By using appropriate instrumentation, we have found that cochlear microphonics (CM) advance or delay their appearance, depending on the sound pressure that generates them. This time variation is on the order of microseconds. We have not found any reference to this behaviour, which is why we make the finding known.
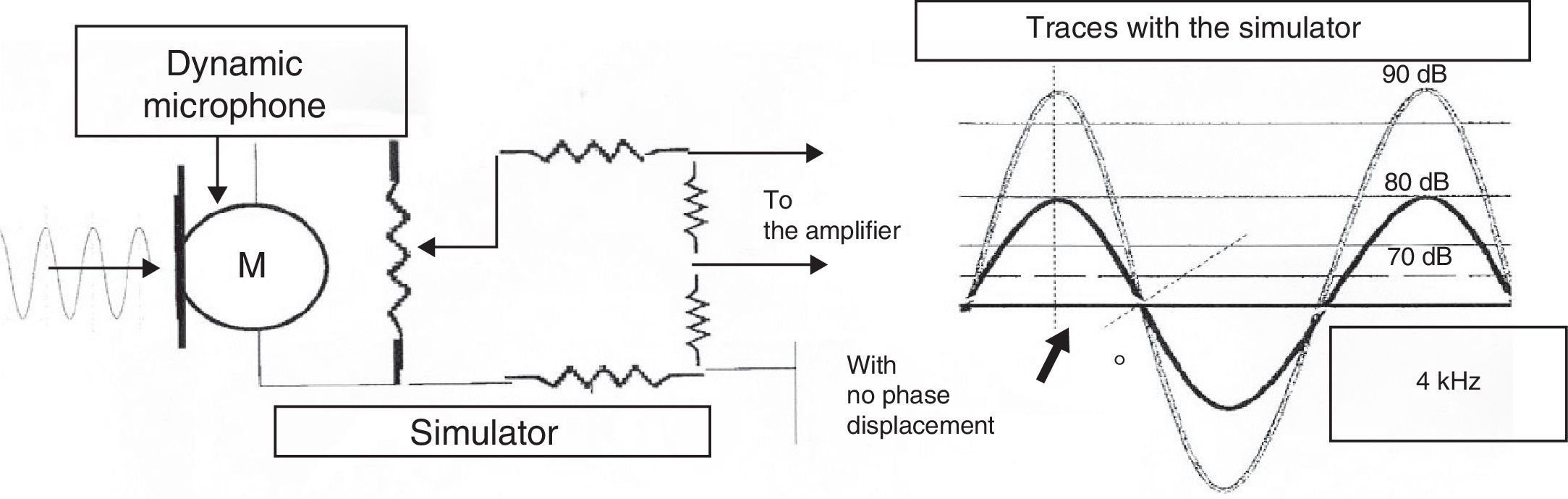
Materials and methodWe used the standard instrumentation specified for the study of CM. The method was based on the phase shift function of the CM according to the intensity of the stimulus.
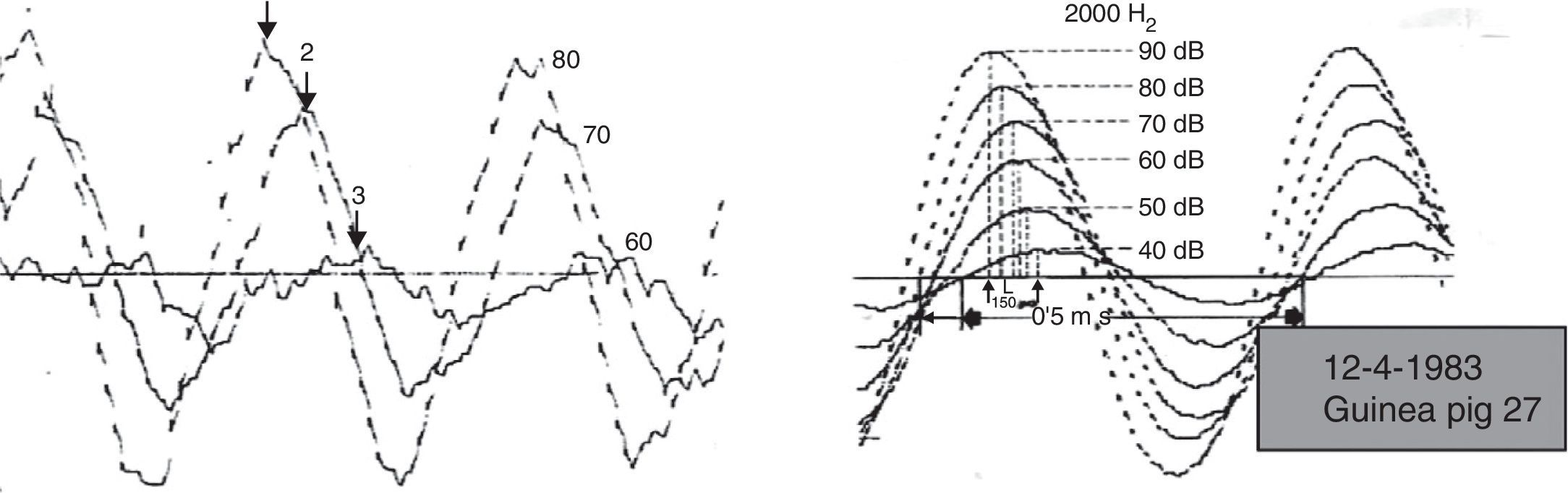
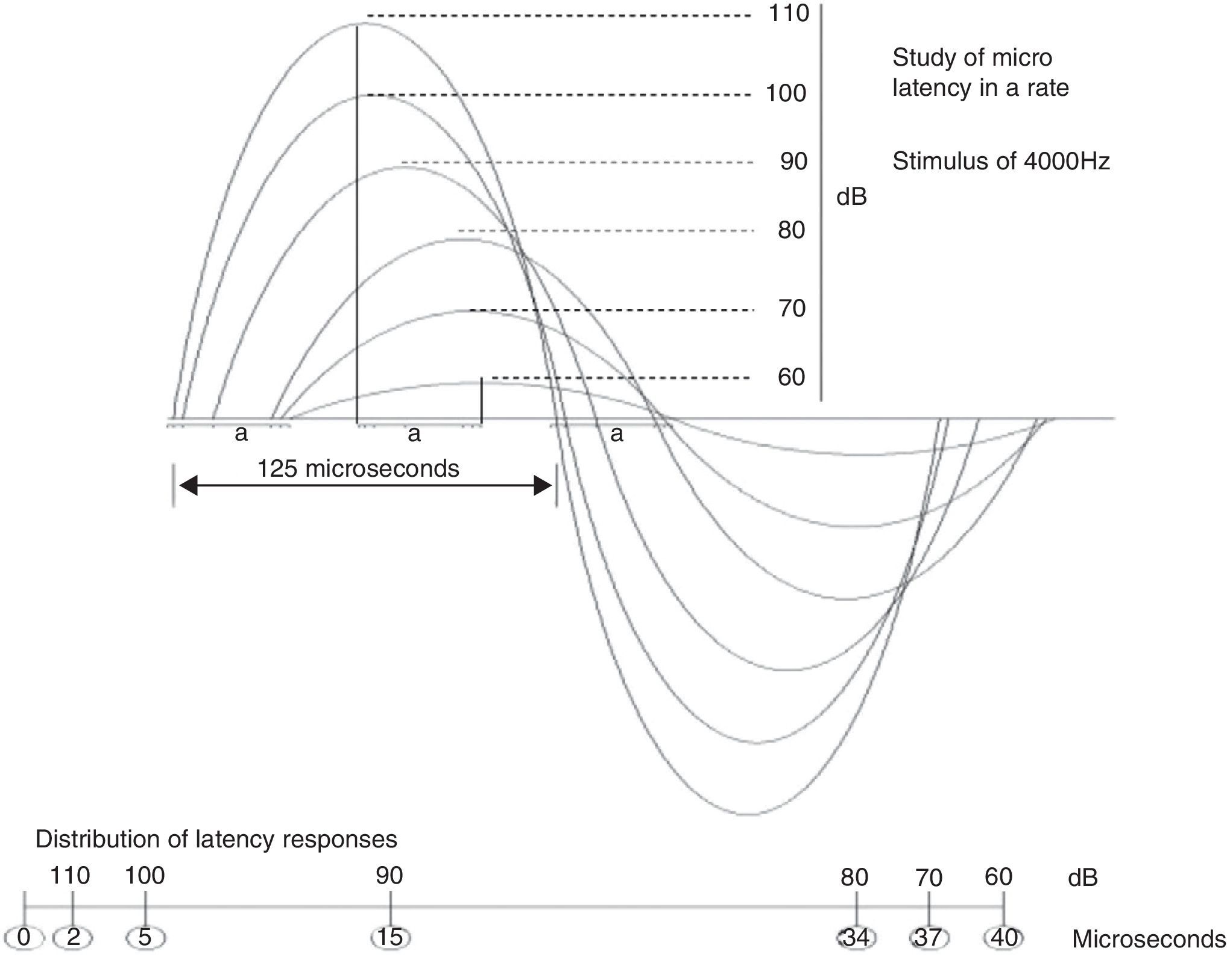
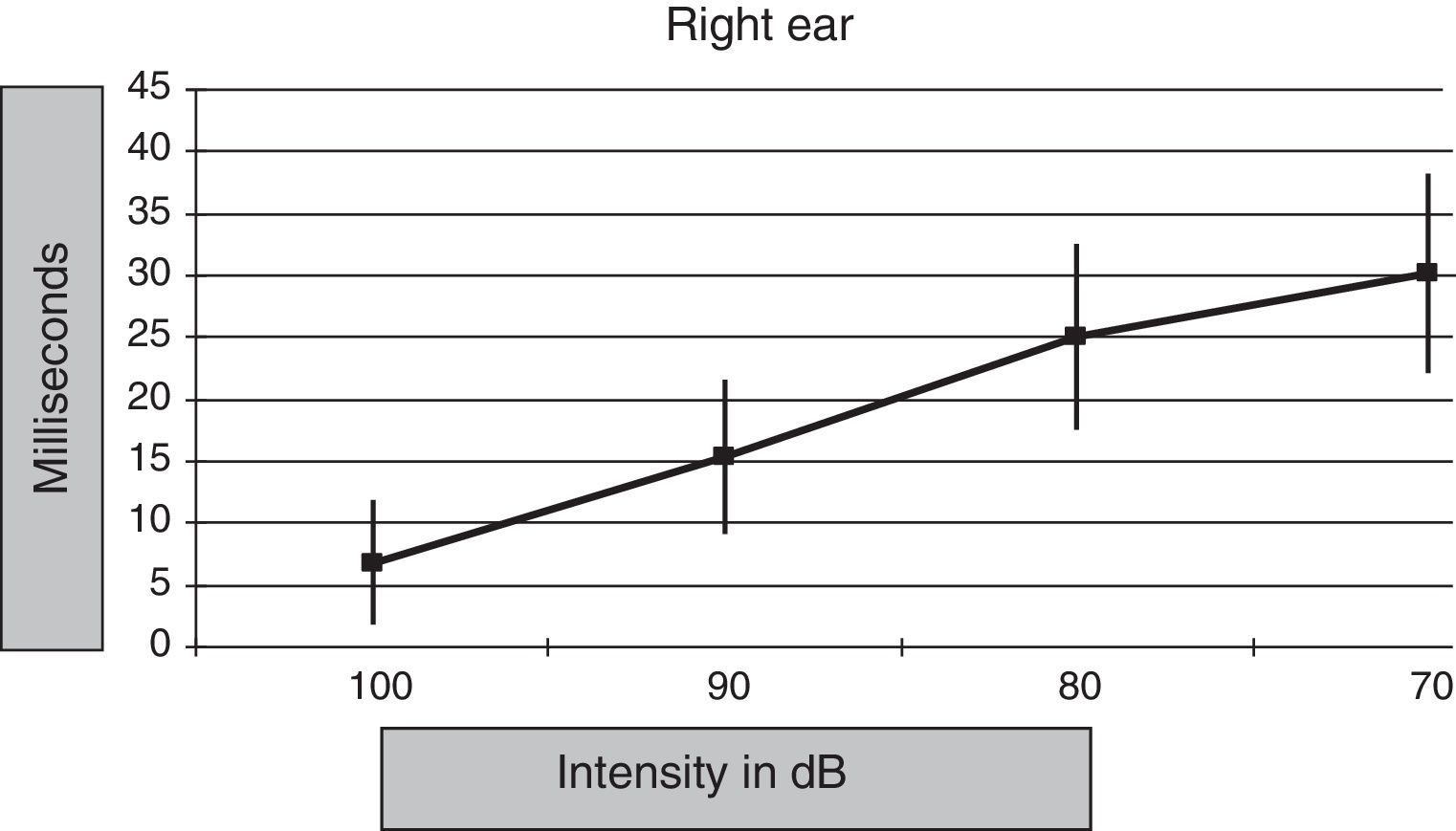
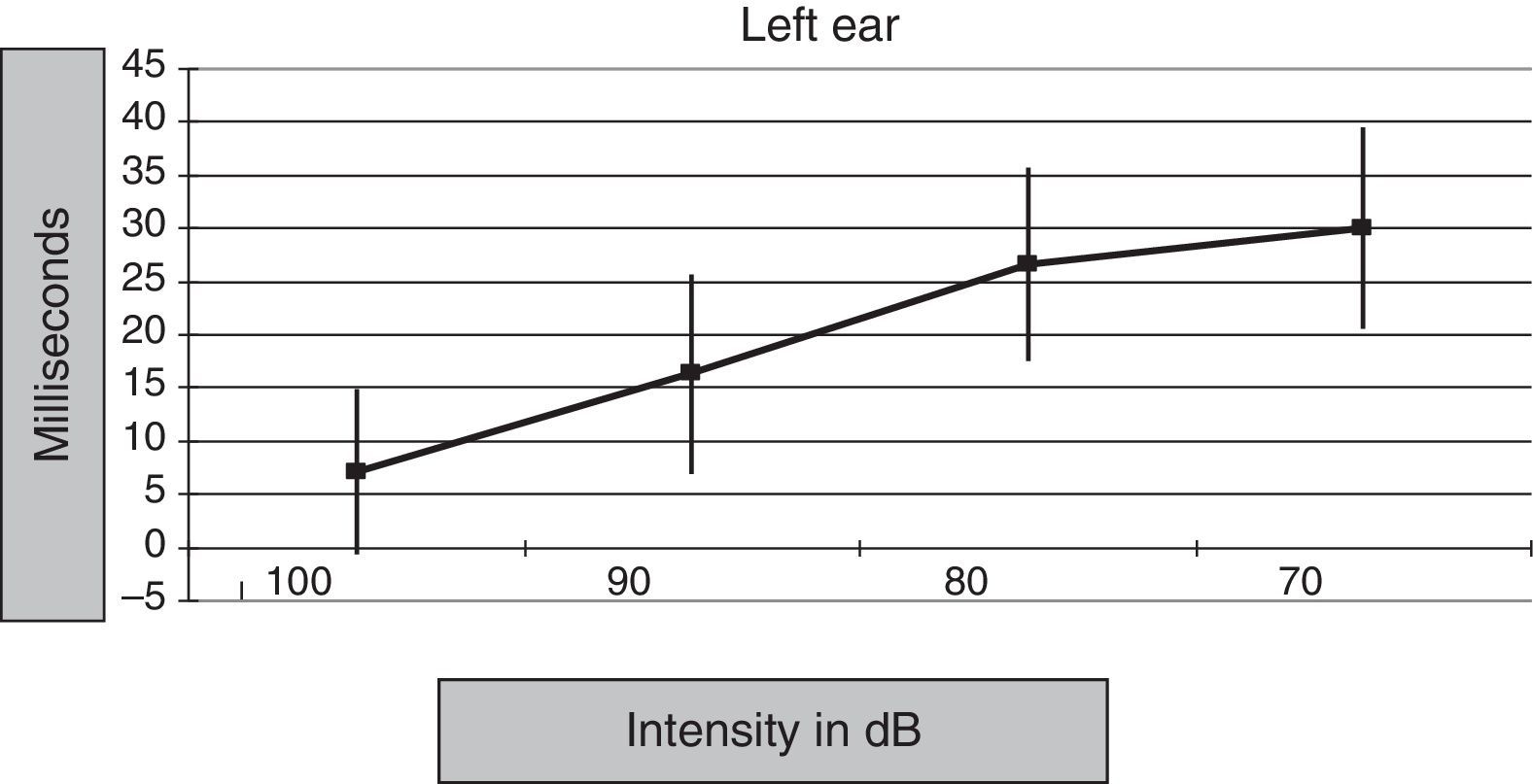
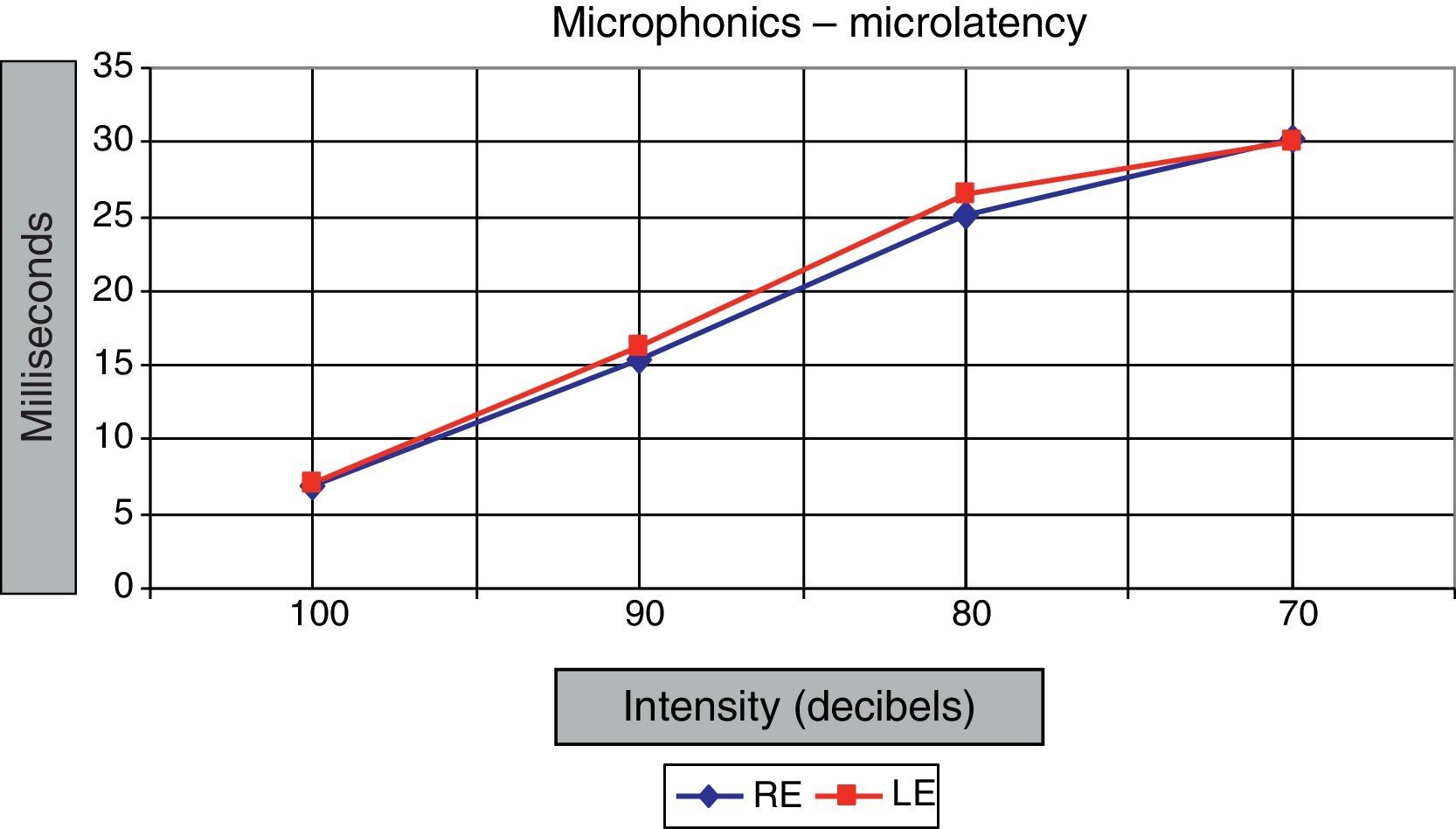
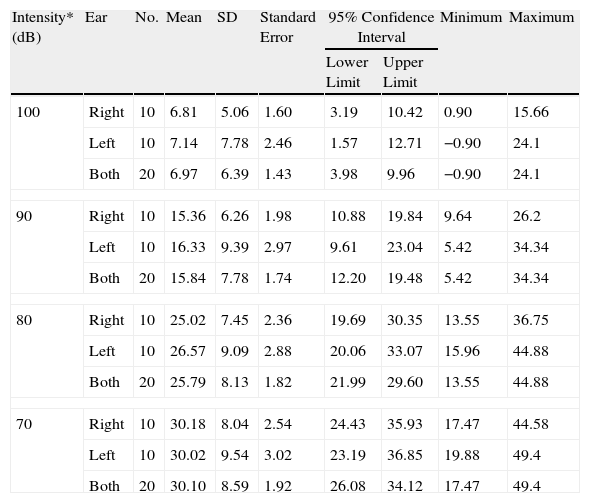
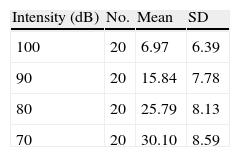
ResultsLatency was observed in CM, and we determined that latency time diminishes as the intensity of the stimulus increases.
ConclusionsFrom the sound stimulus to the bioelectric potential transduction, there is a time period of microseconds, the shorter the more powerful the stimulus. This suggests that electromechanical transduction is not a simple mechanical process.
Empleando la instrumentación adecuada, venimos constatando que los microfónicos cocleares (MC) evocados adelantan o retrasan su aparición en función de la presión sonora que los genera. Esta variación en el tiempo es del orden de microsegundos. No hemos encontrado referencia alguna de este comportamiento, razón por la cual damos conocer el hallazgo.
Material y métodoSe emplea instrumentación específica para el estudio de los MC. El método se basa en el desplazamiento de fase de los MC en función de la intensidad del estímulo.
ResultadosSe constata la latencia en los MC y se observa que la misma disminuye a medida que se incrementa la intensidad del estímulo.
ConclusionesDesde el estímulo sonoro a la traducción en potencial bioeléctrico encontramos un periodo de tiempo en microsegundos, menor a mayor potencia. Esto sugiere que traducción mecano-eléctrica no es un simple proceso de naturaleza mecánica.