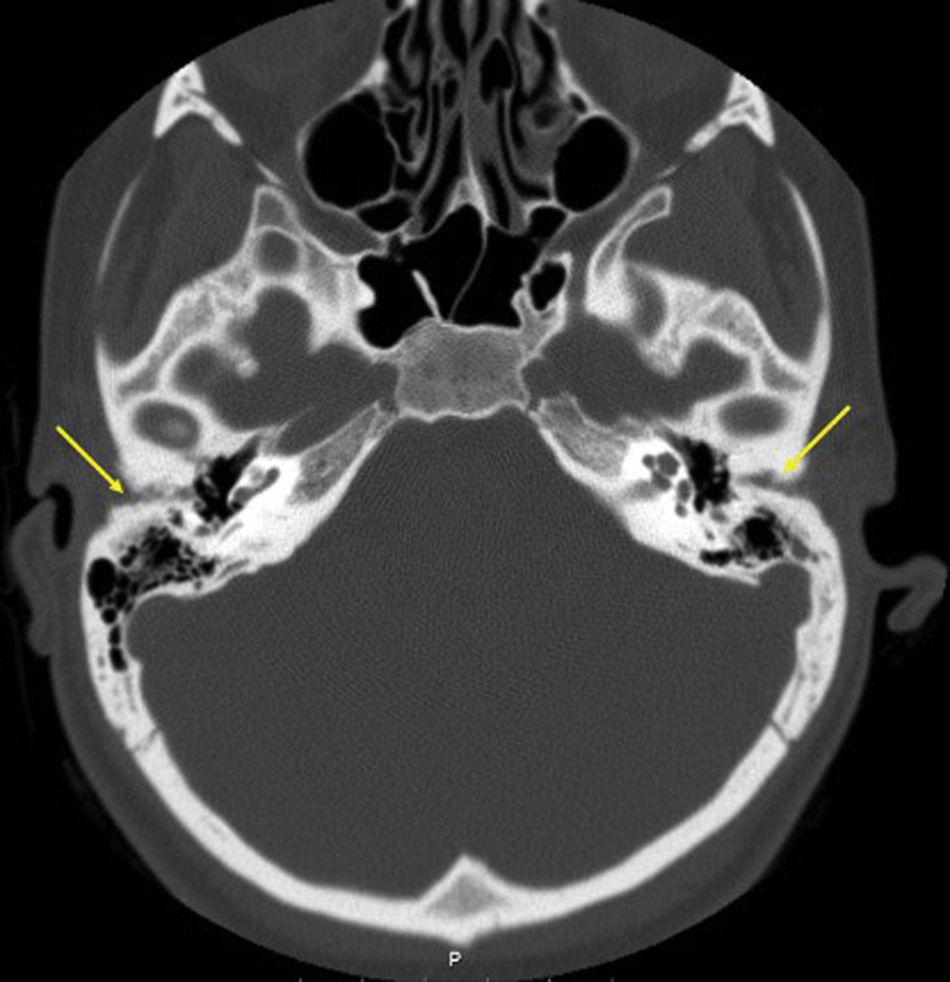
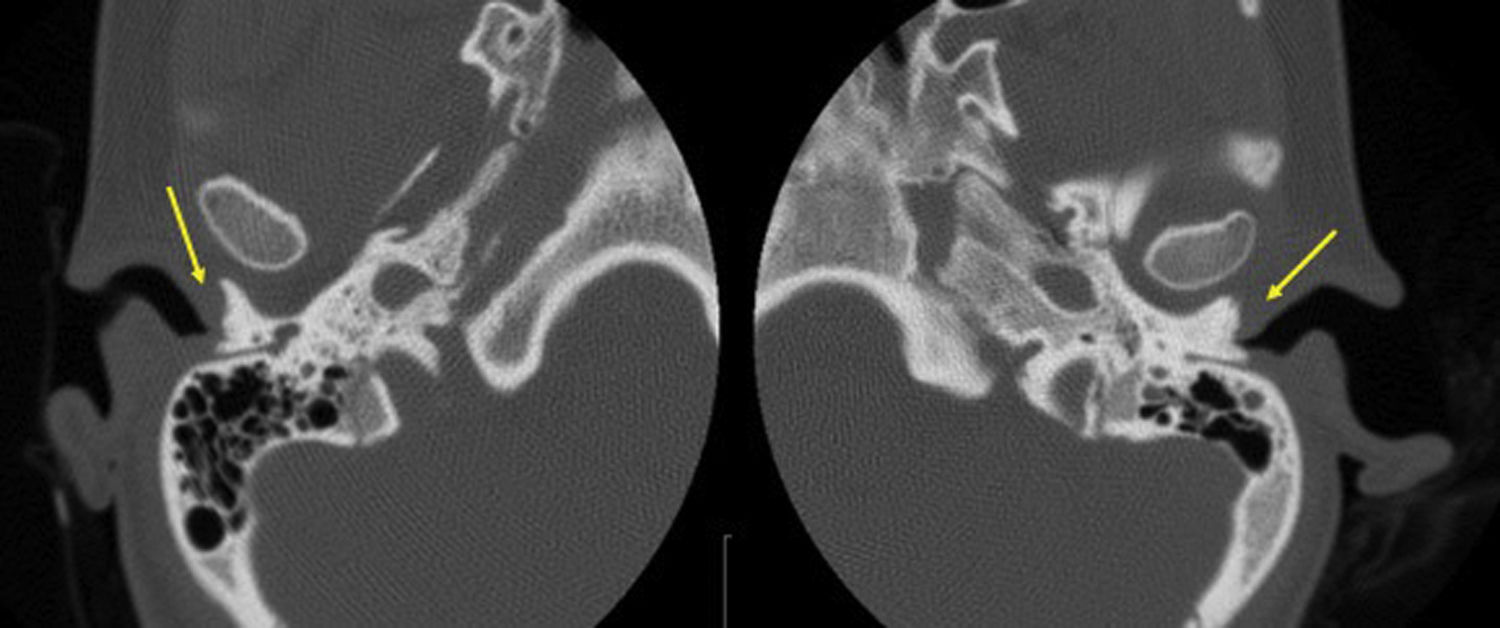
Congenital atresia of the external auditory canal (EAC) is a congenital defect present in one in every 10,000–20,000 births. It causes conductive hearing loss, with an air-bone gap of 50–60dB. Early amplification is essential in bilateral cases to ensure normal language development. The aim of this study is to present the osseointegrated hearing implant as a treatment for bilateral EAC atresia, reviewing the audiometric results and the rate of complications.
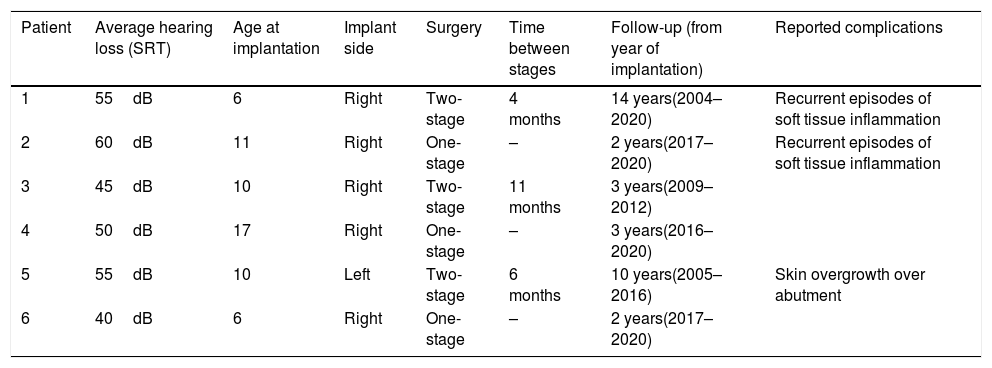
Material and methodsRetrospective analysis of patients diagnosed with bilateral congenital EAC atresia under follow-up in the pediatric ENT clinic of the ENT and Head and Neck Surgery department of a Portuguese Tertiary Hospital, between 2003 and 2019. We reviewed the medical records and collected information on the assessment of the initial audiometric status. In the cases submitted for implantation with an osseointegrated hearing implant, we analyzed the details of follow-up, including immediate and long-term post-operative complications, as well as the audiometric results.
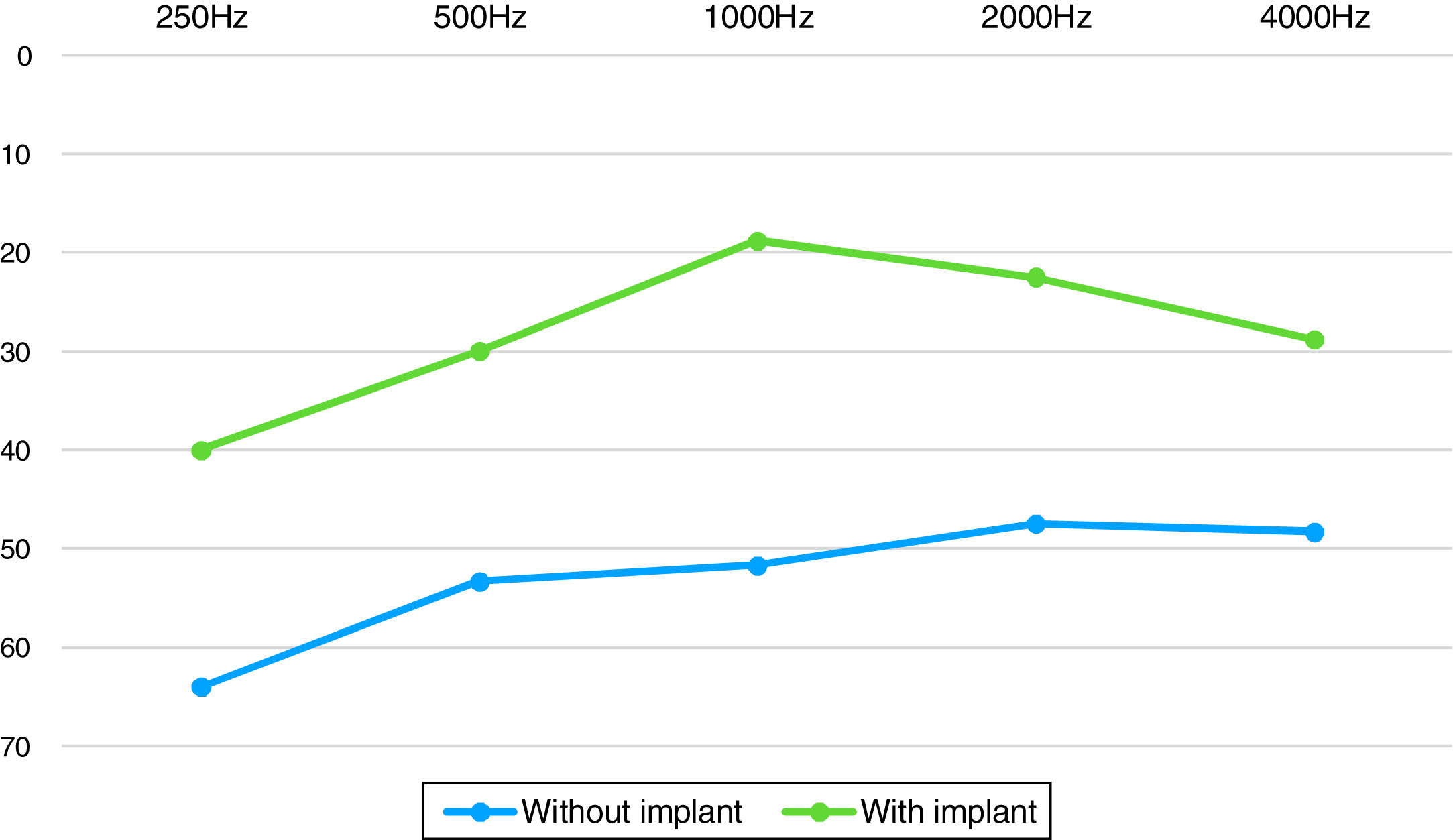
ResultsWe present 8 pediatric patients, 6 girls and 2 boys, with a diagnosis of bilateral congenital EAC atresia. The audiometric assessment revealed moderate to severe bilateral conductive hearing loss with a mean speech recognition threshold (SRT) of 51dB. Six patients underwent osseointegrated hearing implantation. All 6 patients showed good audiometric results, with an average SRT of 20dB and closure of the air-bone gap.
ConclusionsThe osseointegrated hearing implant was an effective treatment option in these patients, without significant morbidity or complications. Osseointegrated hearing implantation should be considered first line treatment for children with bilateral congenital EAC atresia, as it presents good functional results and a high level of patient satisfaction.
La atresia congénita del canal auditivo externo (CAE) es un defecto congénito presente en uno de cada 10.000-20.000 nacimientos. Origina una pérdida auditiva conductiva, con un gap aire-hueso de 50-60dB. La amplificación temprana es fundamental en casos bilaterales para garantizar el normal desarrollo del lenguaje. El objetivo de este estudio es presentar el implante auditivo osteointegrado como tratamiento para la atresia bilateral del CAE, revisando los resultados audiométricos y la tasa de complicaciones.
Material y métodosAnálisis retrospectivo de pacientes diagnosticados con atresia congénita bilateral del CAE en seguimiento en la consulta de otorrinolaringología pediátrica del departamento de otorrinolaringología y cirugía de cabeza y cuello, en un centro hospitalario terciario portugués, entre 2003 y 2019. Revisamos los registros médicos y recopilamos información sobre la evaluación del estado audiométrico inicial. En los casos sometidos a la implantación con implante auditivo osteointegrado, se analizaron los detalles del seguimiento, incluyendo las complicaciones postoperatorias inmediatas y a largo plazo, así como los resultados audiométricos.
ResultadosPresentamos los casos de 8 pacientes pediátricos, 6 niñas y 2 niños, con diagnóstico de atresia congénita bilateral del CAE. La evaluación audiométrica reveló una pérdida auditiva de conducción bilateral de grado moderado a grave, con un Speech Recognition Threshold (SRT) medio de 51dB. Seis pacientes han sido sometidos a implantación con implante auditivo osteointegrado. Los 6 pacientes presentaron buenos resultados audiométricos, con un SRT medio de 20dB y cierre del gap aire-hueso.
ConclusionesEl implante auditivo osteointegrado fue una opción de tratamiento eficaz en estos pacientes, sin morbilidad o complicaciones significativas. El implante auditivo osteointegrado debe ser considerado un tratamiento de primera línea para niños con atresia congénita bilateral del CAE, ya que presenta buenos resultados funcionales y un alto nivel de satisfacción por parte de los pacientes.