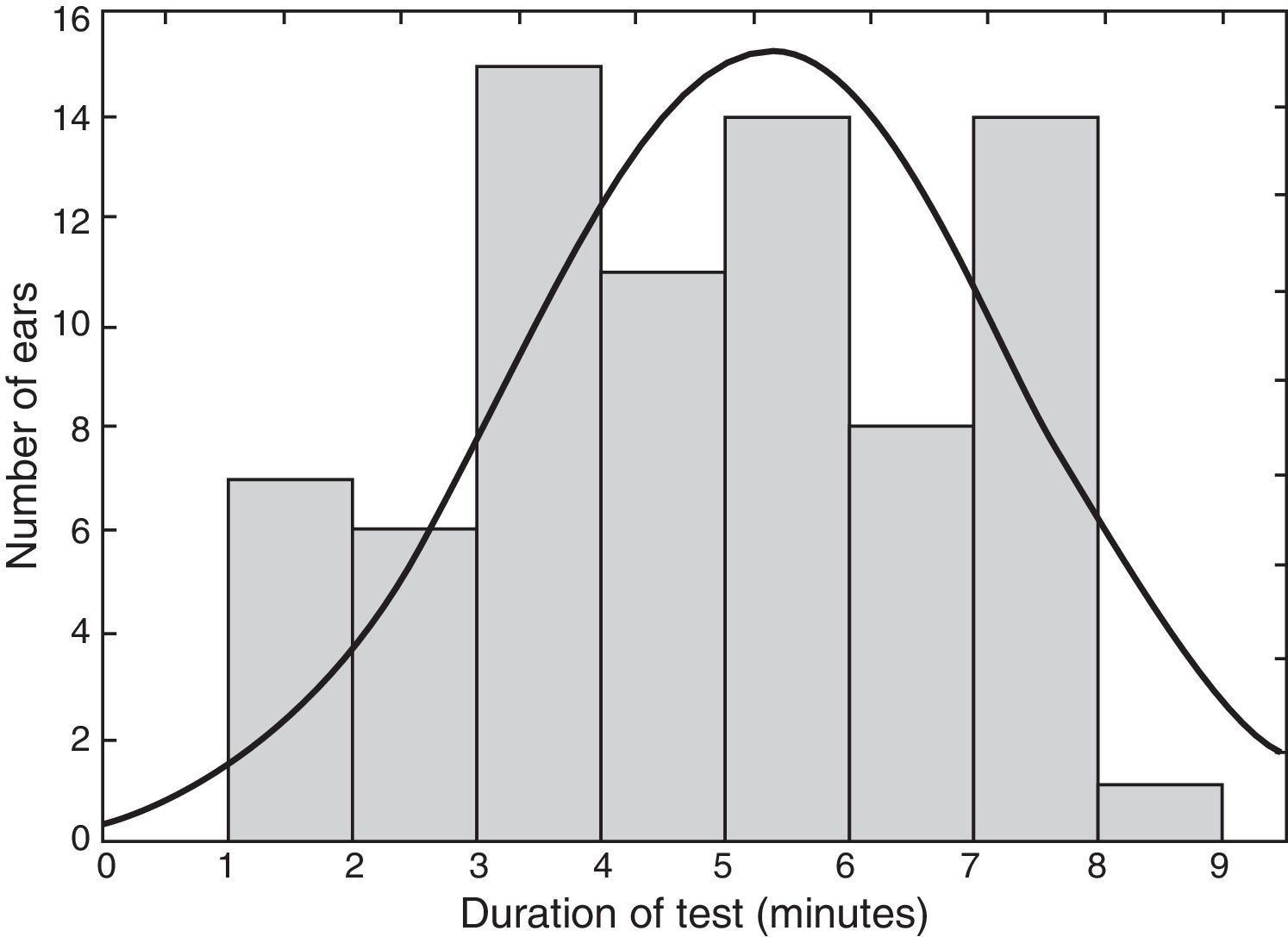
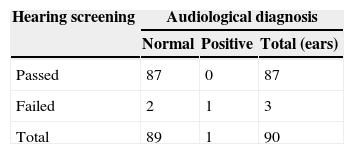
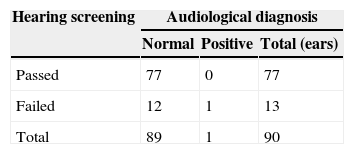
ResultsThe estimated diagnostic efficiency of this screening test was equivalent (100% sensitivity and 97.7% specificity) to the efficiency reported for otoacoustic emissions and automated auditory brainstem responses. The introduction of bone conduction in the screening reduced the false positive rate from 13.3% to 2.2%. The test duration was 5.3 (±1.9)min. In 34% of babies only one repetition of the test was needed to raising the result.
ConclusionsThe screening test performed quite well in this initial clinical trial, differentiating transient conductive hearing losses from permanent neurosensory impairments and improving the diagnostic efficiency of auditory steady state responses.
Minimizar los falsos positivos constituye un objetivo de los programas de cribado auditivo universal. Una manera de lograrlo sería diferenciar entre los trastornos neurosensoriales (verdaderos positivos) y los conductivos transitorios (falsos positivos) mediante un método que permita estudiar la respuesta del sistema auditivo ante la estimulación tanto por vía aérea como por vía ósea.
El objetivo de este trabajo es evaluarla eficiencia diagnóstica de una prueba automatizada de cribado basada en el registro de potenciales evocados auditivos de estado estable obtenidos por estimulación simultánea de vía aérea y vía ósea.
MétodosSe estudiaron 80 bebés menores de 2 meses de edad. A todos se les realizó la prueba de cribado, siendo posteriormente citados para el estudio confirmatorio, cuyo resultado se consideró como criterio de verdad del estado audiológico del bebé.
ResultadosCon esta prueba se obtuvo una eficiencia diagnóstica equivalente (un 100% de sensibilidad y un 97,7% de especificidad) a la reportada para otras pruebas utilizadas en el cribado (emisiones otoacústicas y potenciales evocados de tronco cerebral), con la ventaja adicional de que la introducción de la vía ósea en el cribado permitió reducir la cifra de falsos positivos del 13,3 al 2,2%. La duración de la prueba fue de 5,3 (±1,9)min, siendo suficiente en el 34% de los casos una sola repetición para llegar al resultado.
ConclusionesEsta prueba automatizada de cribado basada en el registro de potenciales evocados auditivos de estado estable permitió discriminar entre los trastornos conductivos transitorios y los neurosensoriales, reduciendo así los falsos positivos y elevando la eficiencia diagnóstica de esta metodología.