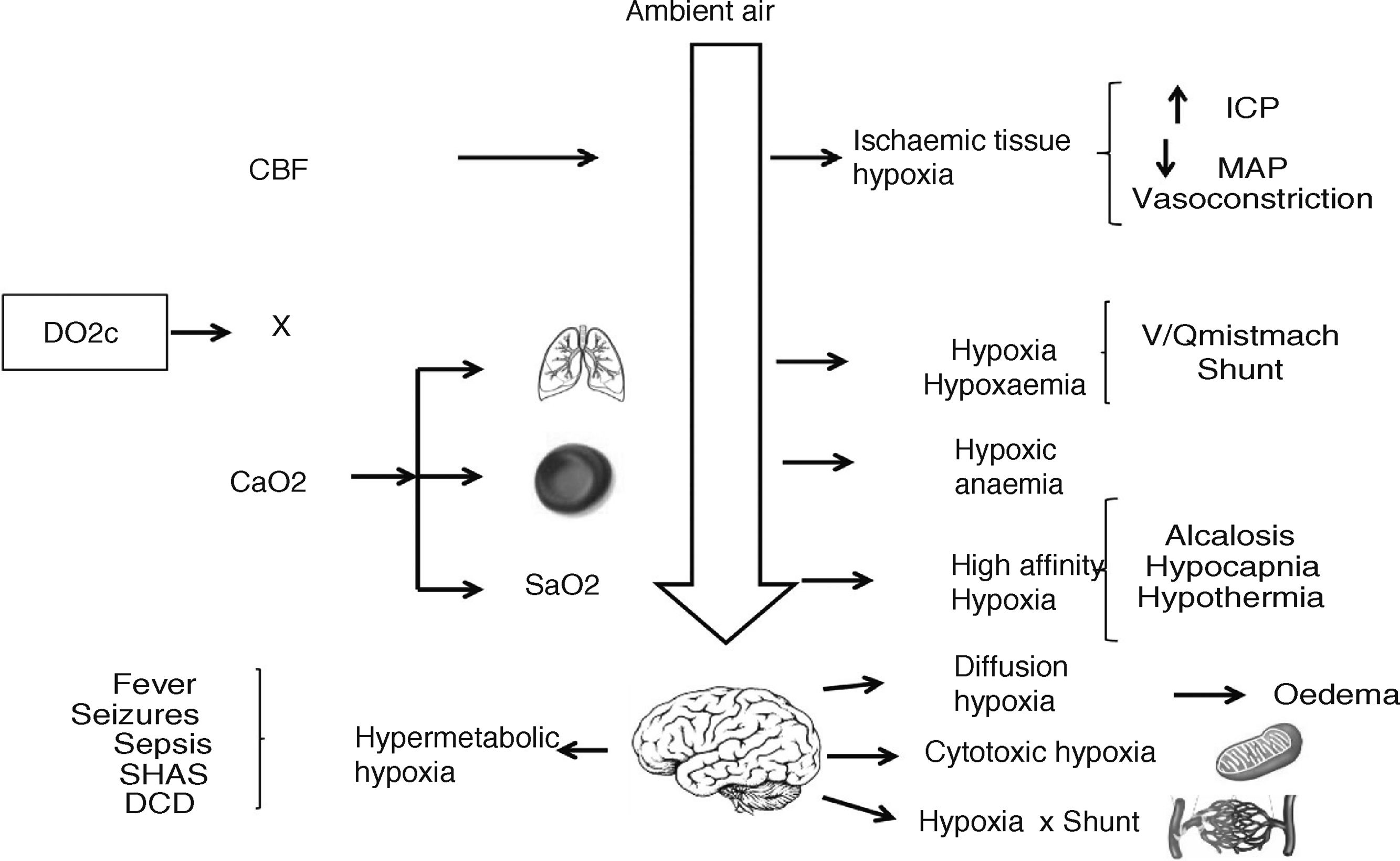
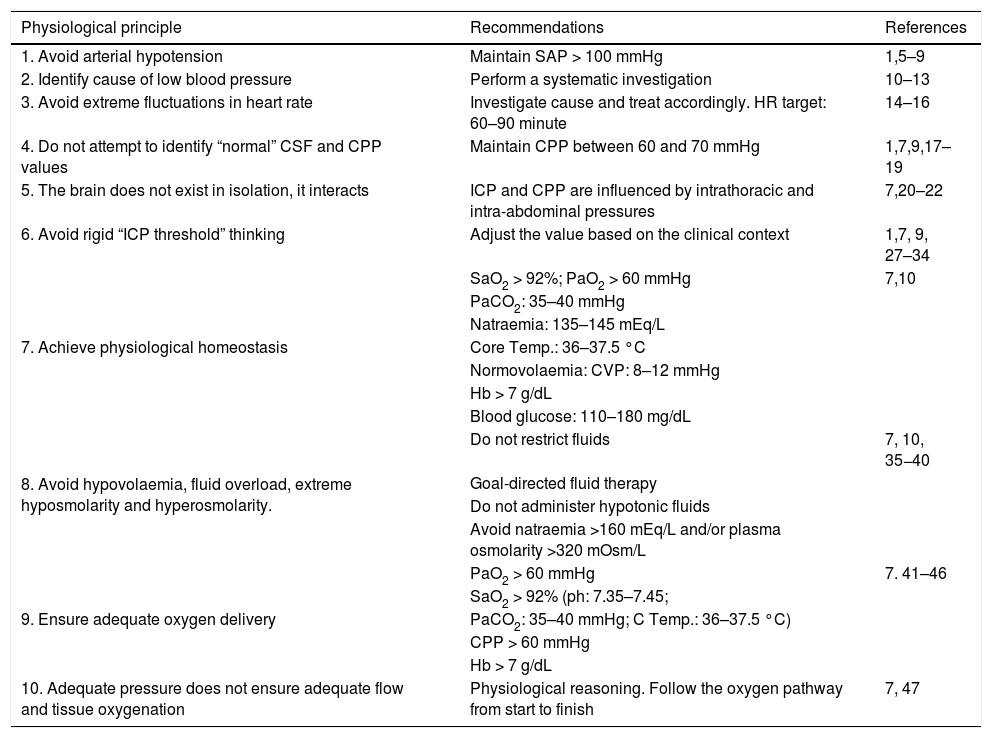
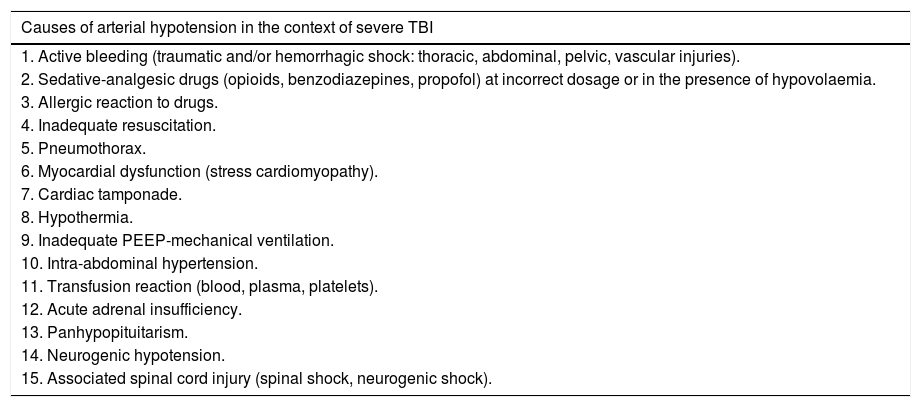
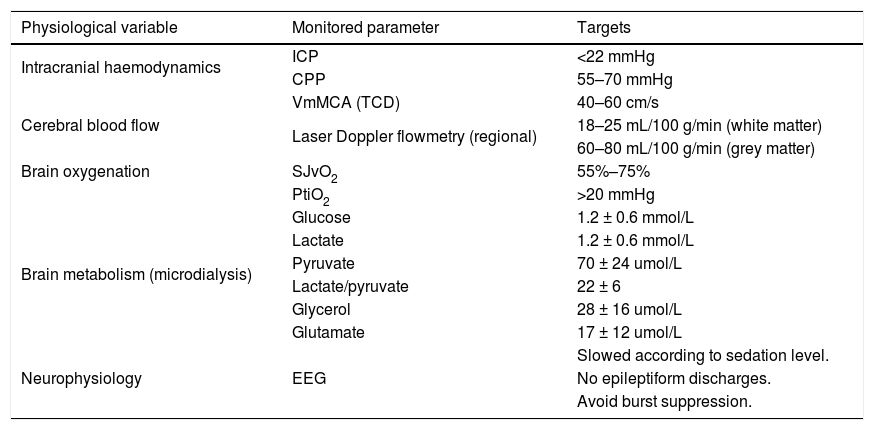
Advances in multiparametric brain monitoring have allowed us to deepen our knowledge of the physiopathology of head injury and how it can be treated using the therapies available today. It is essential to understand and interpret a series of basic physiological and physiopathological principles that, on the one hand, provide an adequate metabolic environment to prevent worsening of the primary brain injury and favour its recovery, and on the other hand, allow therapeutic resources to be individually adapted to the specific needs of the patient.
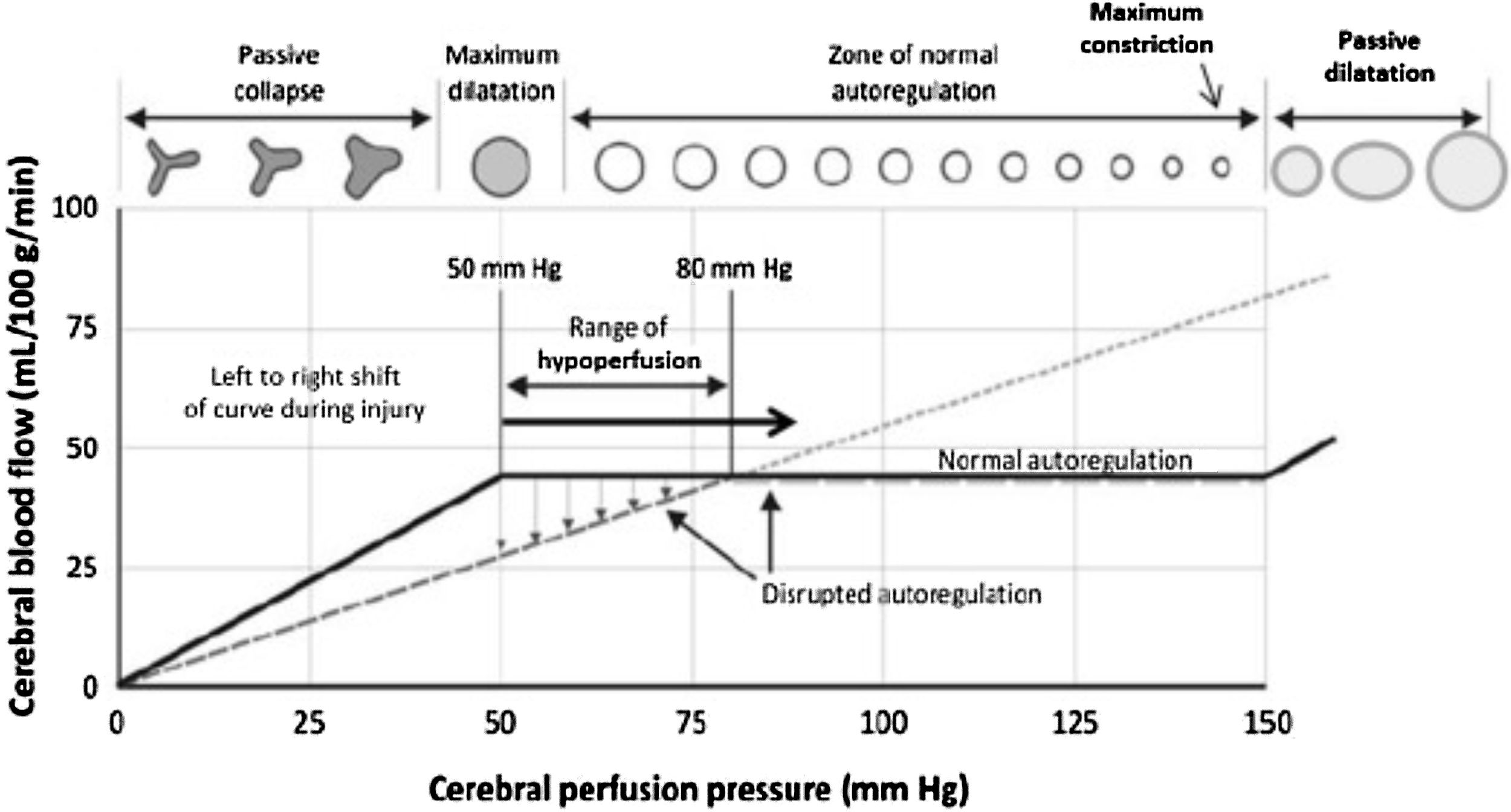
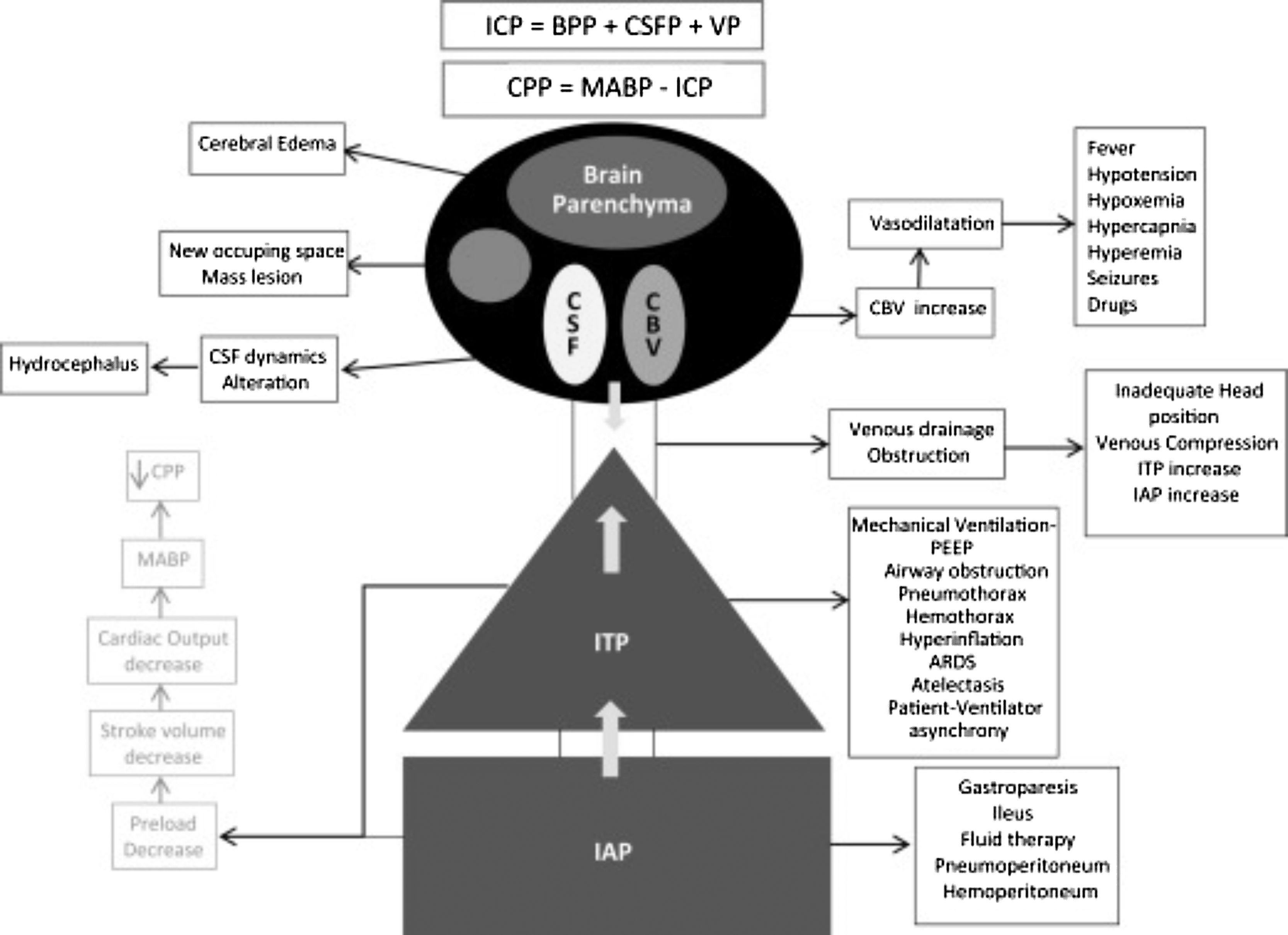
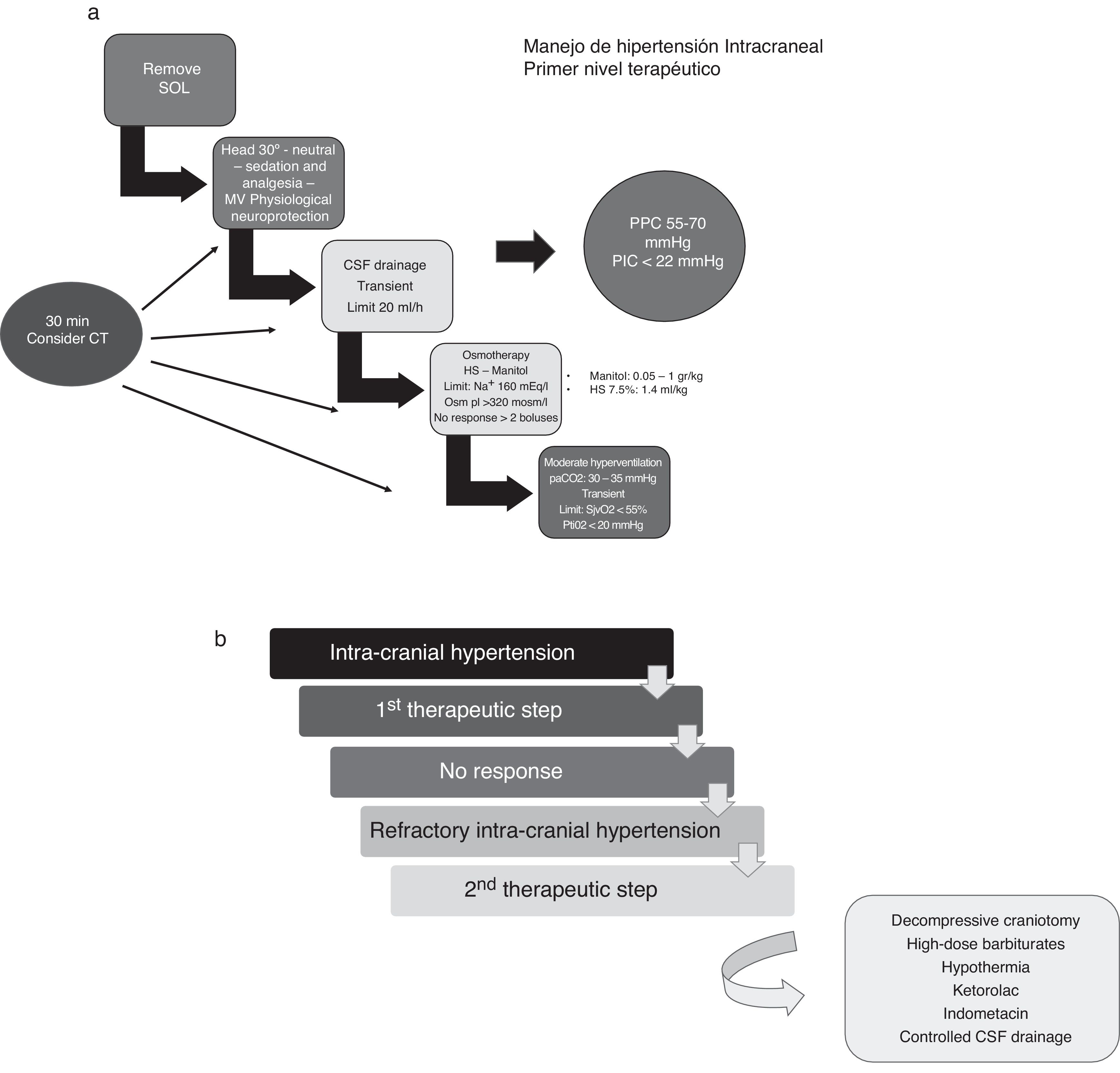
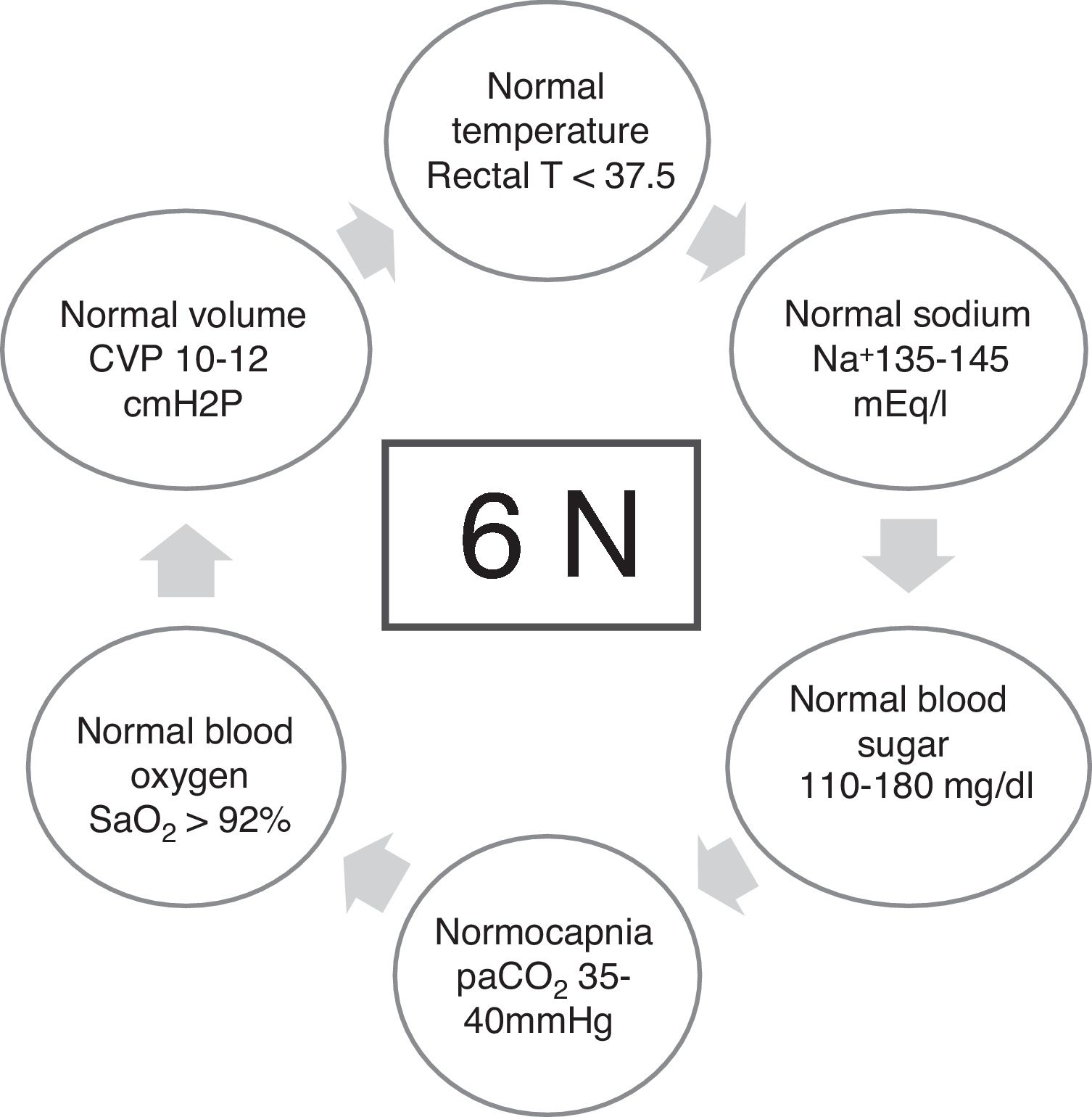
Based on these notions, this article presents a decalogue of the physiological objectives to be achieved in brain injury, together with a series of diagnostic and therapeutic recommendations for achieving these goals. We emphasise the importance of considering and analysing the physiological variables involved in the transport of oxygen to the brain, such as cardiac output and arterial oxygen content, together with their conditioning factors and possible alterations. Special attention is paid to the basic elements of physiological neuroprotection, and we describe the multiple causes of cerebral hypoxia, how to approach them, and how to correct them. We also examine the increase in intracranial pressure as a physiopathological element, focussing on the significance of thoracic and abdominal pressure in the interpretation of intracranial pressure. Treatment of intracranial pressure should be based on a step-wise model, the first stage of which should be based on a physiopathological reflection combined with information on the tomographic lesions rather than on rigid numerical values.
Los avances en la monitorización cerebral multiparamétrica han permitido ahondar en el conocimiento de la fisiopatología del traumatismo craneoencefálico, y en cómo la terapéutica disponible puede modularla. Para ello, se antoja imprescindible conocer e interpretar una serie de principios fisiológicos y fisiopatológicos básicos que propician, por un lado, un entorno metabólico cerebral adecuado para prevenir un incremento de la lesión cerebral primaria y favorecer su recuperación, y por otro lado, permiten adaptar de forma individualizada los recursos terapéuticos a la situación concreta del paciente.
En el presente artículo se exponen, en forma de decálogo, sustentados en dichas nociones, los objetivos fisiológicos a conseguir, junto con una serie de recomendaciones diagnósticas y terapéuticas que posibiliten su logro. Se hace énfasis en la consideración y análisis de las variables fisiológicas implicadas en el transporte de oxígeno al cerebro, como el gasto cardiaco y el contenido arterial de oxígeno, junto con sus condicionantes y las posibles alteraciones de cada uno de ellos. Cobran especial atención los elementos básicos que constituyen la neuroprotección fisiológica. Asimismo, se razonan las múltiples causas que provocan hipoxia cerebral y el modo de abordarlas y corregirlas. El aumento de la presión intracraneal, como elemento fisiopatológico, se examina, subrayándose para interpretarla la interconexión e influencia de la presión torácica y abdominal sobre la intracraneal. El tratamiento de la presión intracraneal debe efectuarse sobre un modelo de acciones escalonadas, cuyo inicio debería cimentarse más que en valores numéricos rígidos, en una reflexión fisiopatológica unida a la información de las lesiones tomográficas.