Percutaneous implantation of an aortic valve prosthesis is a therapeutic alternative for patients with severe aortic stenosis. The procedure is traditionally performed under general anaesthesia; however, sedation is now gaining in popularity because it reduces the need for vasoactive drugs and shortens the patient’s stay in the critical care unit and on the ward. The aim of this study is to evaluate the clinical efficacy, safety and potential benefits of sedation with dexmedetomidine in patients undergoing percutaneous implantation of an aortic valve prosthesis in terms of haemodynamic and respiratory complications.
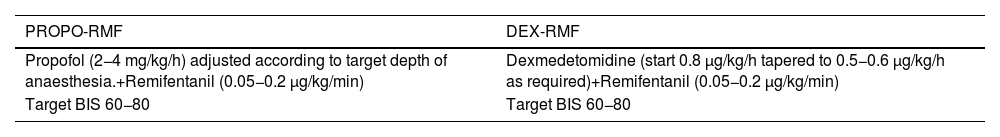
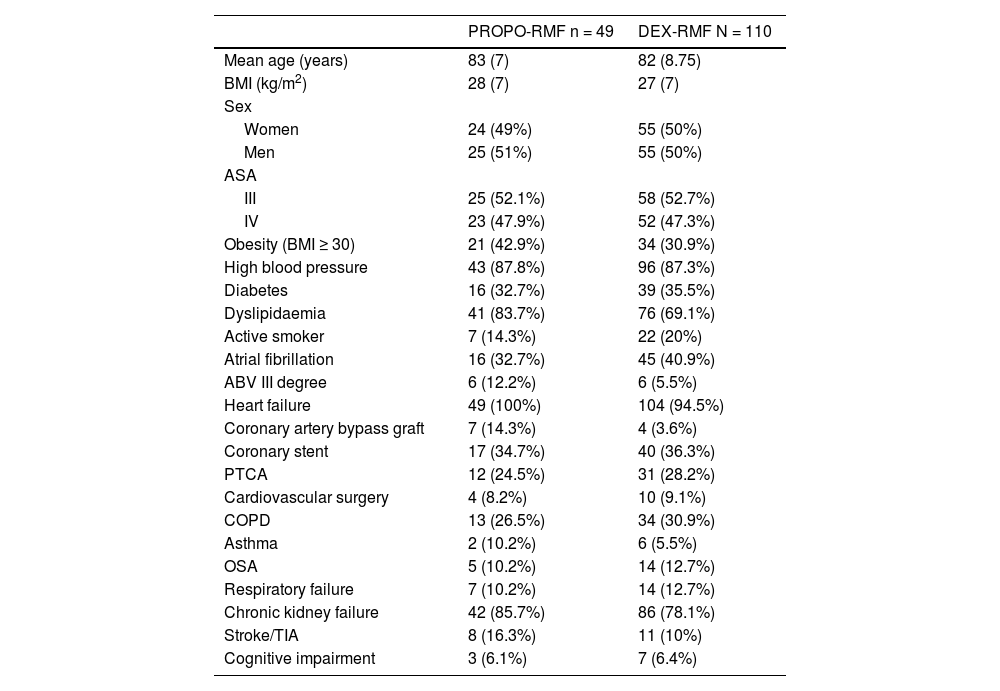
Materials and methodsWe performed a retrospective study of 222 patients that had undergone percutaneous implantation of an aortic valve prosthesis between 2012 and 2019 under sedation with either dexmedetomidine plus remifentanil (DEX-RMF) or propofol plus remifentanil (PROPO-RMF). We collected data on complications, mainly haemodynamic and respiratory, during and after the procedure.
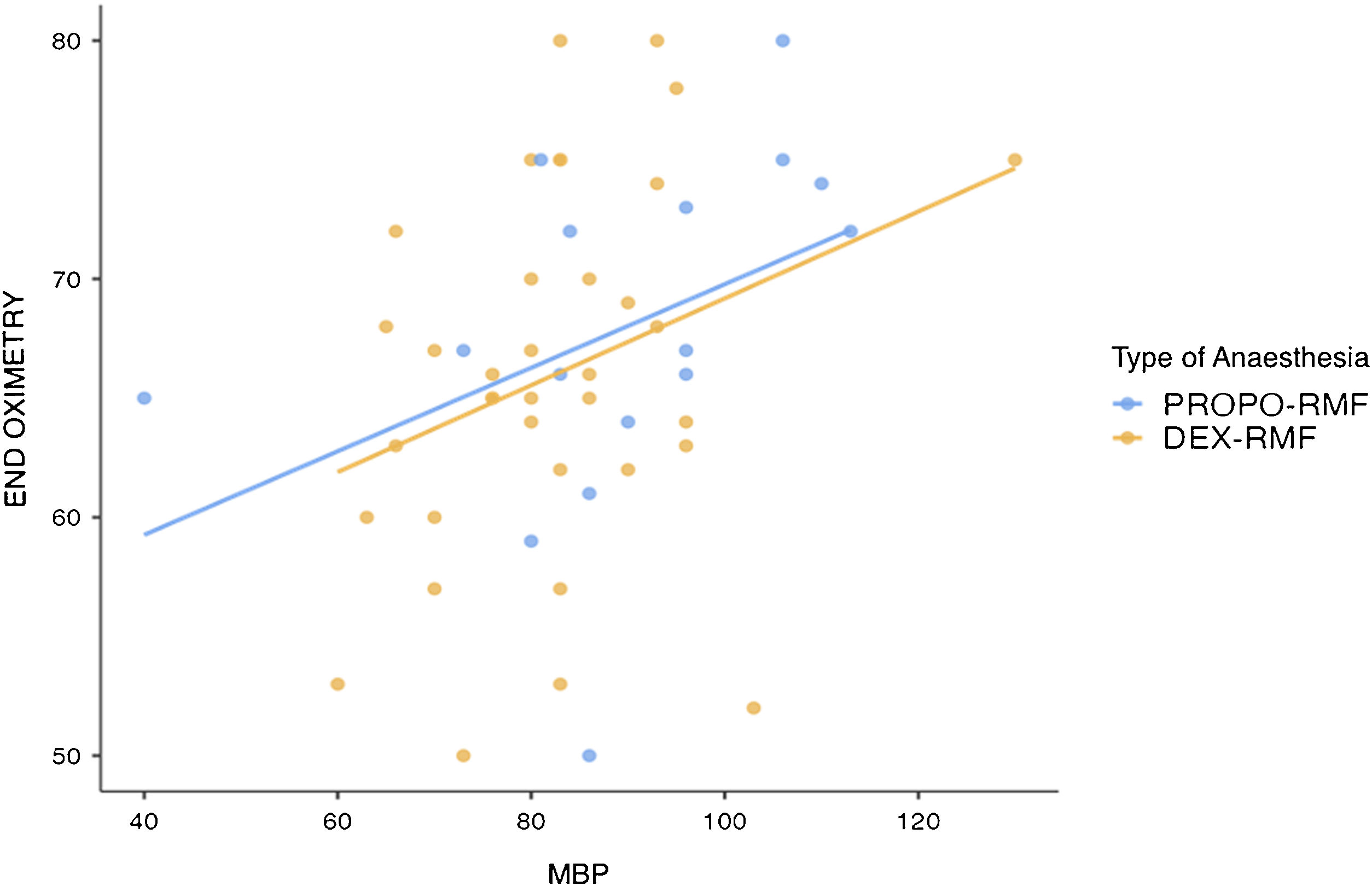
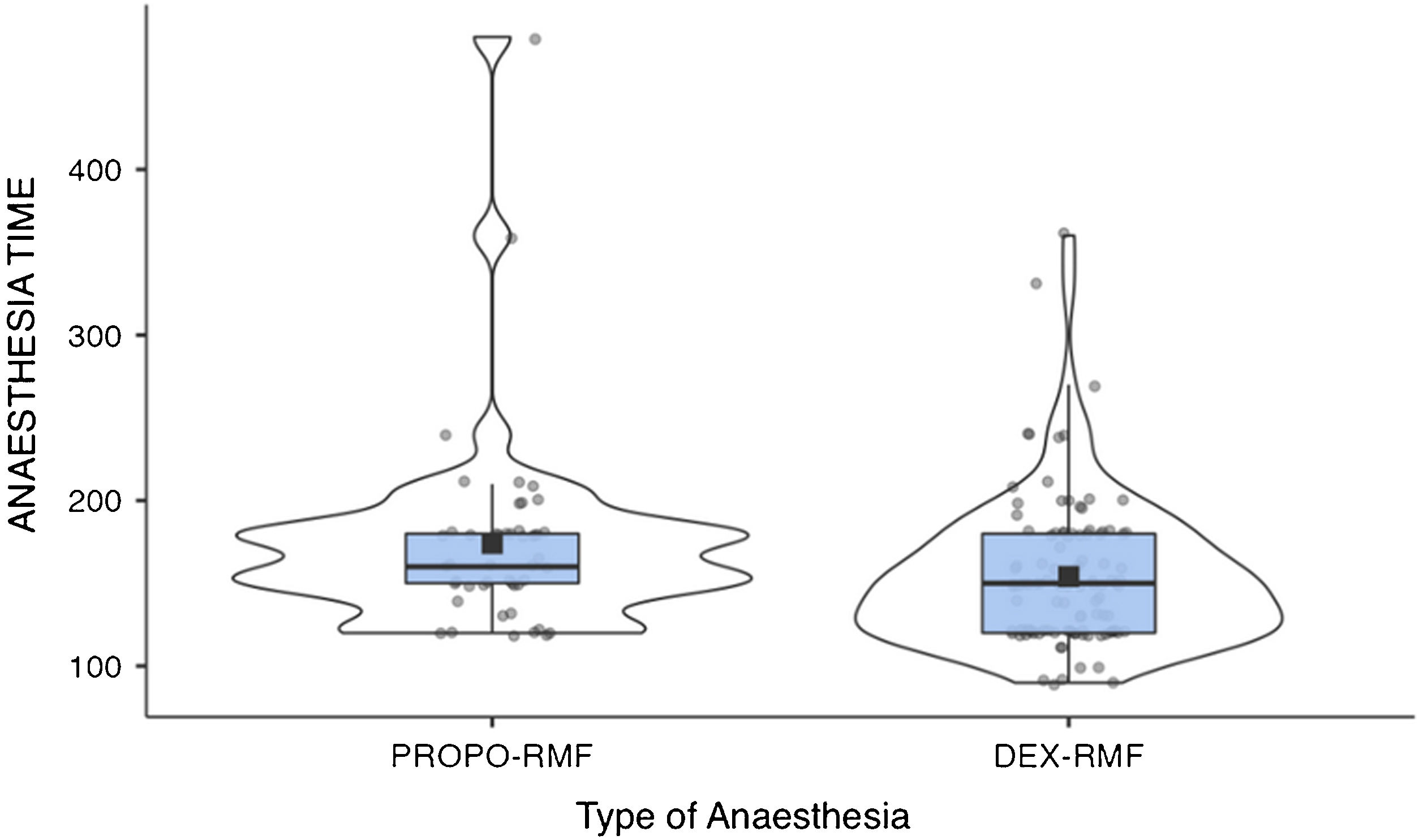
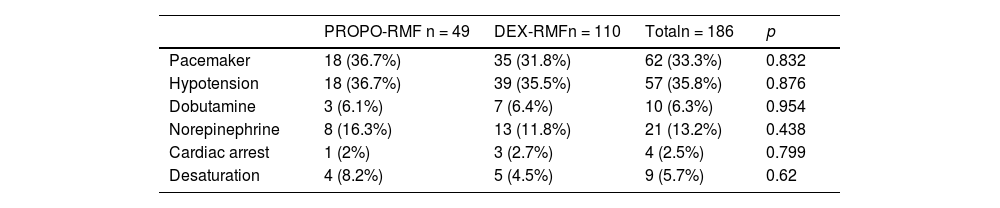
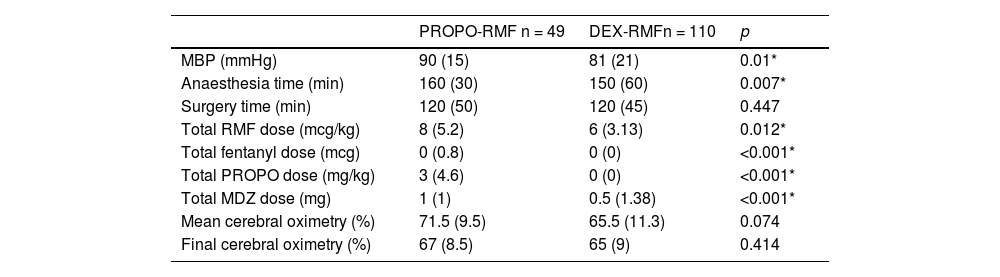
ResultsNo significant differences were found between sedation with dexmedetomidine and propofol (in combination with remifentanil) in terms of haemodynamic stability and intraprocedural cerebral blood oxygen. In the DEX-RMF group, however, mean blood pressure, midazolam dose, and duration of anaesthesia were lower compared with the PROPO-RMF group, but the incidence of haemodynamic and respiratory complications did not differ significantly between groups.
ConclusionsOur results show that sedation, particularly with adjuvant dexmedetomidine, is a valid anaesthetic techniques in percutaneous aortic valve prosthesis implantation.
El implante percutáneo de prótesis valvular aórtica es una alternativa terapéutica para pacientes con estenosis aórtica severa. El manejo anestésico para este procedimiento se ha basado inicialmente en la anestesia general. Sin embargo, en los últimos años, la sedación ha presentado una tendencia creciente, ya que ha demostrado una disminución del uso de fármacos vasoactivos y una menor estancia hospitalaria y en unidad de críticos. El objetivo de este trabajo es evaluar la eficacia y seguridad clínica de la dexmedetomidina, así como sus posibles beneficios en la sedación de pacientes sometidos a implante percutáneo de válvula aórtica, en términos de complicaciones hemodinámicas y respiratorias durante el procedimiento.
Materiales y métodosSe realizó un estudio retrospectivo de 222 pacientes sometidos a la implantación percutánea de prótesis valvular aórtica, entre 2012 y 2019, bajo sedación con dexmedetomidina más remifentanilo o propofol más remifentanilo. Se analizaron las complicaciones durante y tras el procedimiento, principalmente hemodinámicas y respiratorias.
ResultadosNo se hallaron diferencias significativas entre la sedación con dexmedetomidina y propofol (en combinación con remifentanilo), en términos de estabilidad hemodinámica y oximetría cerebral intraprocedimiento. Se encontraron diferencias significativas entre los valores de PAM, dosis de midazolam y en tiempo de duración de la anestesia, siendo menores en el grupo DEX-RMF. No hubo diferencias significativas entre ambos grupos, en cuanto a complicaciones hemodinámicas, ni respiratorias.
ConclusionesLos resultados encontrados apoyan la sedación como una buena técnica anestésica para el implante percutáneo de prótesis válvula aórtica. La dexmedetomidina es una buena opción farmacológica.